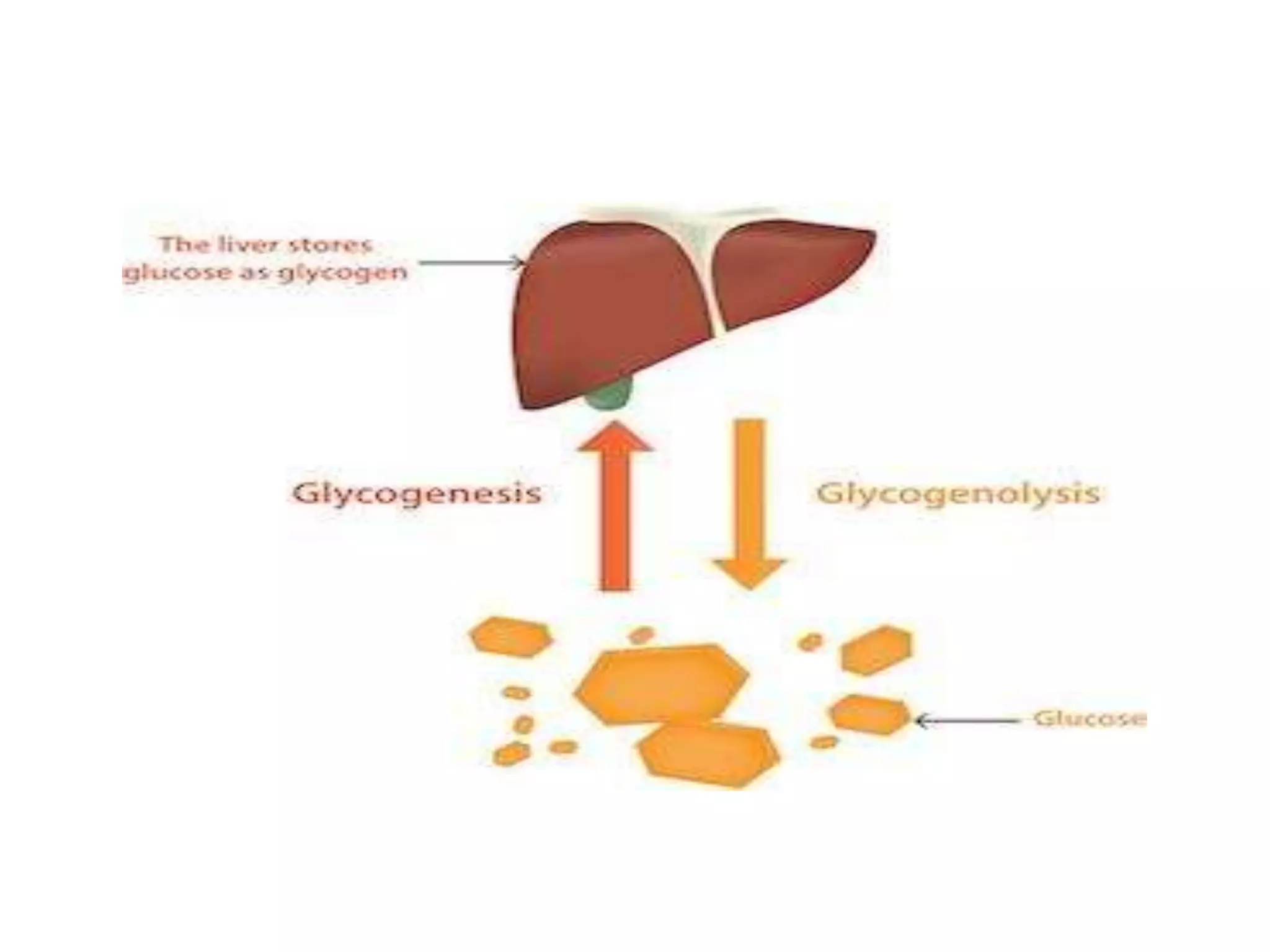
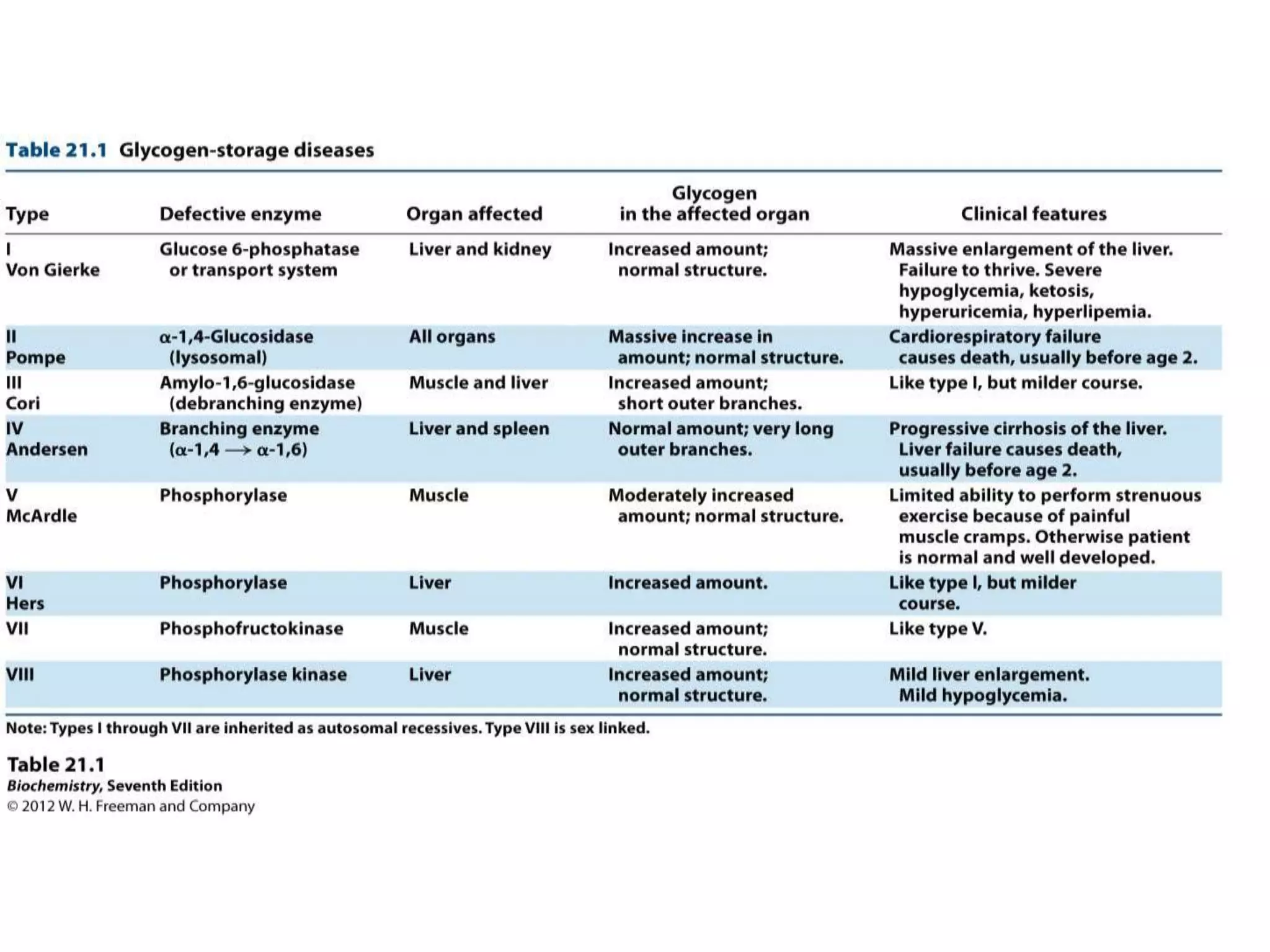
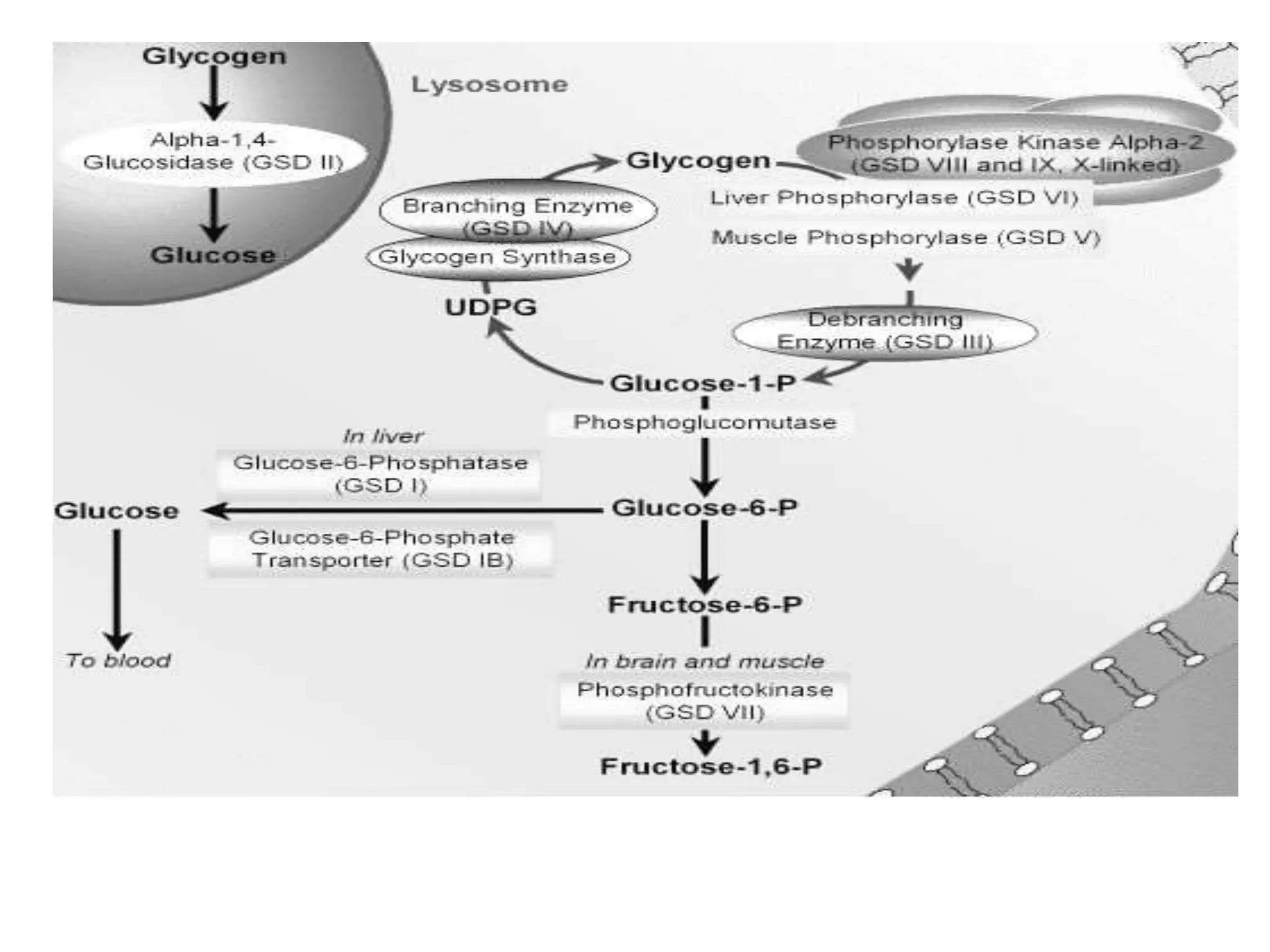
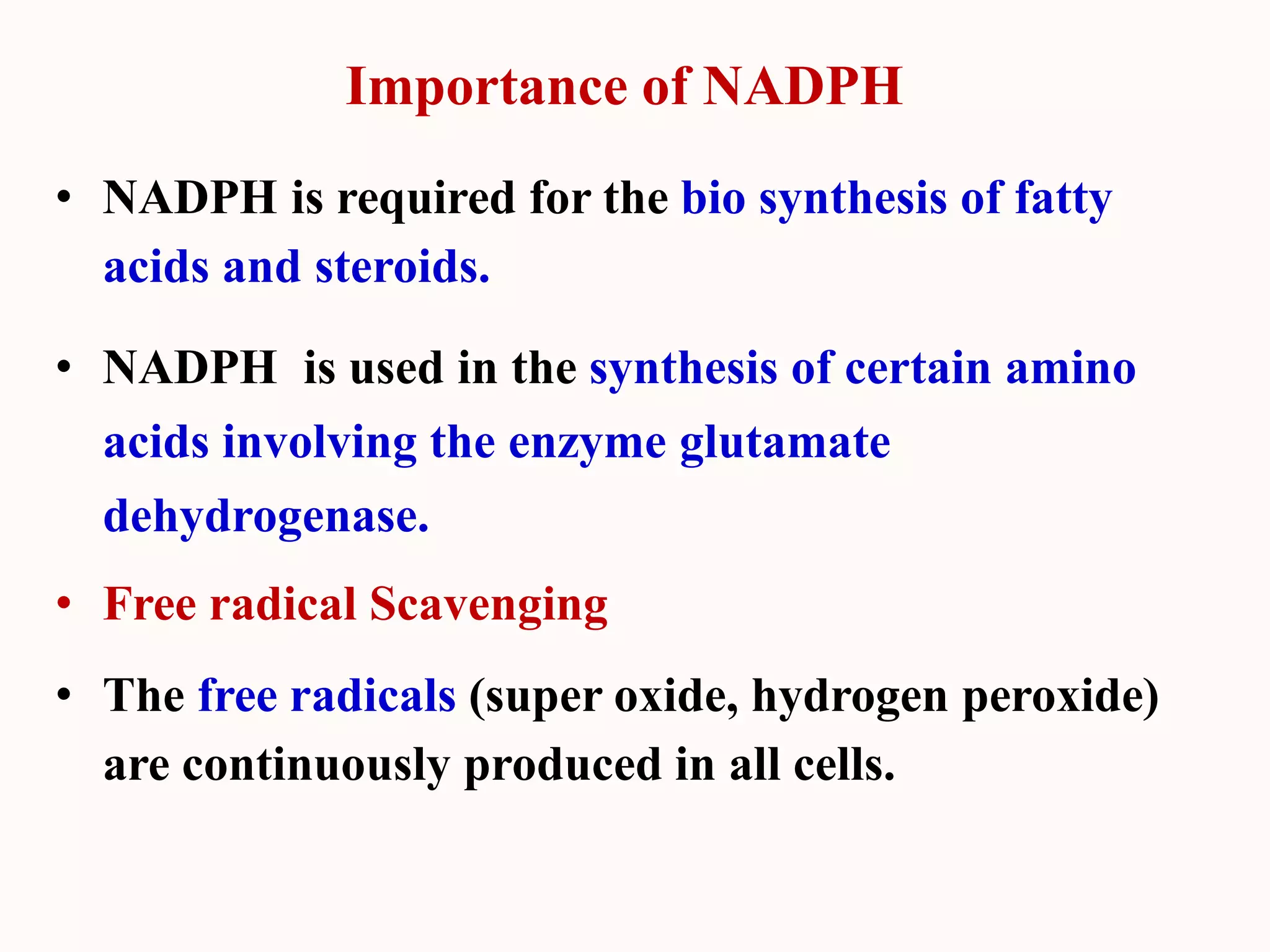
Glycogen storage diseases are caused by defects in enzymes involved in glycogen metabolism, leading to abnormal glycogen deposition. Von Gierke's disease is caused by glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency, resulting in fasting hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia, and hyperuricemia. The pentose phosphate pathway generates NADPH and pentoses, which are important for lipid, steroid, and nucleic acid synthesis. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency can cause hemolytic anemia when exposed to oxidative drugs due to the inability to maintain glutathione levels without NADPH production.