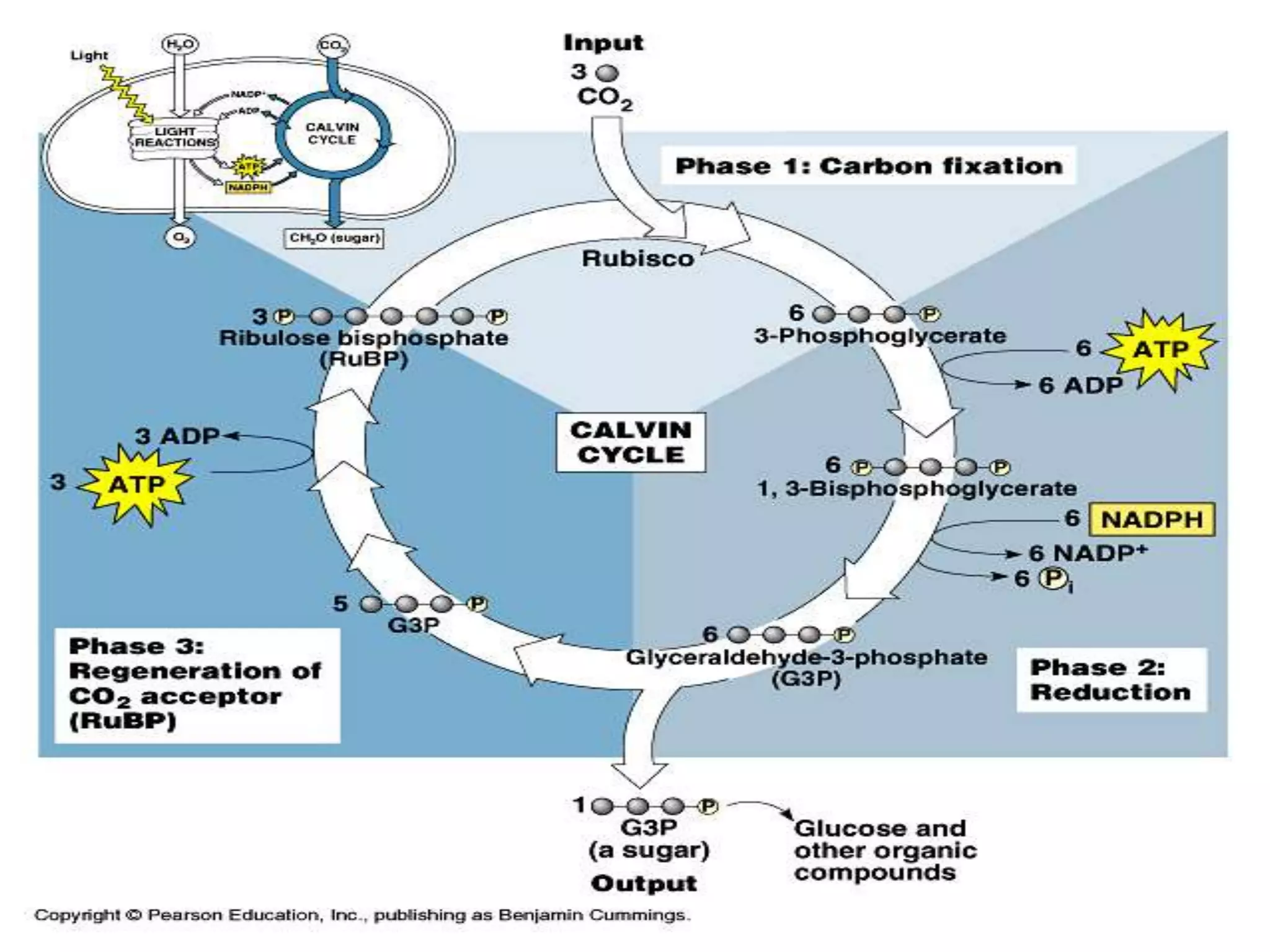
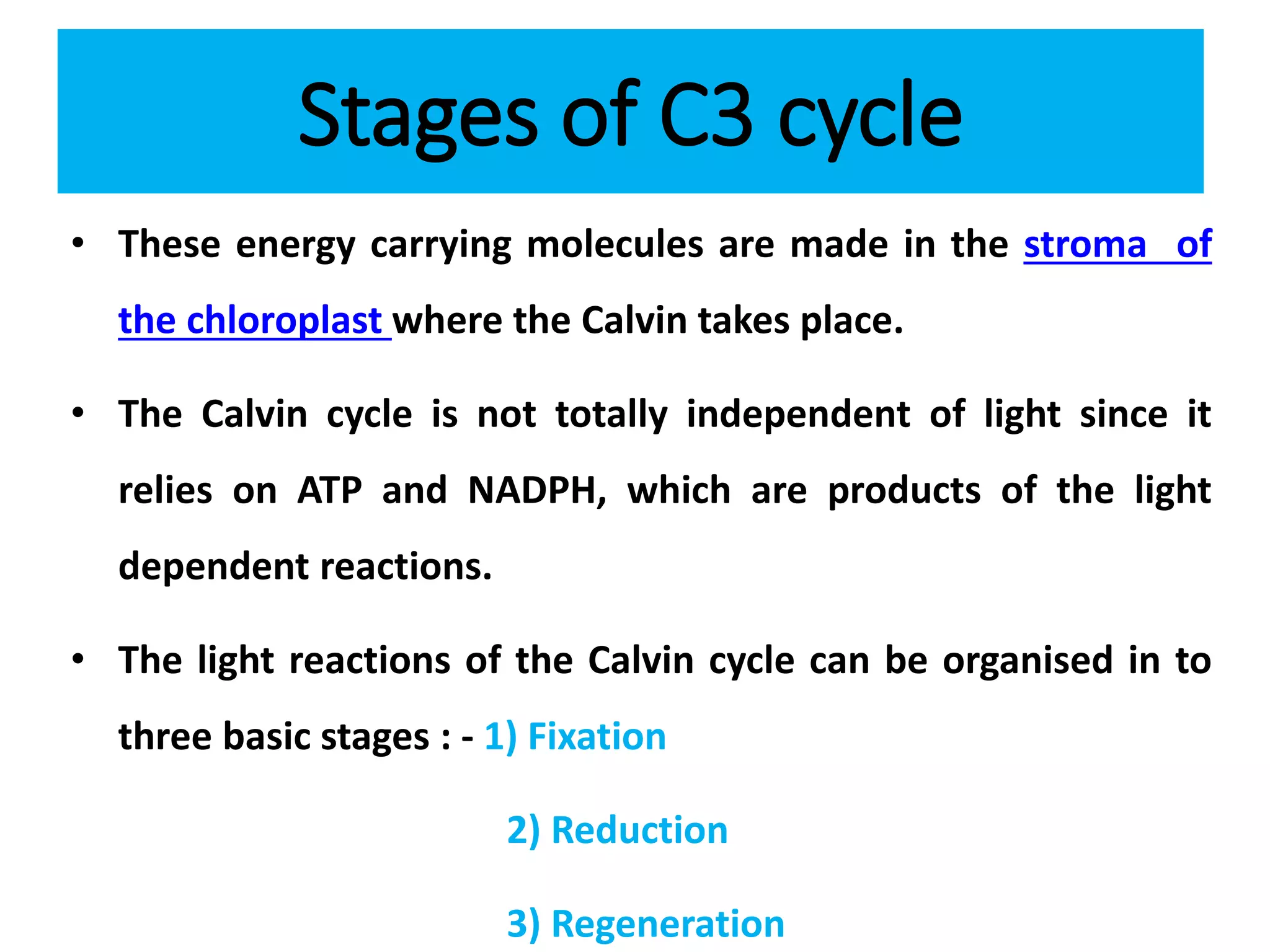
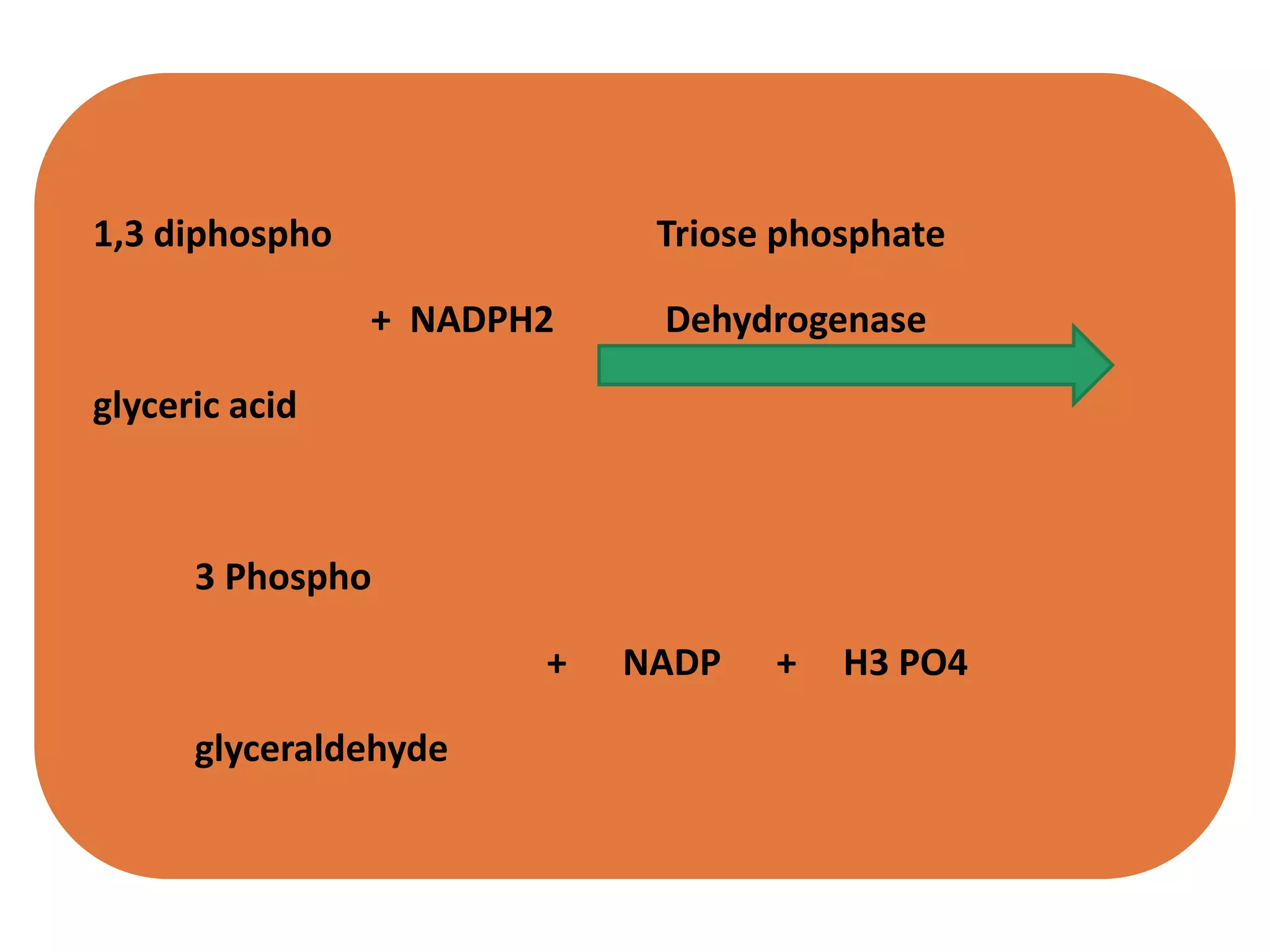
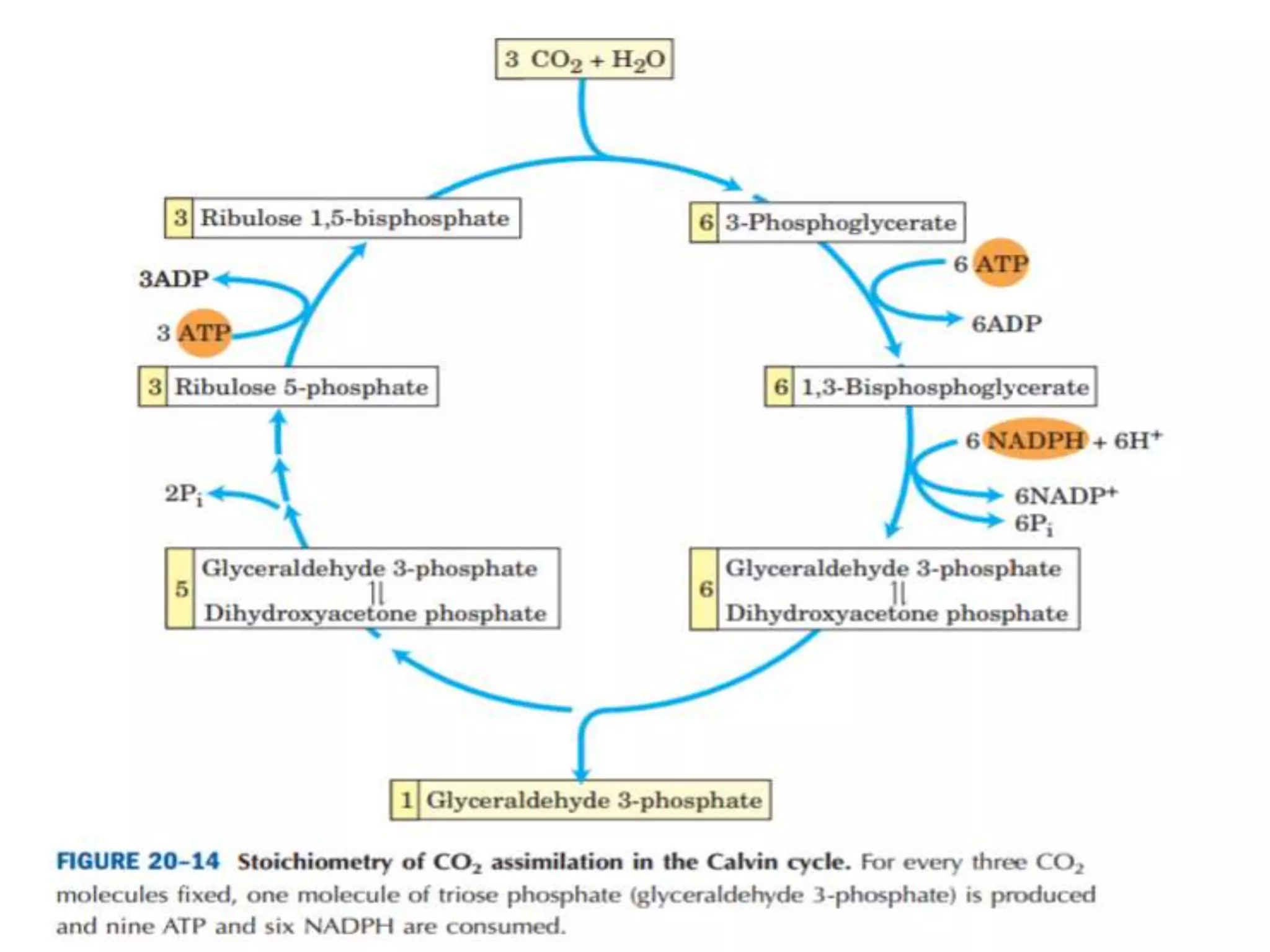
The C3 cycle, also known as the Calvin cycle, occurs in the dark phase of photosynthesis and involves fixing carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose. It consists of three main stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration. During fixation, the enzyme rubisco incorporates CO2 into ribulose bisphosphate, producing two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. These are then reduced using ATP and NADPH in the reduction stage. Finally, the cycle is regenerated as the original ribulose bisphosphate is reformed, allowing it to fix another CO2. The C3 cycle is essential for carbon assimilation in photosynthesis and the primary producer of organic compounds and food energy in plants. It occurs in all photosynthetic organisms



![Other names for Calvin Cycle : —
1) Dark reactions
2) C3 Cycle
3) Reductive Pentose phosphate Cycle
4) Calvin Cycle
5) Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle [ PCR ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c3cycle-180815173305/75/C3-cycle-4-2048.jpg)









![SIGNIFICANCE OF C3 CYCLE
• It is the main biochemical pathway during the dark reaction
(phase – II) of Photosynthesis.
• It result in the synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2 [ assimilation
of carbon ].
• It depends on the light reaction ( phase I ) for the supply of the
assimiatory power ( ATP and NADPH2 ) required for carbon
assimilation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c3cycle-180815173305/75/C3-cycle-20-2048.jpg)
![• It stores the ATP energy formed during light reaction in the
carbohydrate molecules as the food energy.
• It is the primary source of organic food and food energy for all
the organisms.
• Calvin cycle [ C3 cycle ] reaction occur in all photosynthetic
plants ; i.e. C3, C4 and CAM plants, during the dark phase of
Photosynthesis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c3cycle-180815173305/75/C3-cycle-21-2048.jpg)