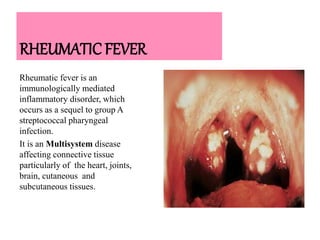
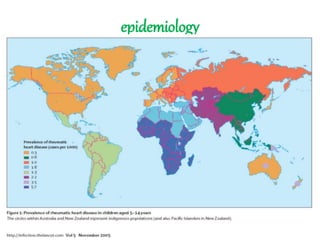
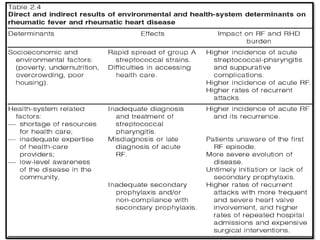
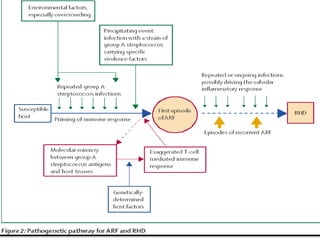
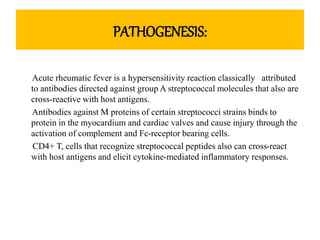
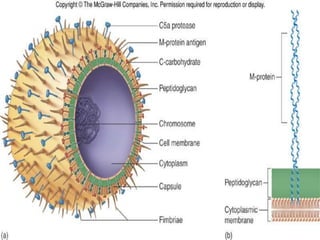
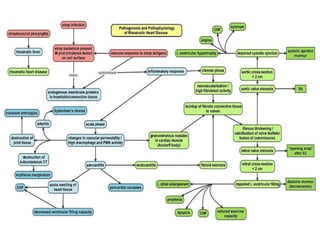
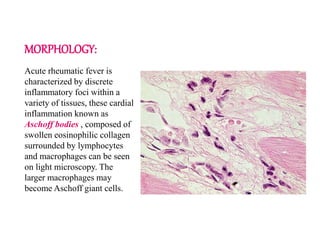
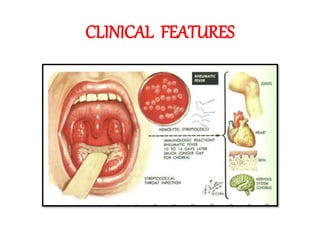
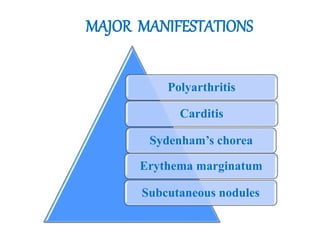
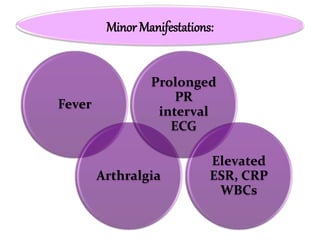
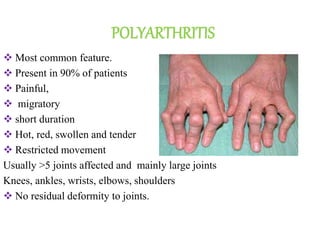
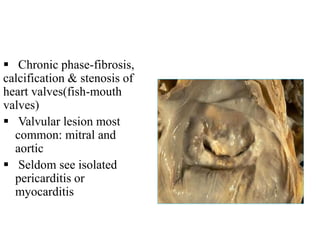
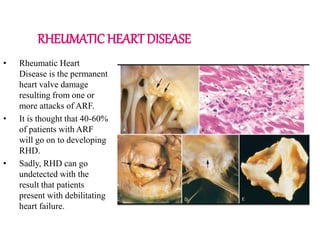
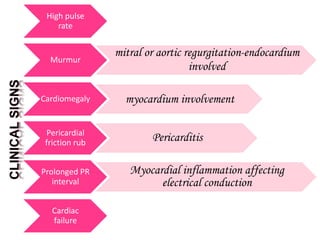
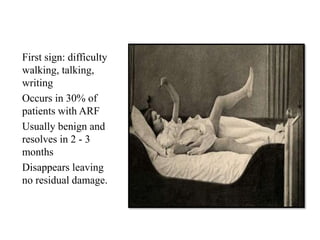
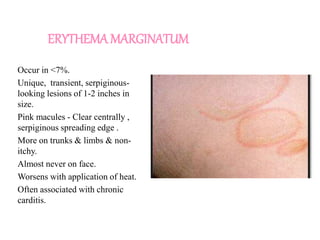
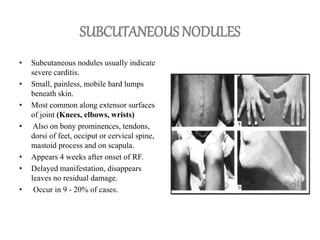
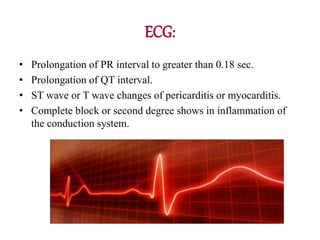
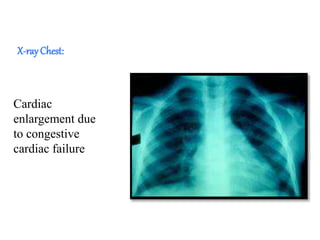
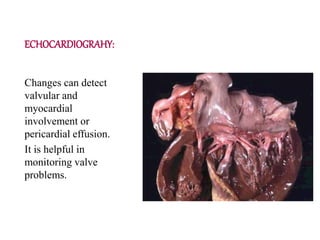
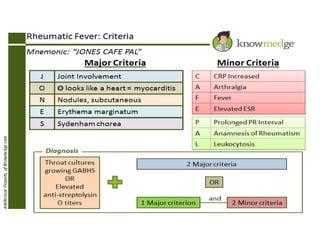
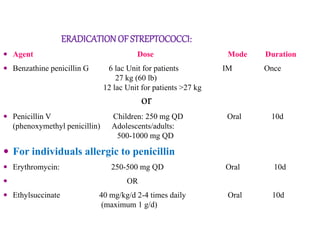
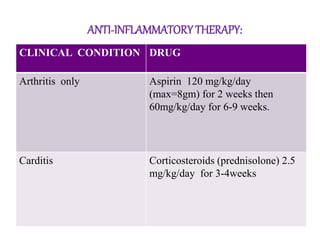
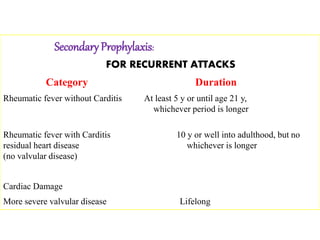
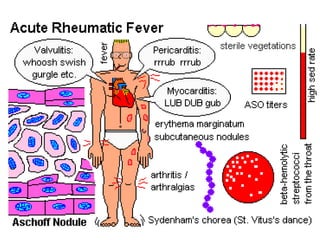
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disorder that occurs as a result of a prior streptococcal throat infection. It affects connective tissues, especially the heart. The disease most commonly affects children ages 5-15. It is characterized by symptoms like polyarthritis, carditis, chorea, and subcutaneous nodules. Long term complications include rheumatic heart disease, which can lead to problems like heart failure. Treatment involves bed rest, antibiotics to eradicate streptococci, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Recurrences can be prevented with long-term antibiotic prophylaxis.