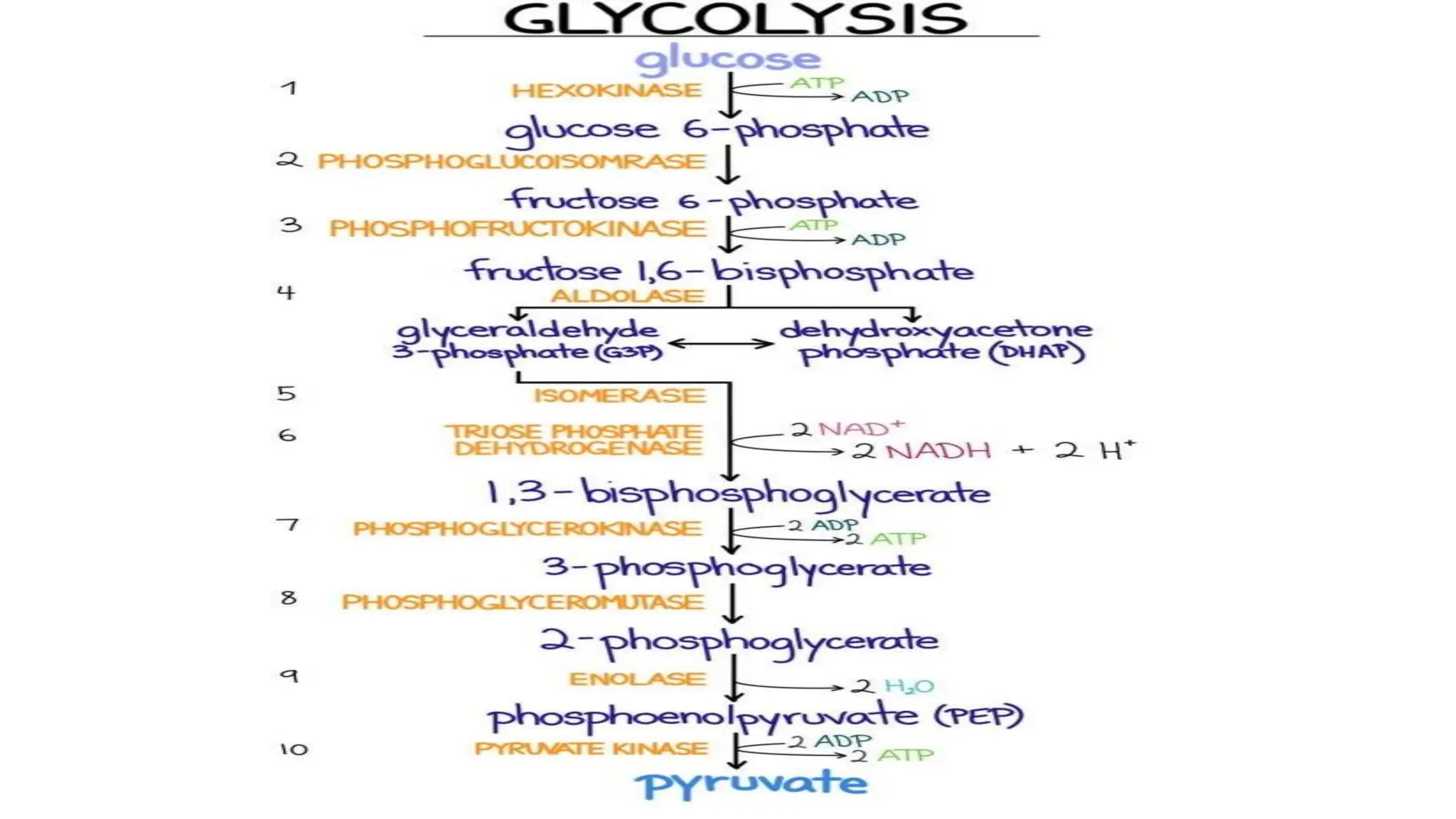
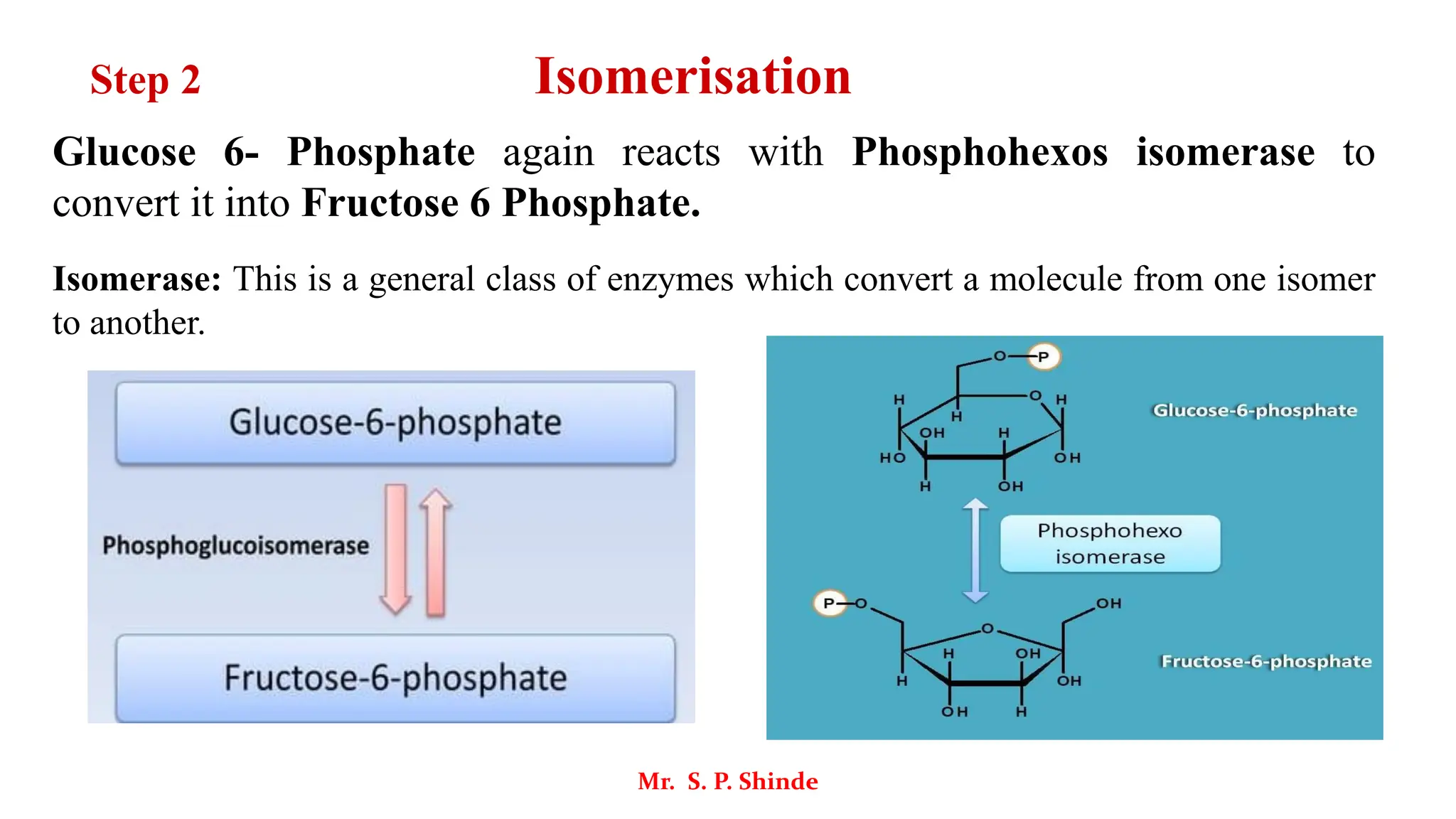
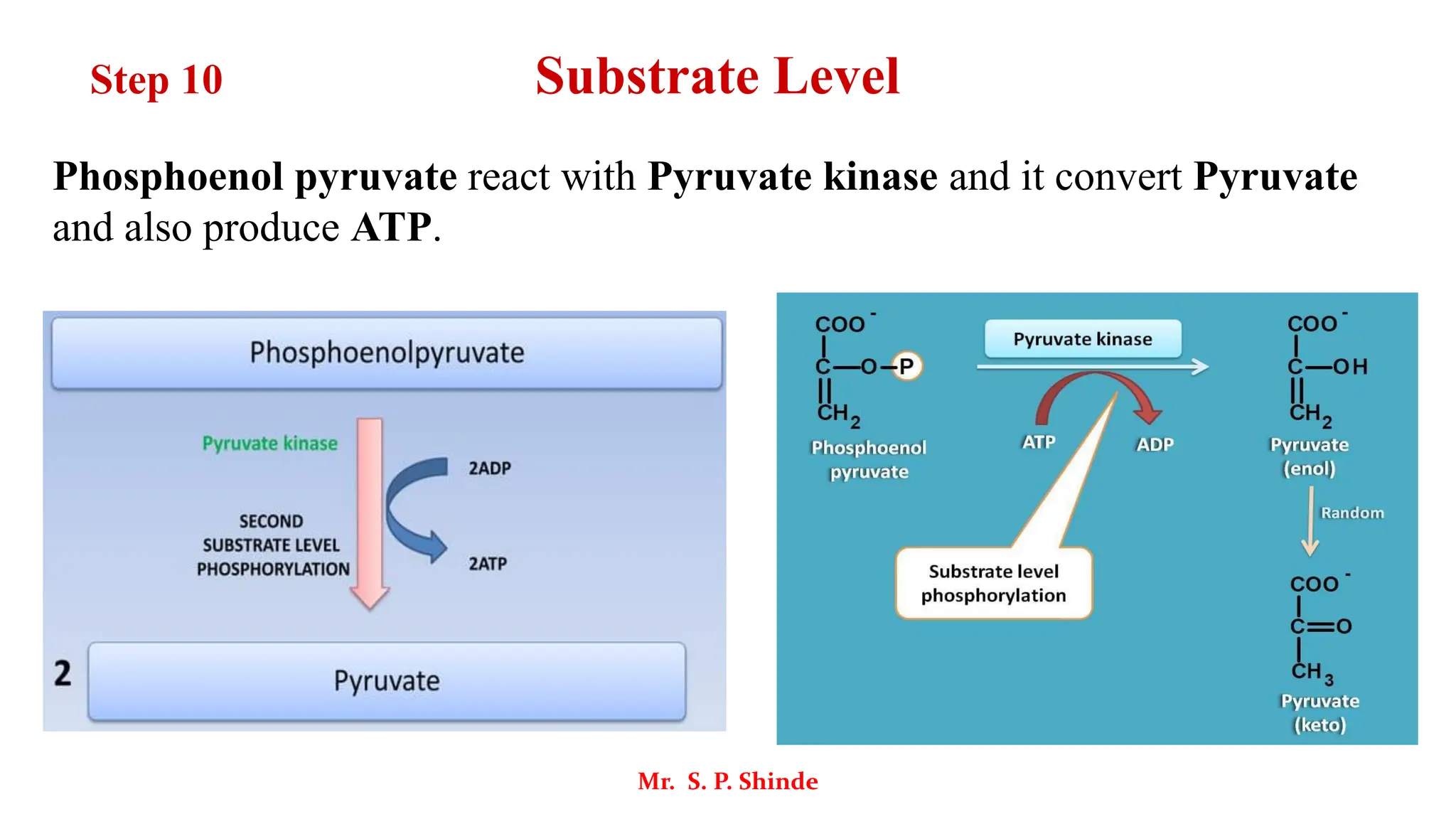
The document outlines the metabolic processes involved in the conversion of food into energy through glycolysis, the first step of carbohydrate metabolism. It describes the various steps and enzymes involved in the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP in an anaerobic process. Key stages include phosphorylation, isomerization, and substrate-level phosphorylation, culminating in the production of energy-rich molecules.