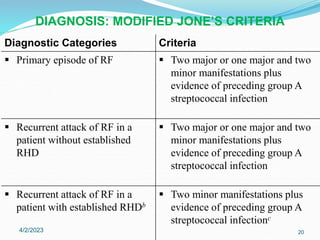
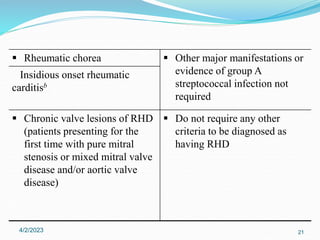
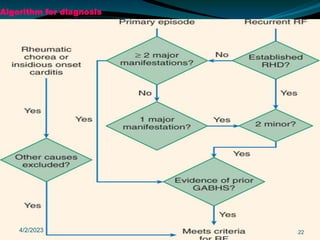
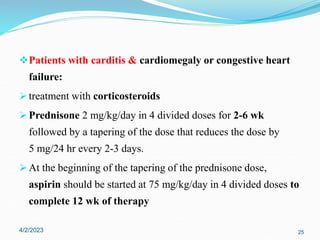
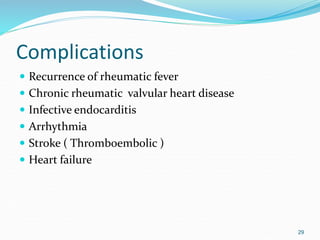
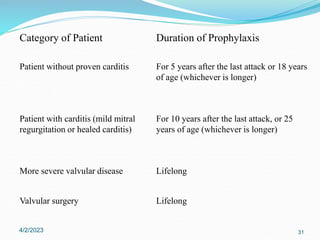
Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) is a multisystem autoimmune disease triggered by infection with group A streptococci, predominantly affecting children aged 5-15 years, particularly in developing nations. Clinical presentations include migratory arthritis, carditis, and chorea, with diagnostics based on the presence of preceding streptococcal infection and characteristic symptoms. Treatment involves antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and long-term prophylaxis to prevent recurrence and complications such as chronic rheumatic heart disease.