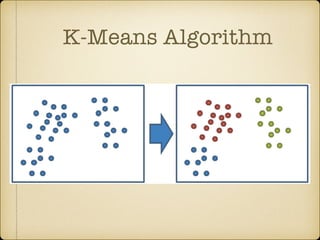
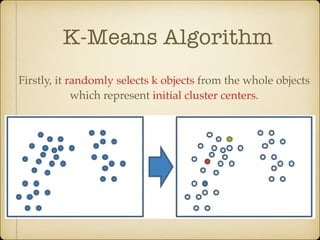
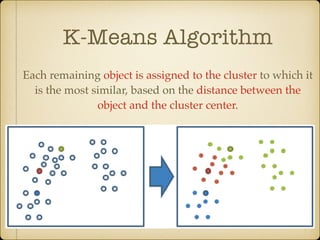
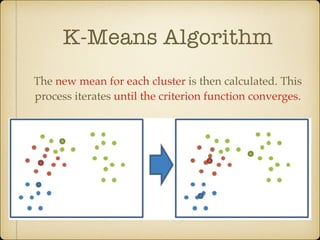
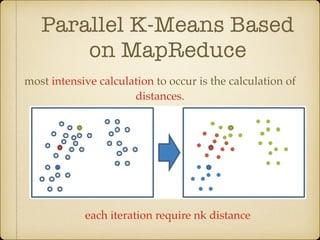
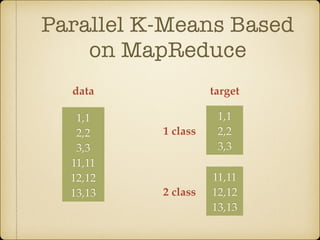
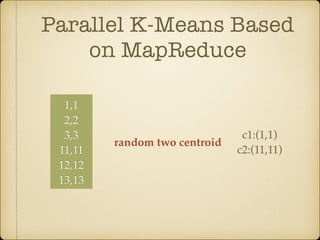
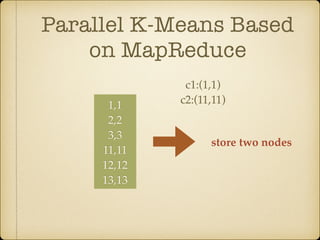
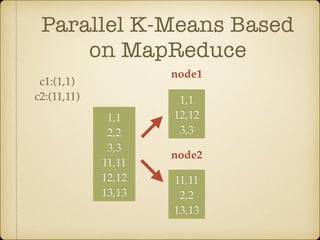
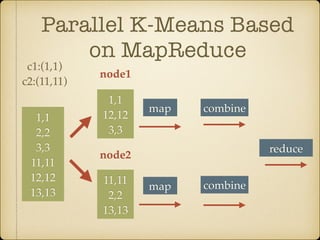
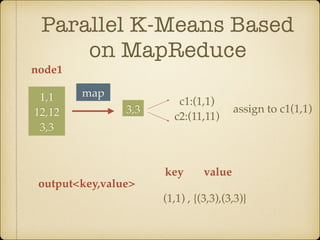
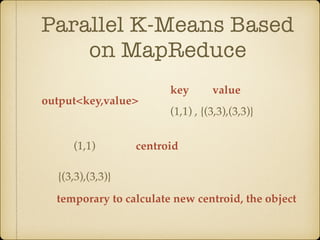
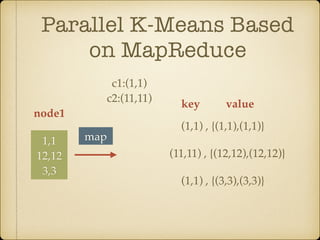
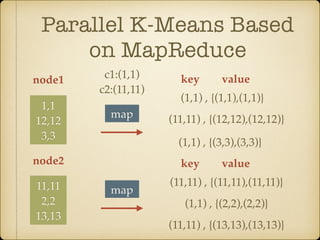
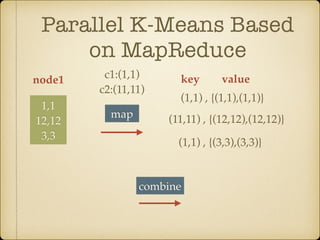
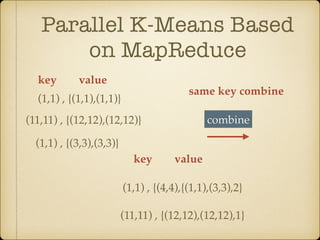
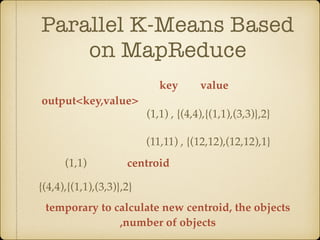
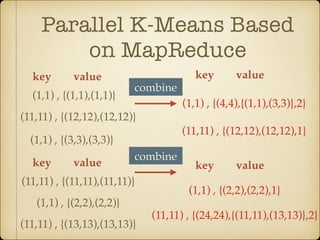
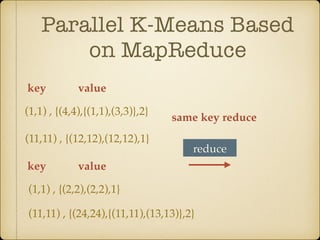
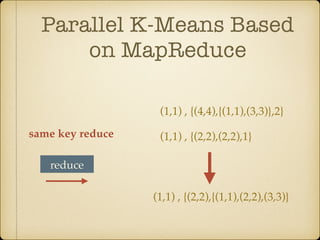
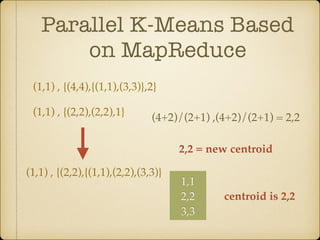
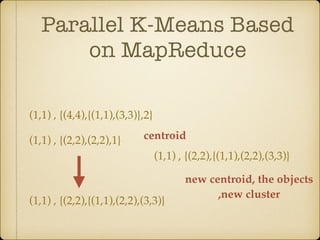
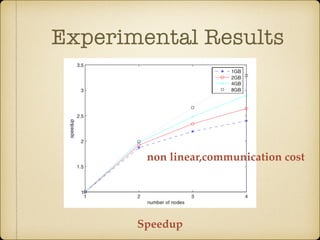
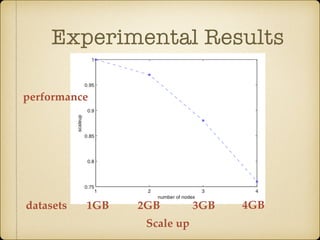
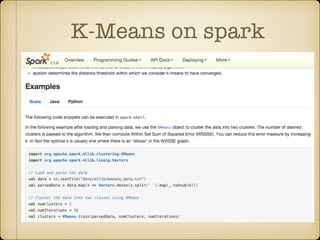
The document discusses parallel k-means clustering algorithms implemented using MapReduce and Spark. It first describes the standard k-means algorithm, which assigns data points to clusters based on distance to centroids. It then presents a MapReduce-based parallel k-means approach where the distance calculations between data points and centroids are distributed across nodes. The map tasks calculate distances and assign points to clusters, combine tasks aggregate results, and reduce tasks calculate new centroids. Experimental results show sub-linear speedup and good scaling to larger datasets. Finally, it briefly mentions k-means implementations on Spark.