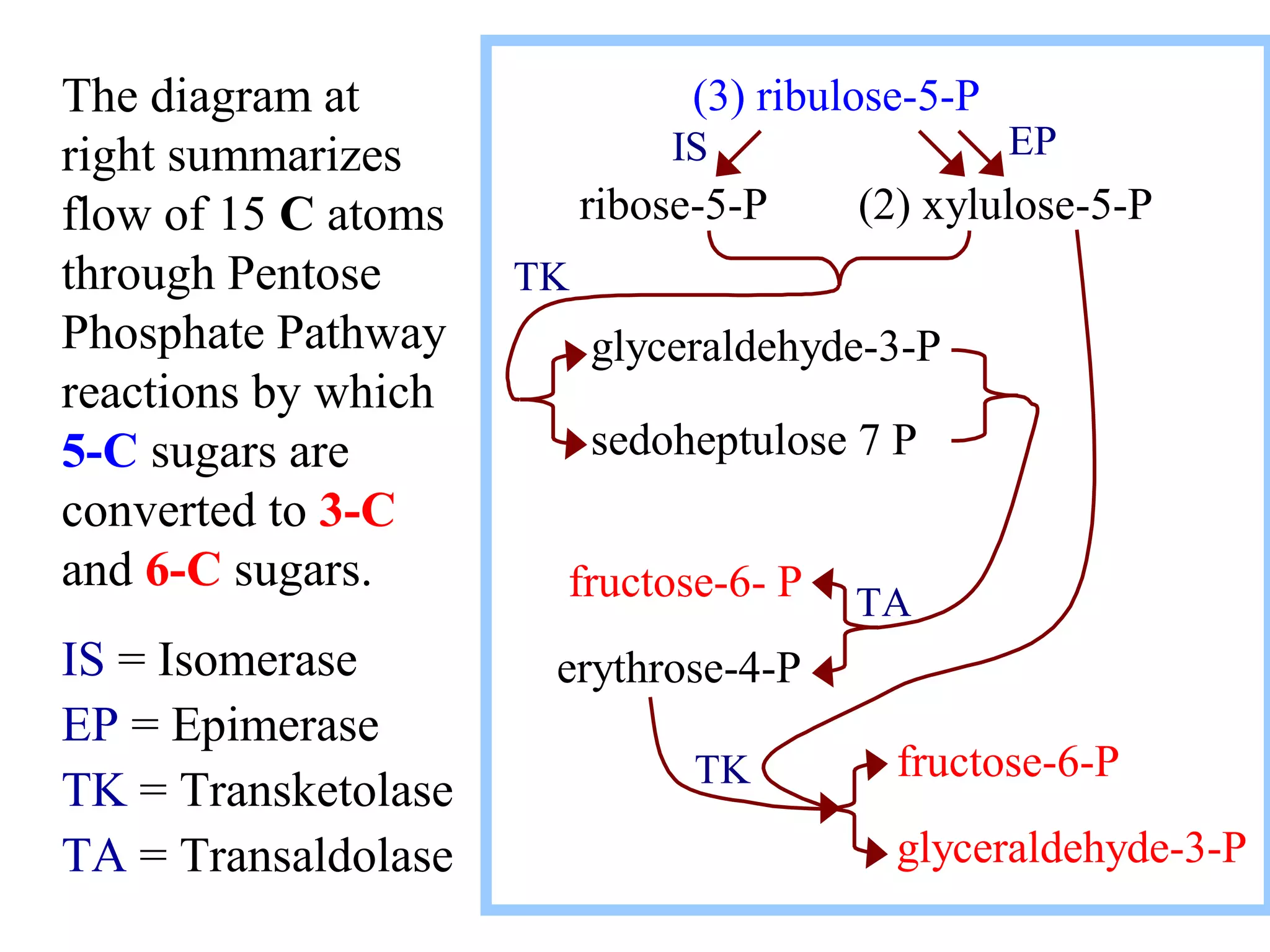
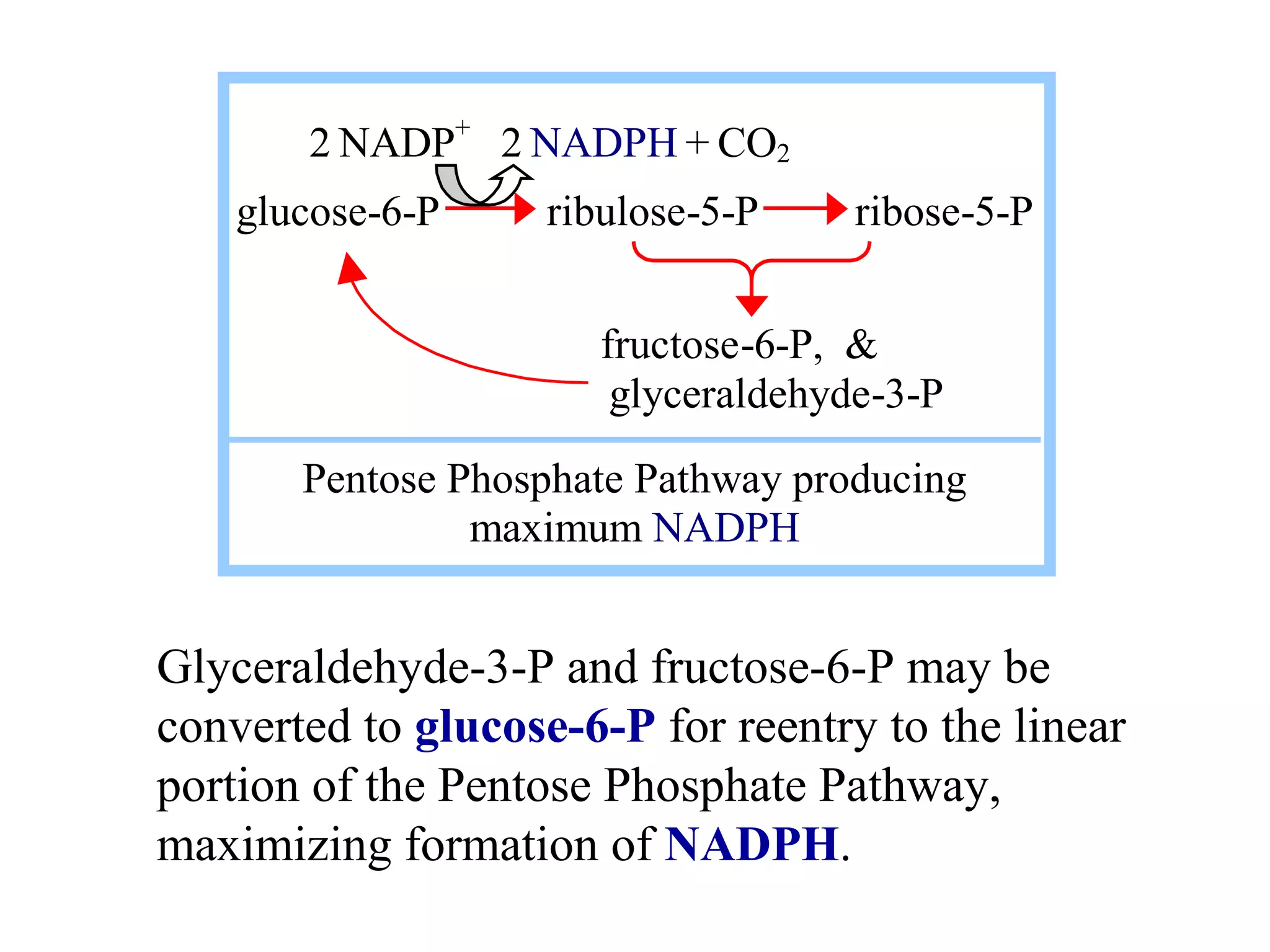
The pentose phosphate pathway generates NADPH and pentose sugars. Glucose-6-phosphate enters the pathway and is oxidized by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, producing 6-phosphogluconolactone. This is hydrolyzed to 6-phosphogluconate by 6-phosphogluconolactonase. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase further oxidizes this to ribulose-5-phosphate, producing NADPH. Ribulose-5-phosphate can be converted to other 5-carbon sugars like ribose-5-phosphate. Transketolase and transaldolase reactions interconvert pentose and triose phosphates to regenerate ribulose























![Regeneration of reduced glutathione requires NADPH,
produced within erythrocytes in the Pentose Phosphate
Pathway.
Glutathione Reductase catalyzes:
GSSG + NADPH + H+
2 GSH + NADP+
Genetic deficiency of Glucose-6-P Dehydrogenase can
lead to hemolytic anemia, due to inadequate [NADPH]
within red blood cells.
The effect of partial deficiency of Glucose-6-phosphate
Dehydrogenase is exacerbated by substances that lead to
increased production of peroxides (e.g., the antimalarial
primaquine).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15-pentose-160523184128/75/15-pentose-27-2048.jpg)