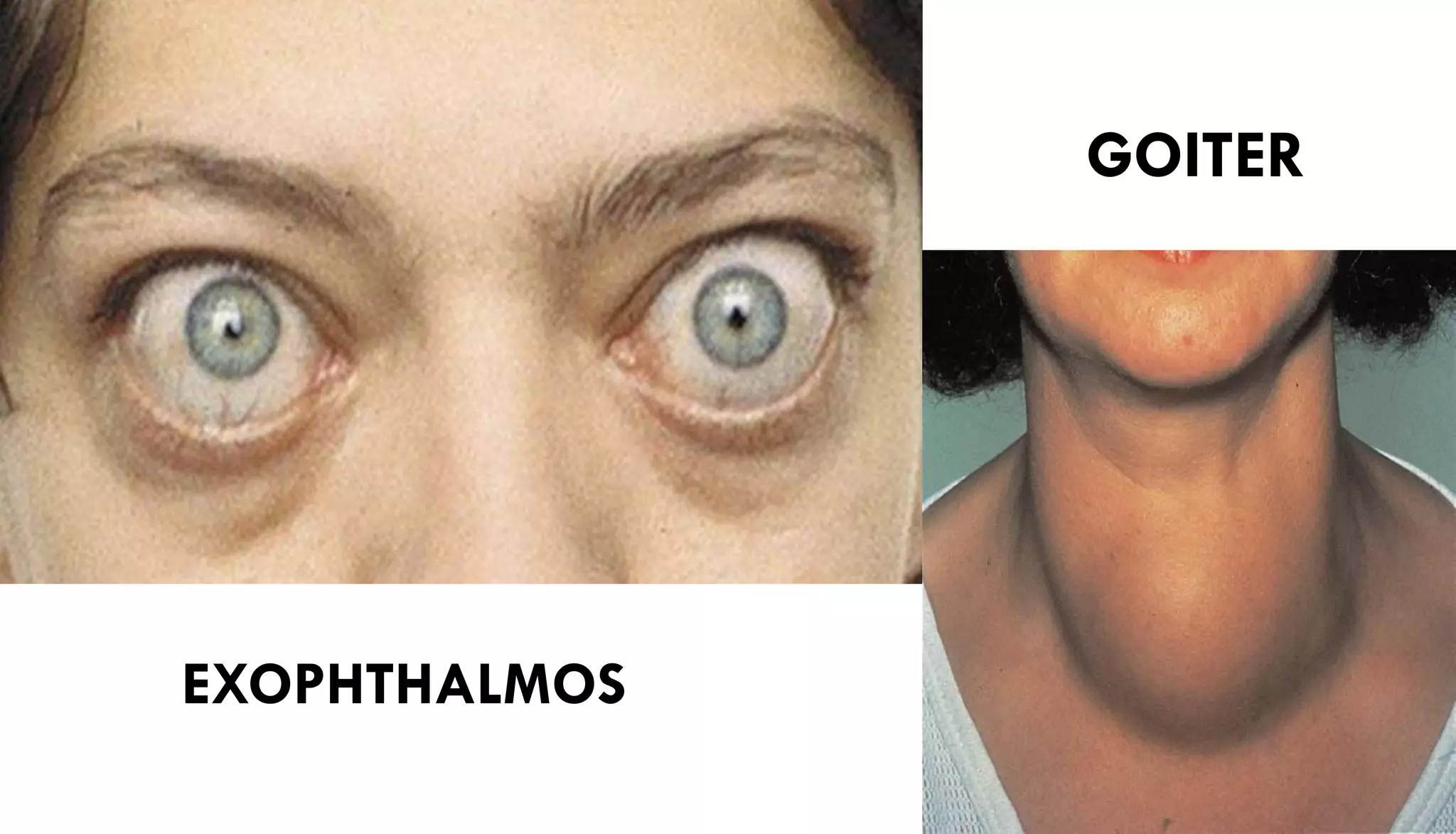
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to excessive thyroid hormone production, particularly affecting women. It results in symptoms such as hyperthyroidism, goiter, and exophthalmos, with genetic and environmental factors contributing to its development. Diagnosis involves physical exams and tests while treatment options include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery.