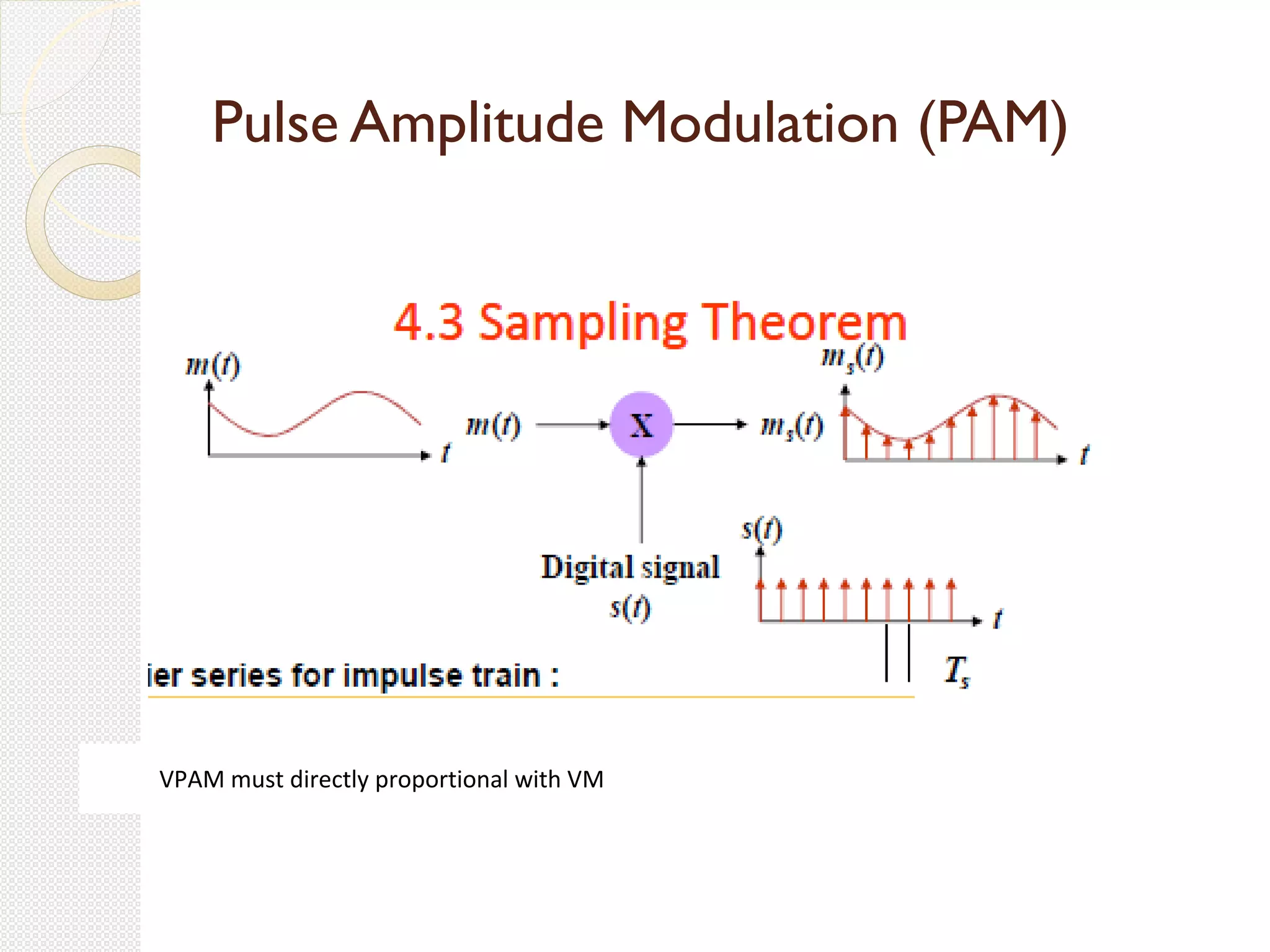
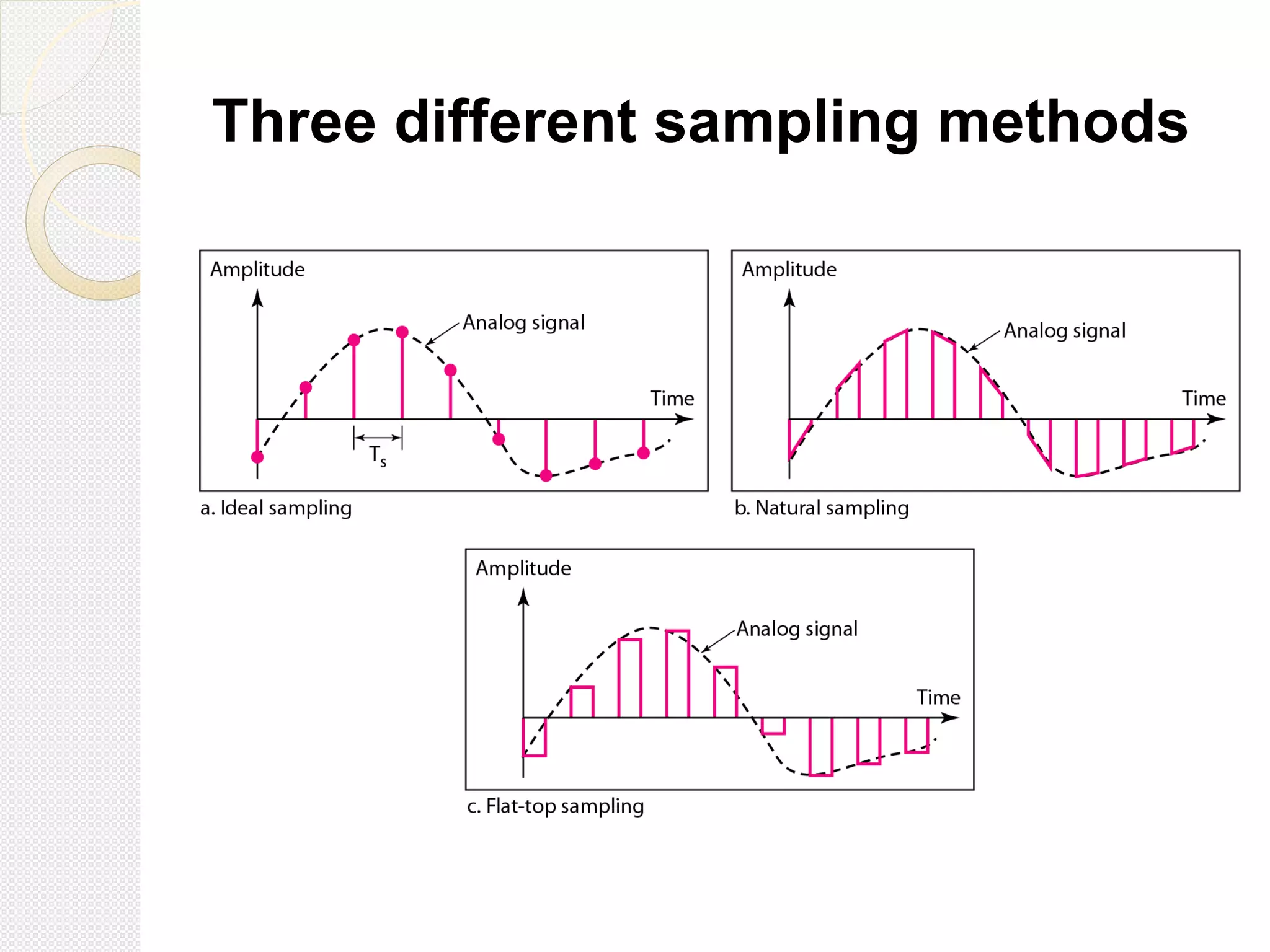
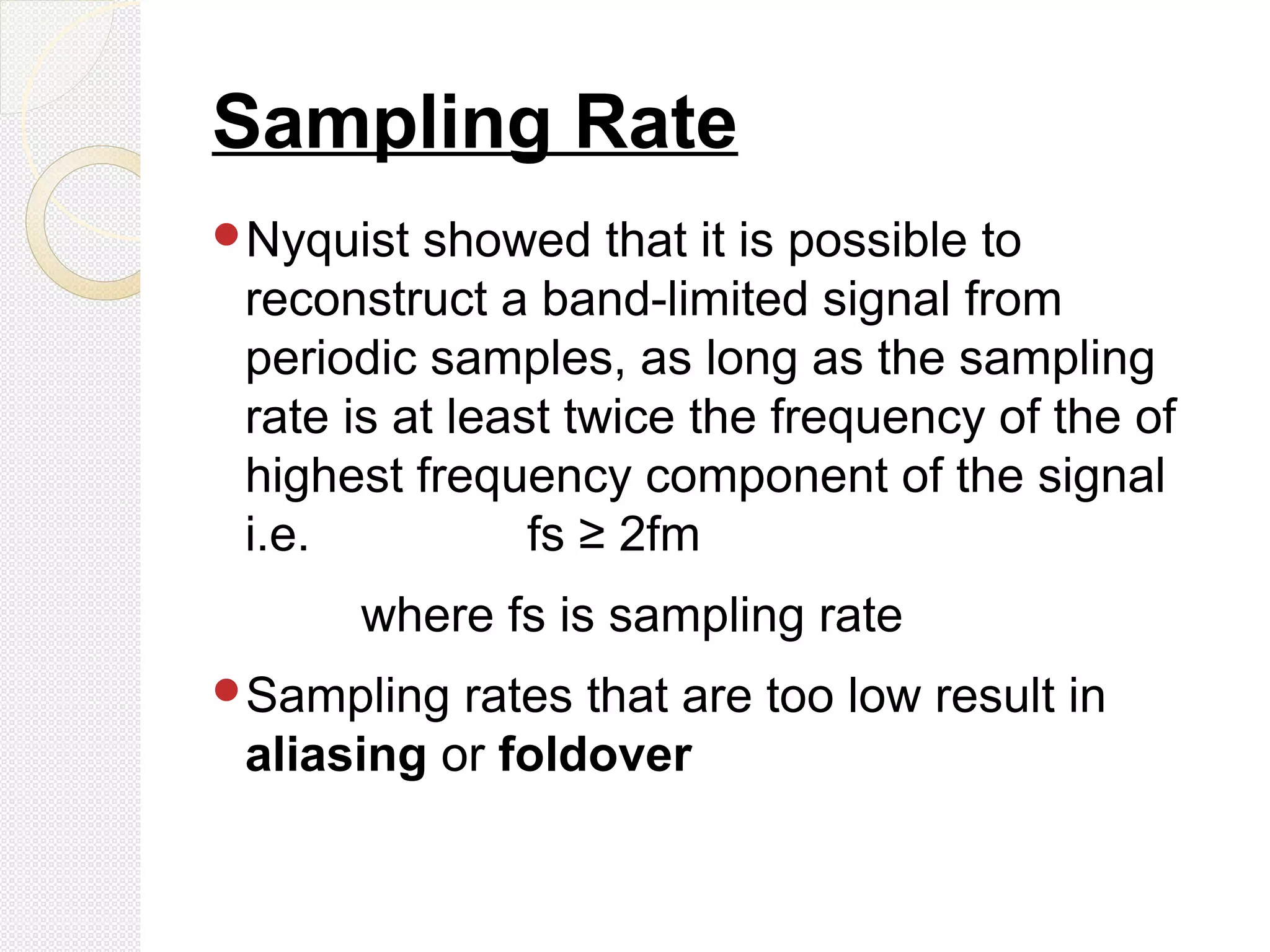
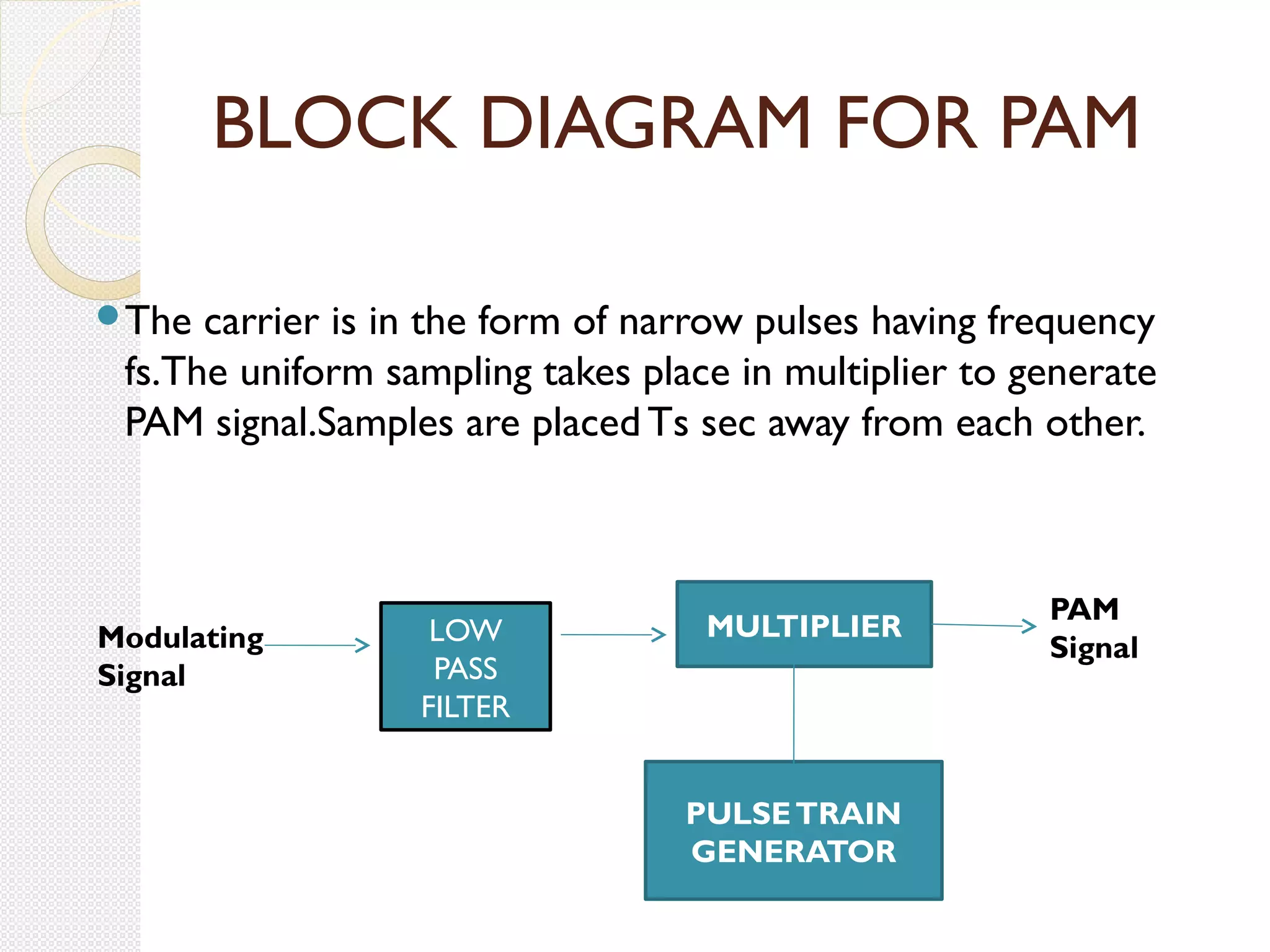
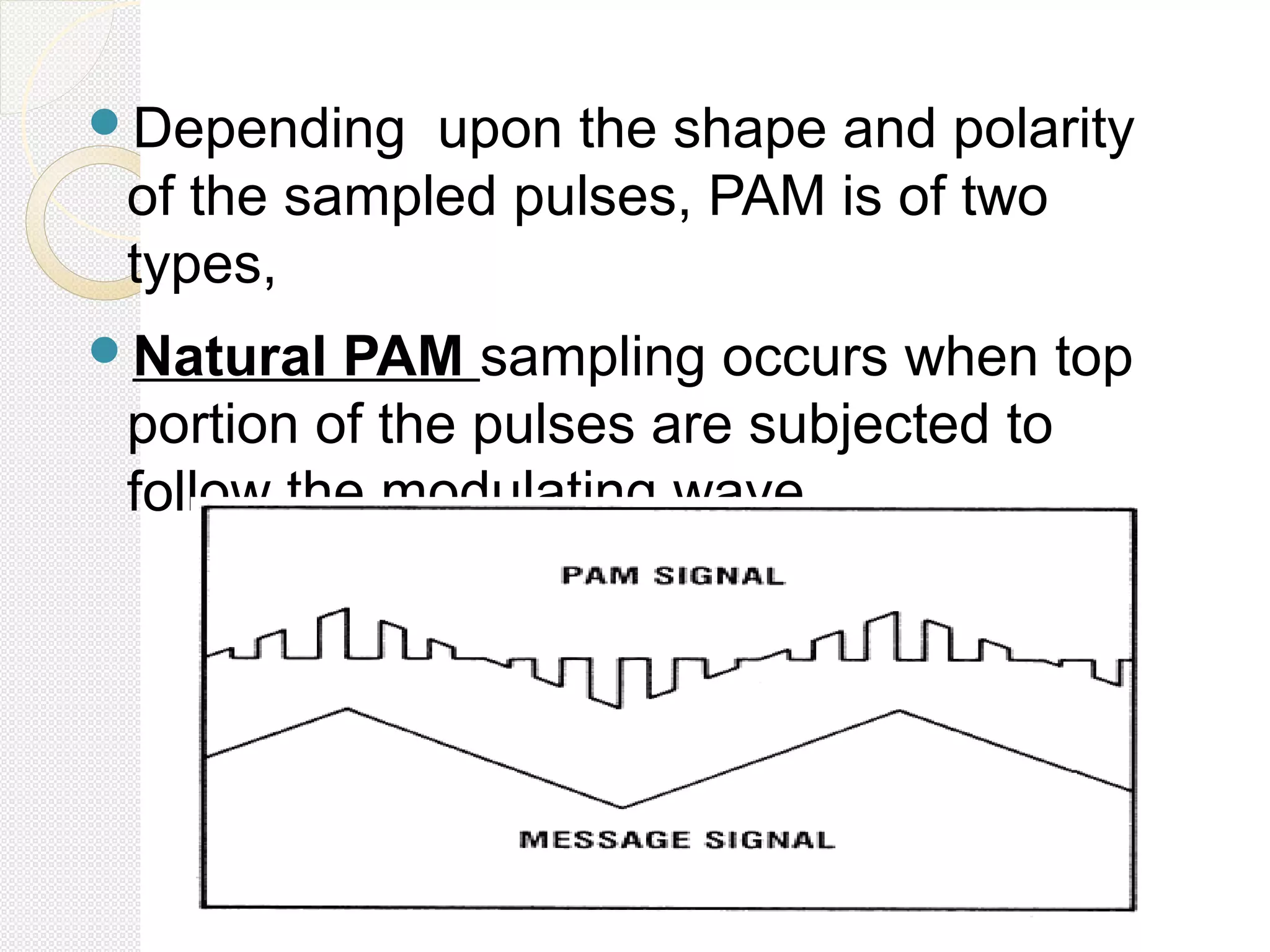
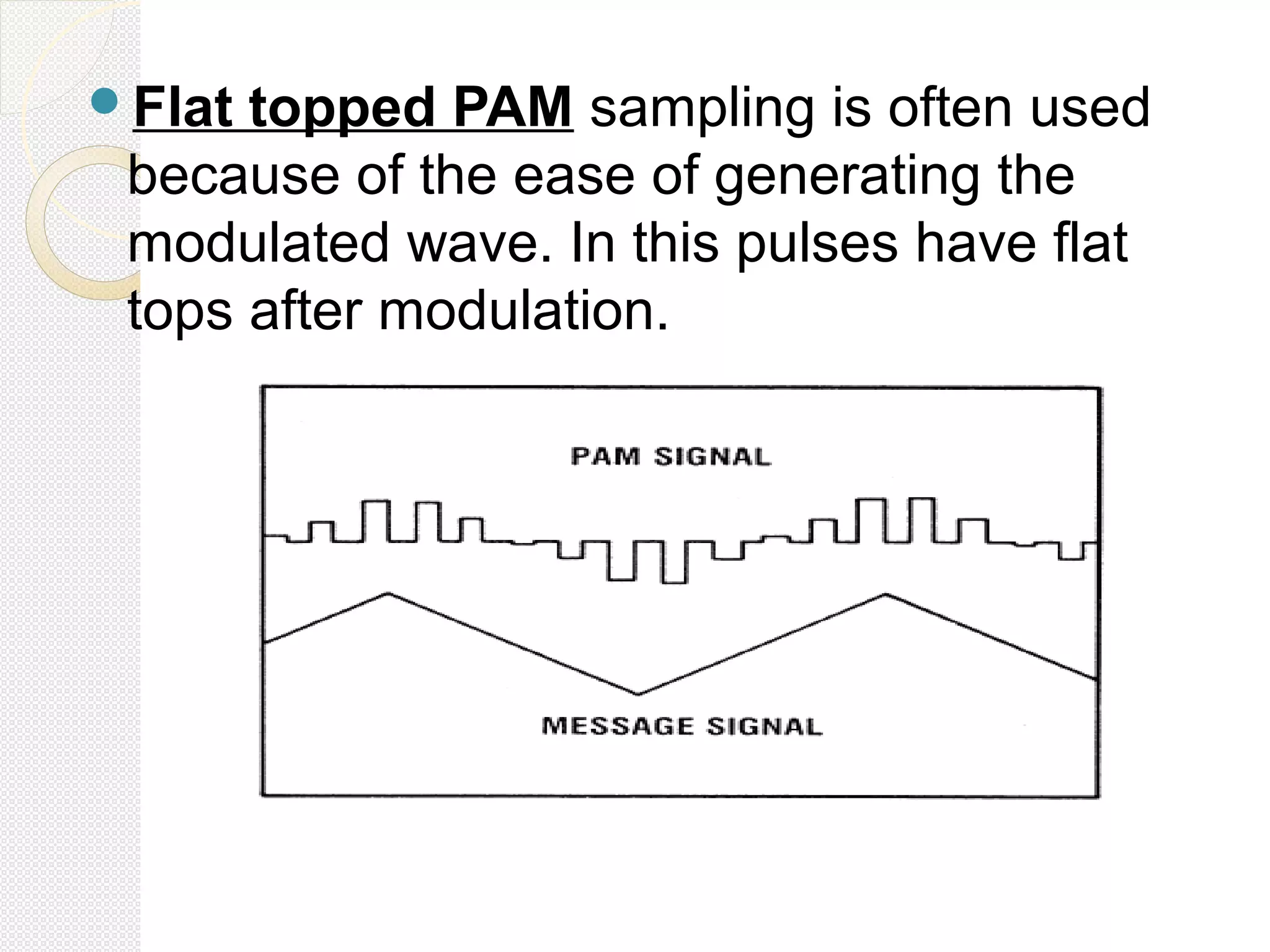
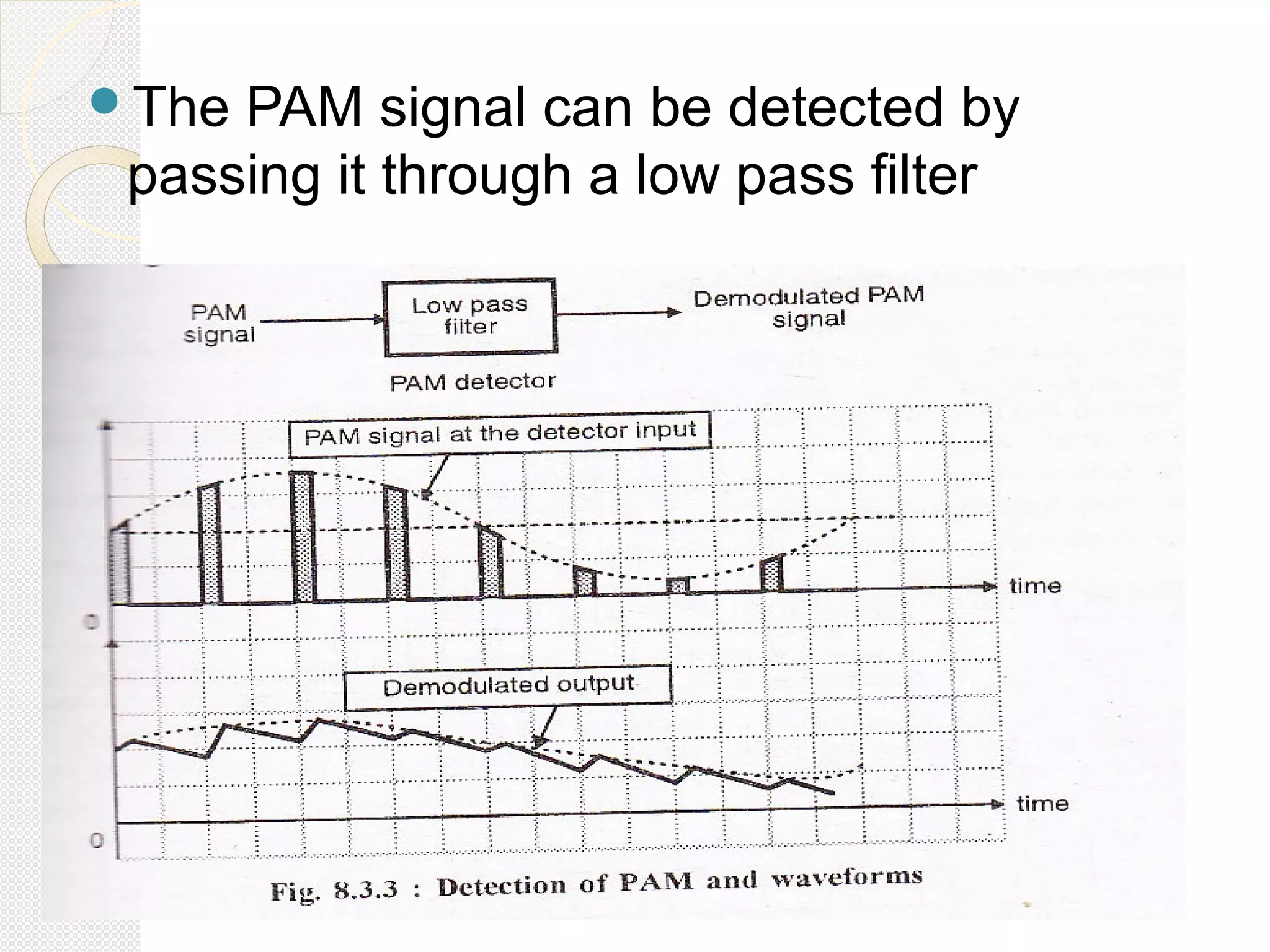
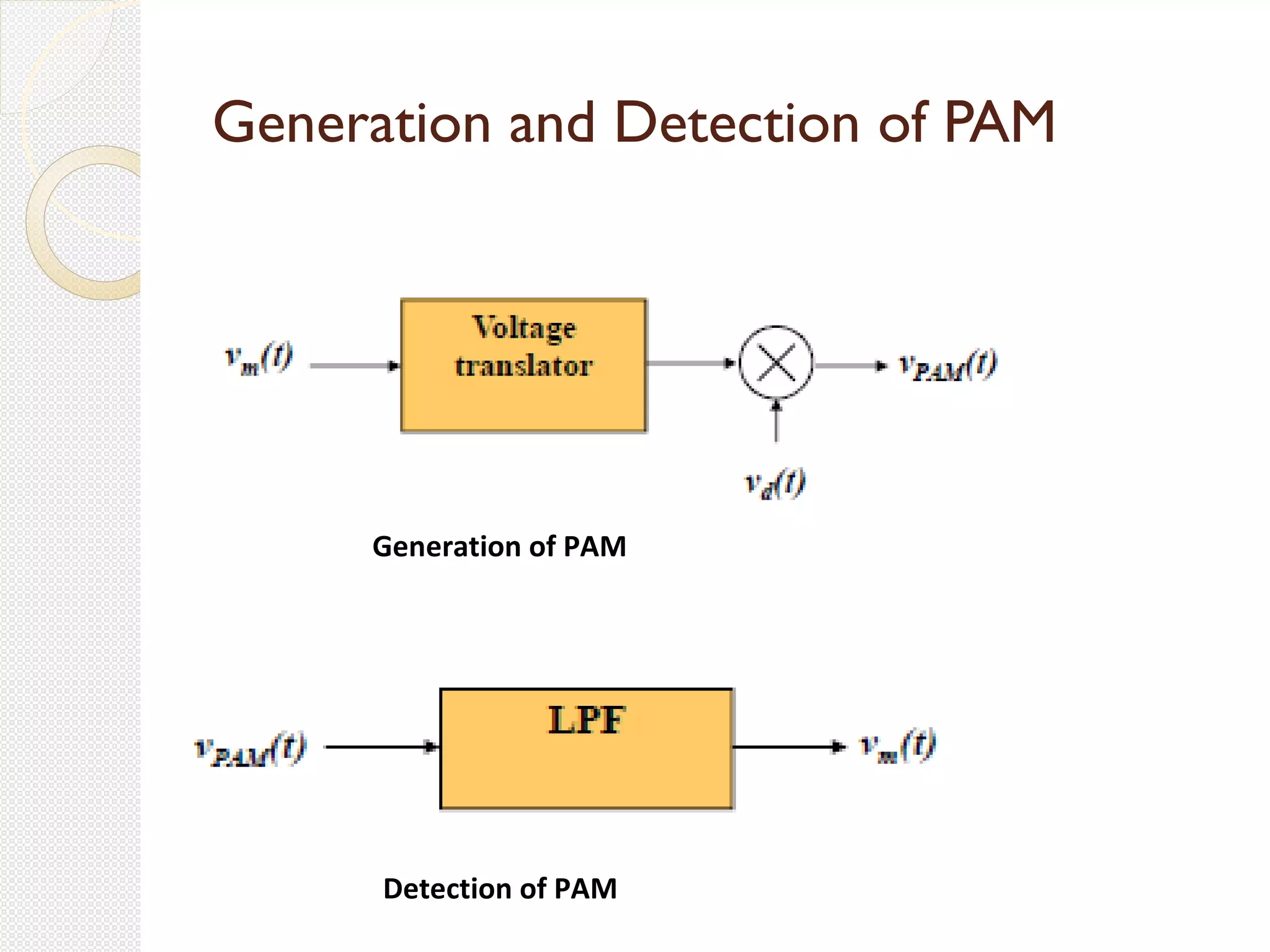
This document discusses pulse amplitude modulation (PAM). It defines modulation as the process of varying a high frequency carrier signal based on a low frequency modulating signal. PAM directly varies the amplitude of uniform pulses proportional to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. The document covers sampling of analog signals, different sampling methods, the Nyquist sampling theorem, block diagrams of PAM systems, types of PAM, and generation and detection of PAM signals. The main advantage of PAM concluded is its better noise immunity and use of repeaters for more reliable communication.