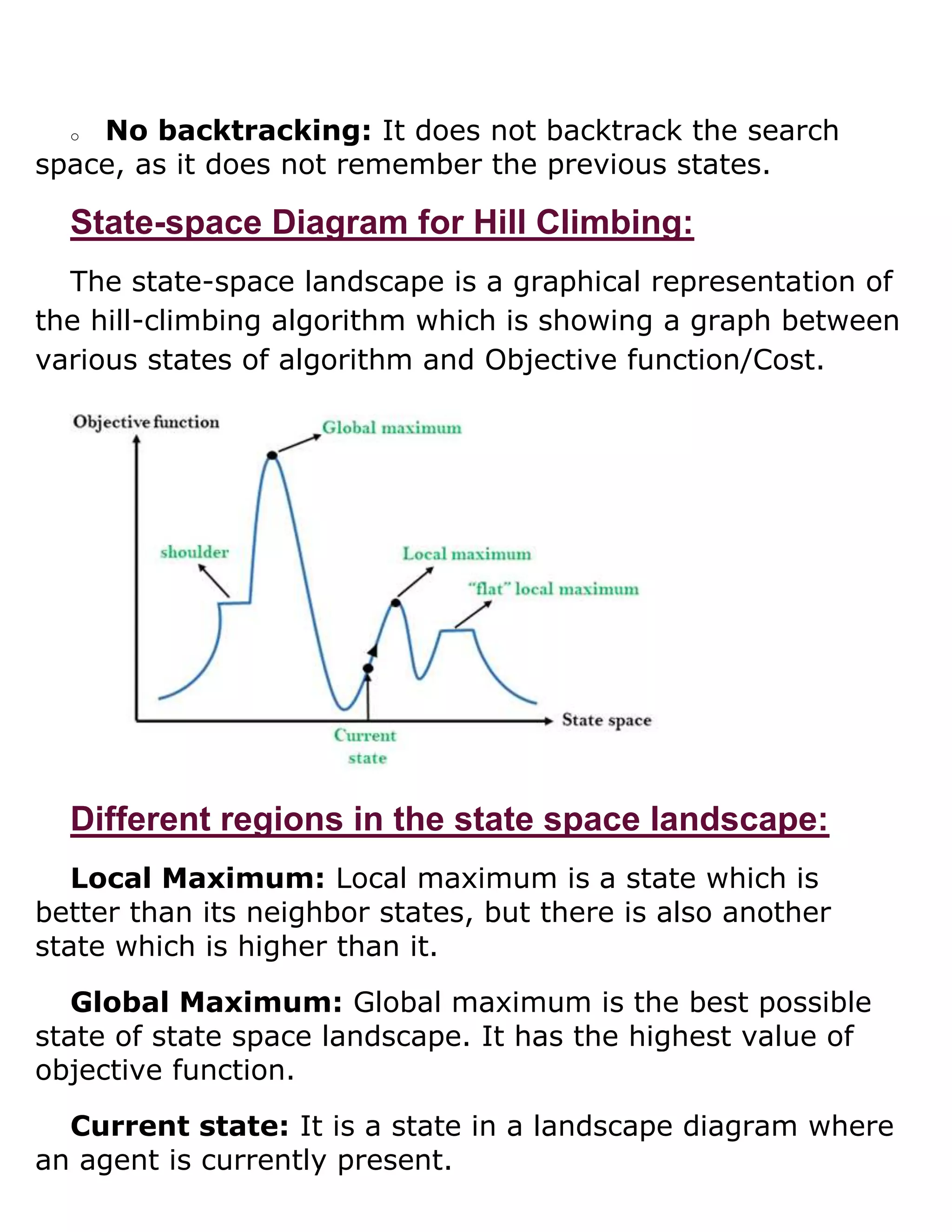
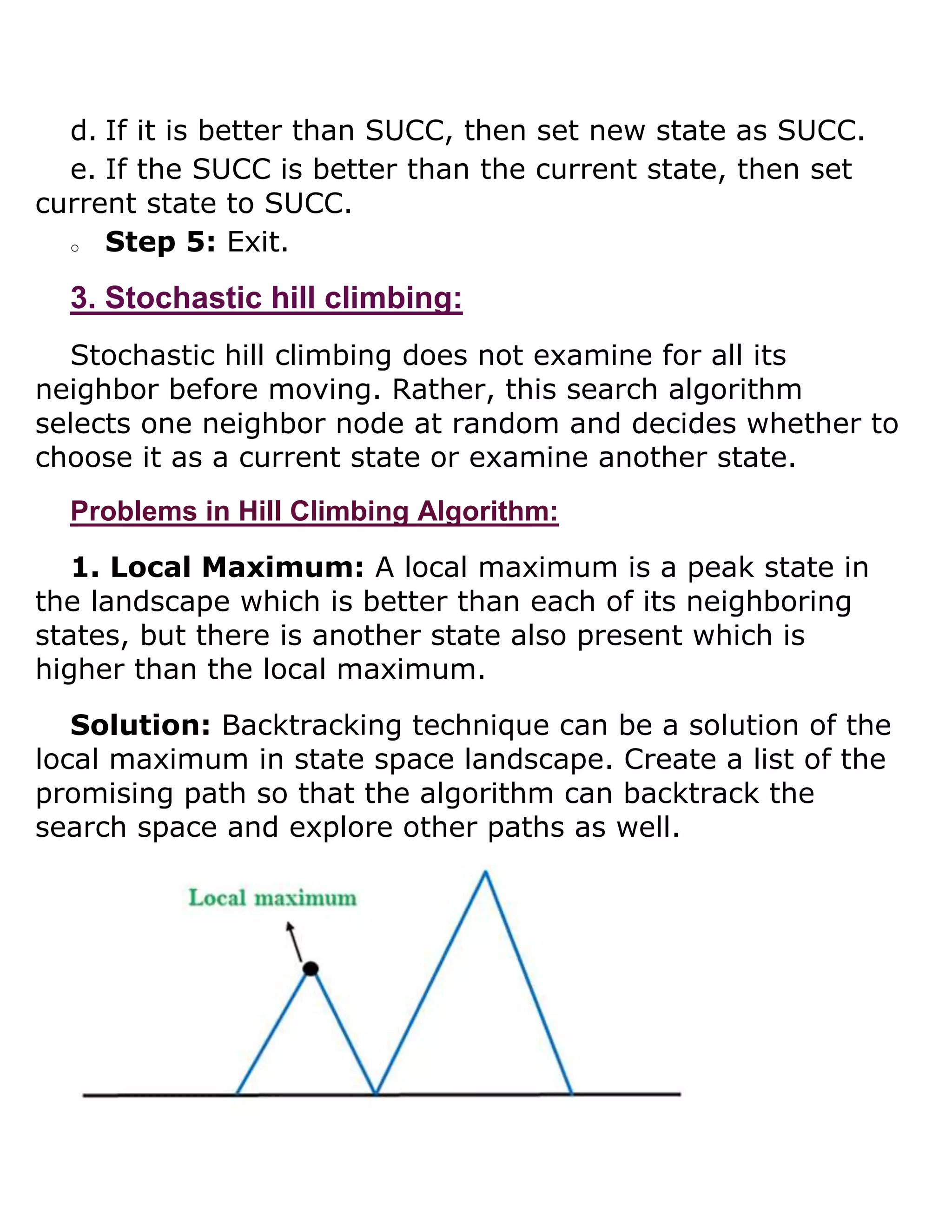
The hill climbing algorithm is a local search technique used to find the optimal solution to a problem. It works by starting with an initial solution and iteratively moving to a neighboring solution that has improved value until no better solutions can be found. Simple hill climbing only considers one neighbor at a time, while steepest ascent examines all neighbors and chooses the one closest to the optimal solution. The algorithm can get stuck at local optima rather than finding the global optimum. Techniques like simulated annealing incorporate randomness to help escape local optima.