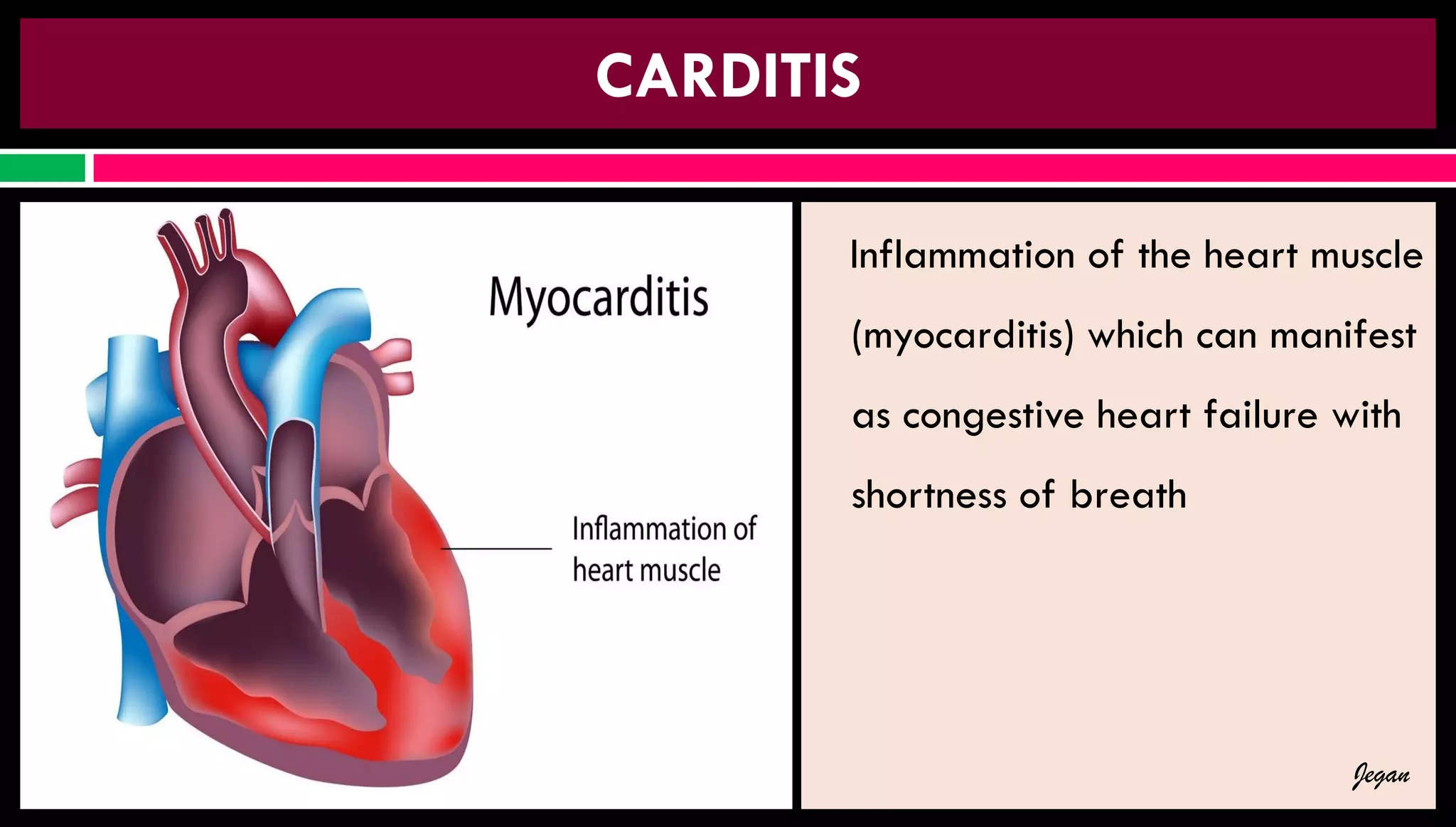
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disorder resulting from an untreated group A streptococcal pharyngeal infection, primarily affecting children aged 5-15 years. It manifests through complications such as polyarthritis, carditis, and rheumatic heart disease, driven by antibody cross-reactivity between streptococcus and heart proteins. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging, while treatment includes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications.