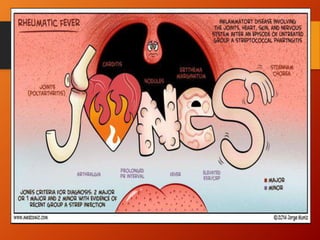
Rheumatic heart disease is a chronic condition caused by rheumatic fever, which is triggered by an autoimmune reaction to a group A streptococcal infection. It most commonly affects the mitral valve, causing inflammation and scarring that can lead to valvular problems like stenosis or regurgitation. In developing countries, rheumatic heart disease remains a major public health problem, with over 15 million cases worldwide resulting in over 200,000 deaths annually. Treatment involves antibiotics to treat the initial strep infection along with medications and potentially surgery to address valvular damage.