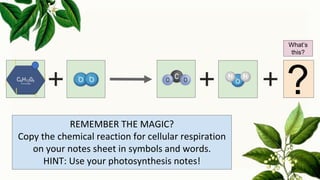
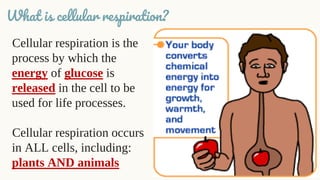
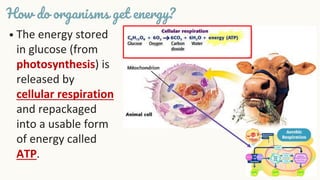
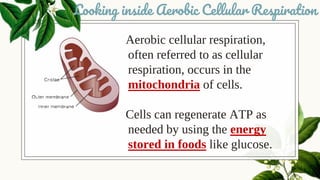
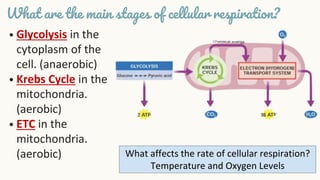
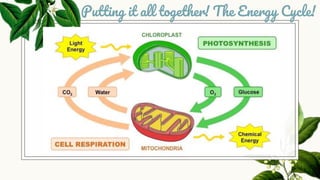
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms generate energy (ATP) from glucose. It occurs in three stages: glycolysis in the cytoplasm, the Krebs cycle in the mitochondria, and the electron transport chain in the mitochondria. Aerobic cellular respiration uses oxygen and produces the most ATP, while anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen and produces less ATP. All organisms undergo cellular respiration to break down glucose and generate energy in the form of ATP, which is required for life processes like growth and repair.