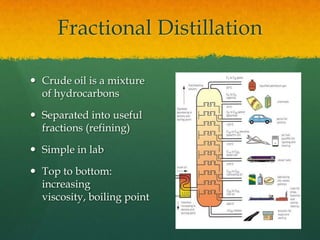
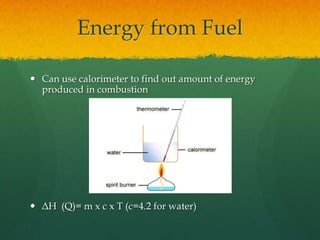
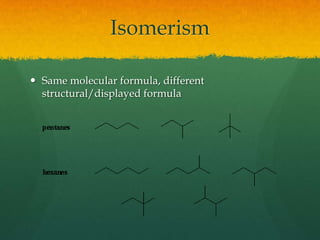
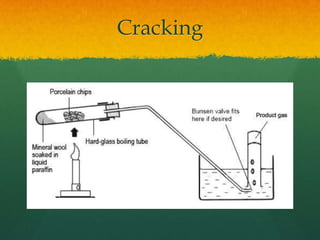
Organic chemistry revision notes cover the formation of fossil fuels like oil from dead marine organisms under heat and pressure. Crude oil is separated into fractions like gasoline and kerosene through fractional distillation, and combustion produces pollution like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. The energy released during combustion can be measured using a calorimeter. Homologous series are families of compounds with the same functional group and general formula that differ by CH2. Main series include alkanes, alkenes, and alcohols, which are named based on their carbon chain and functional group.