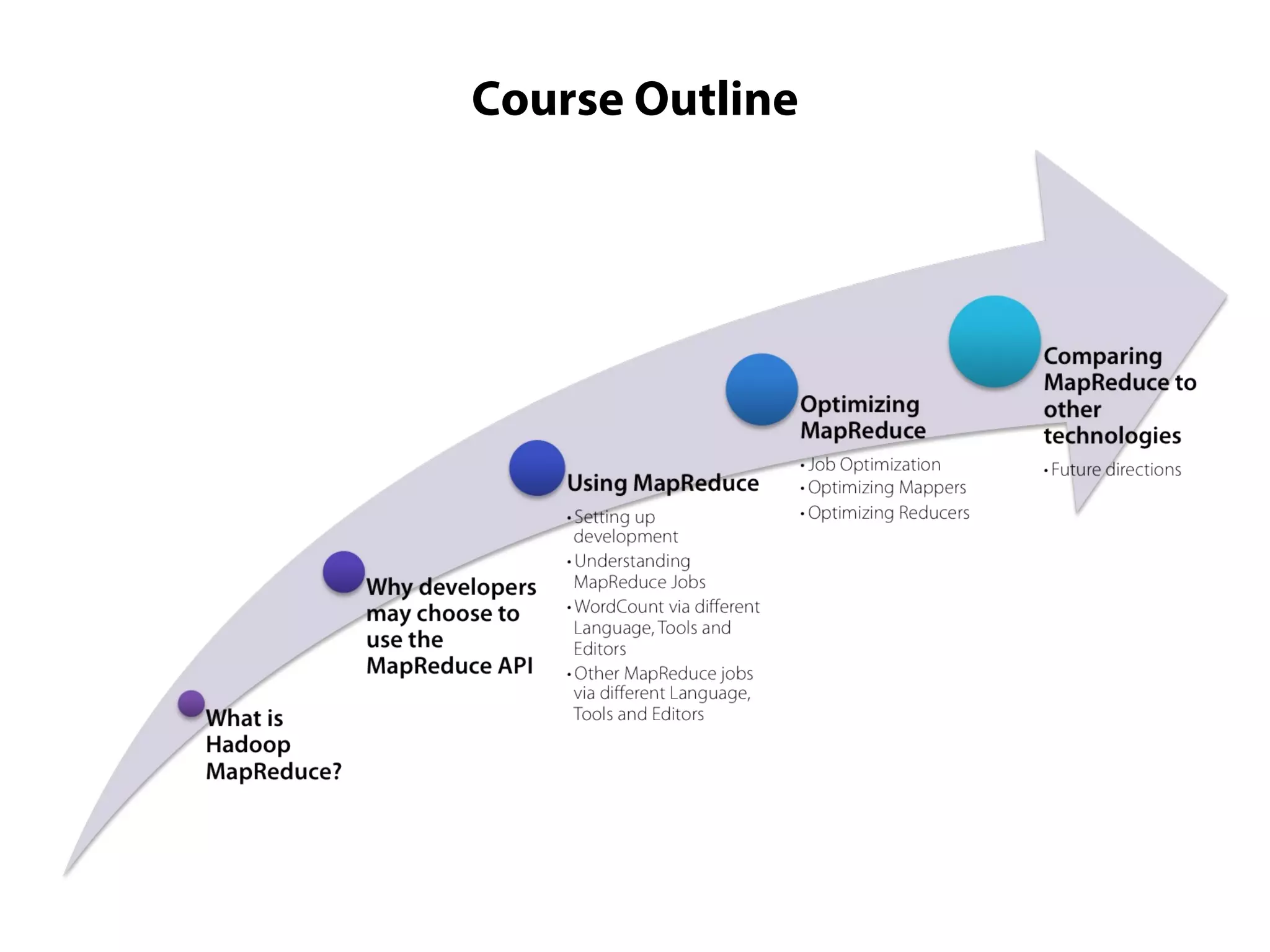
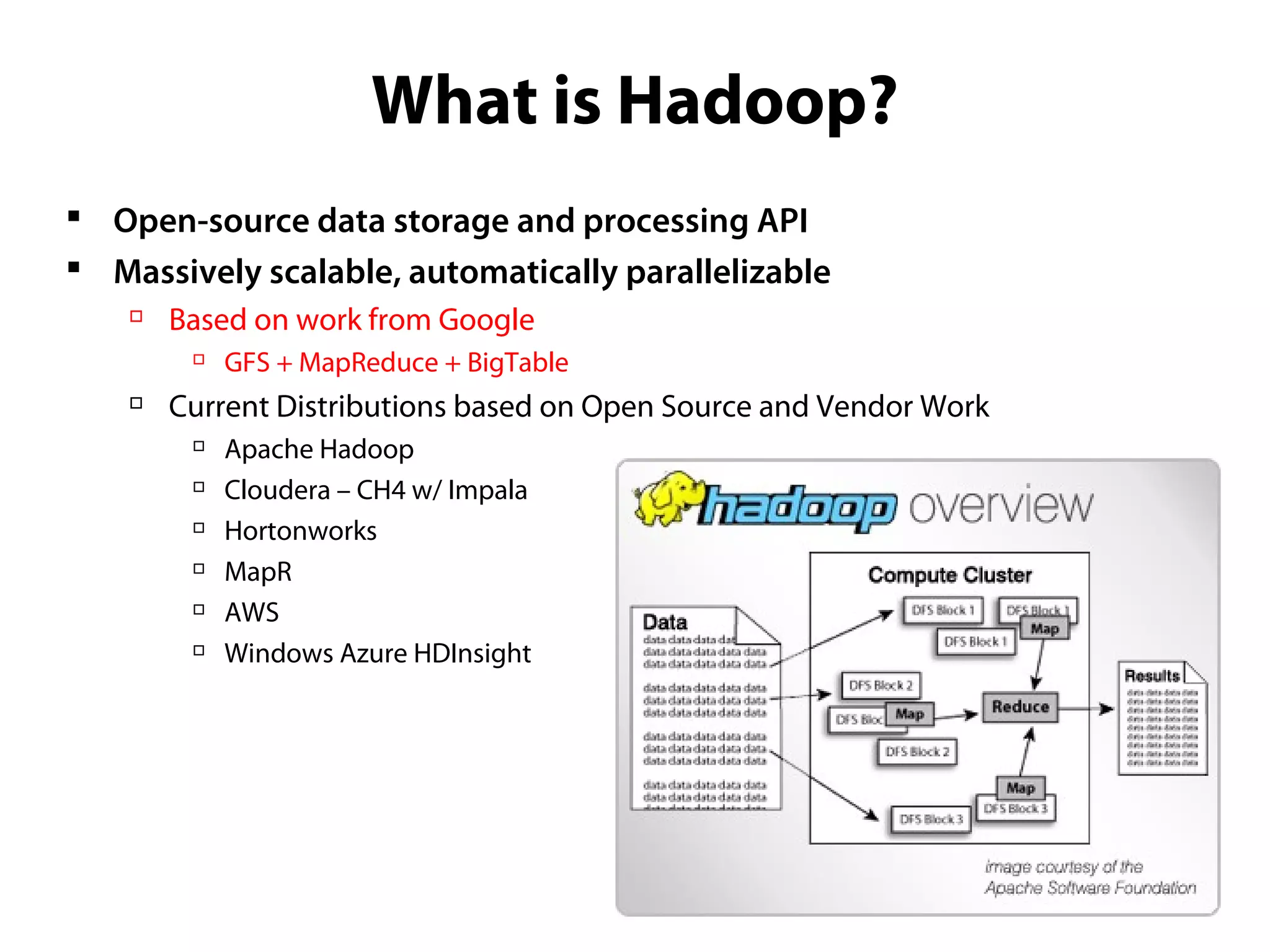
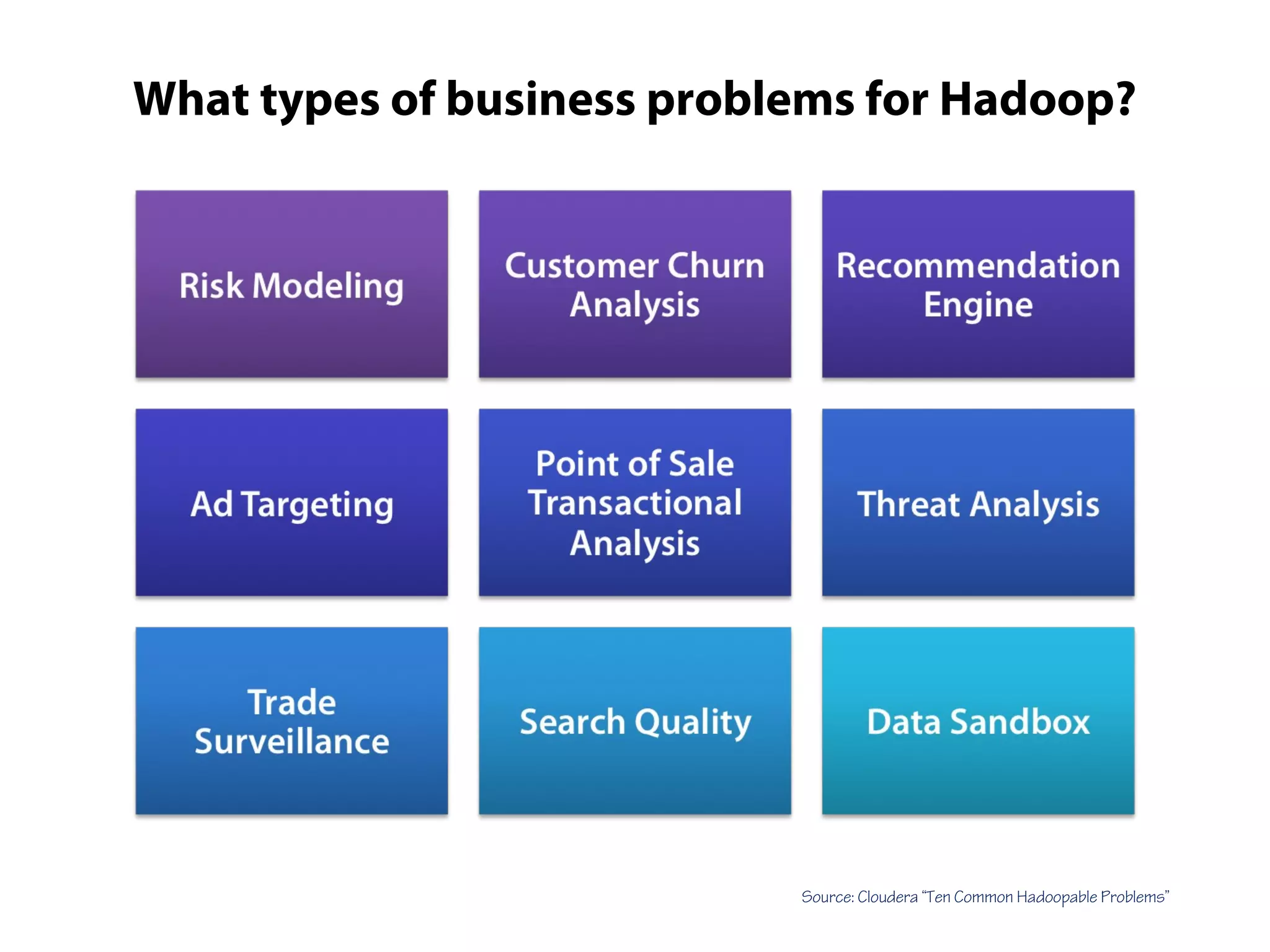
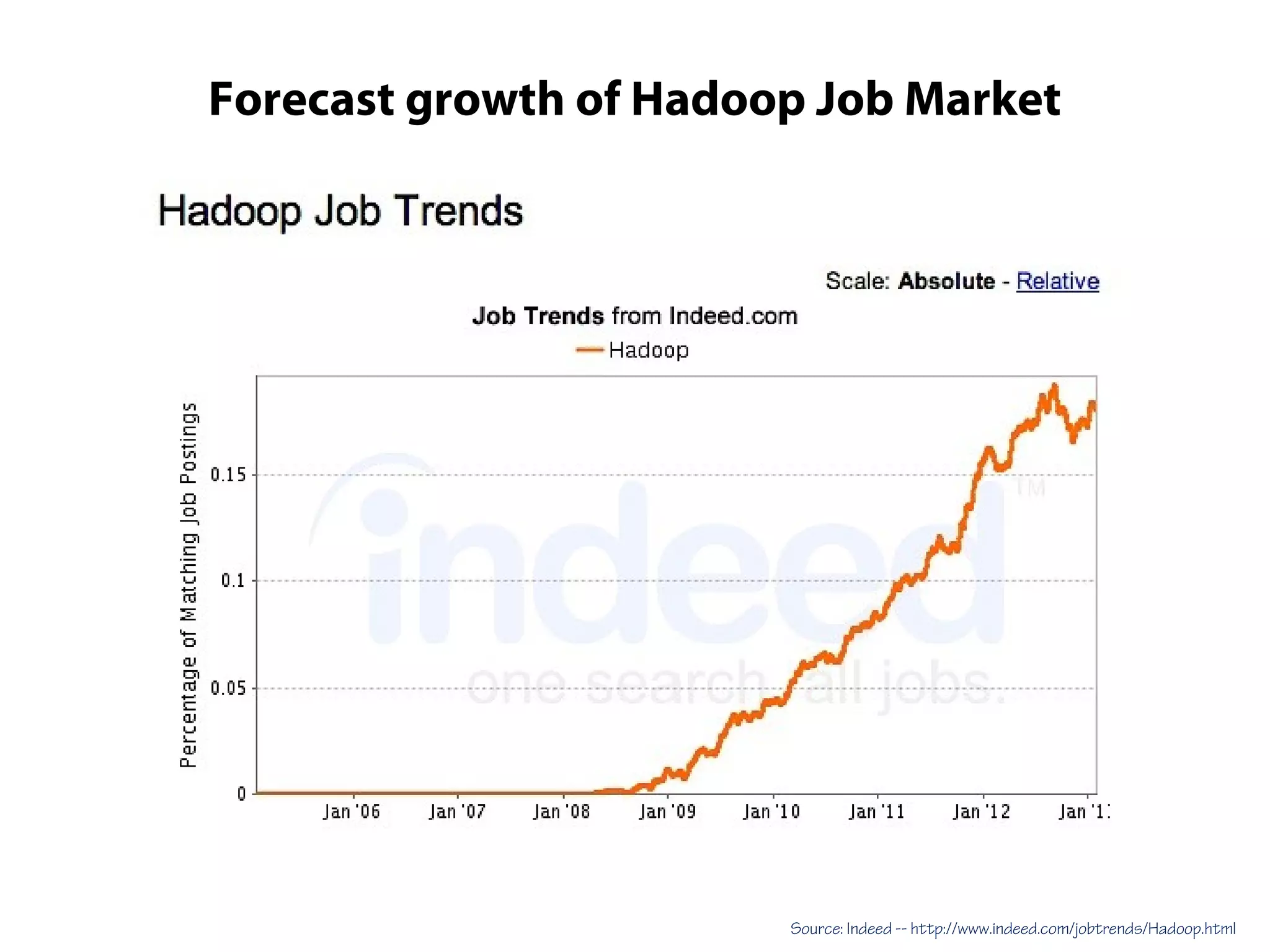
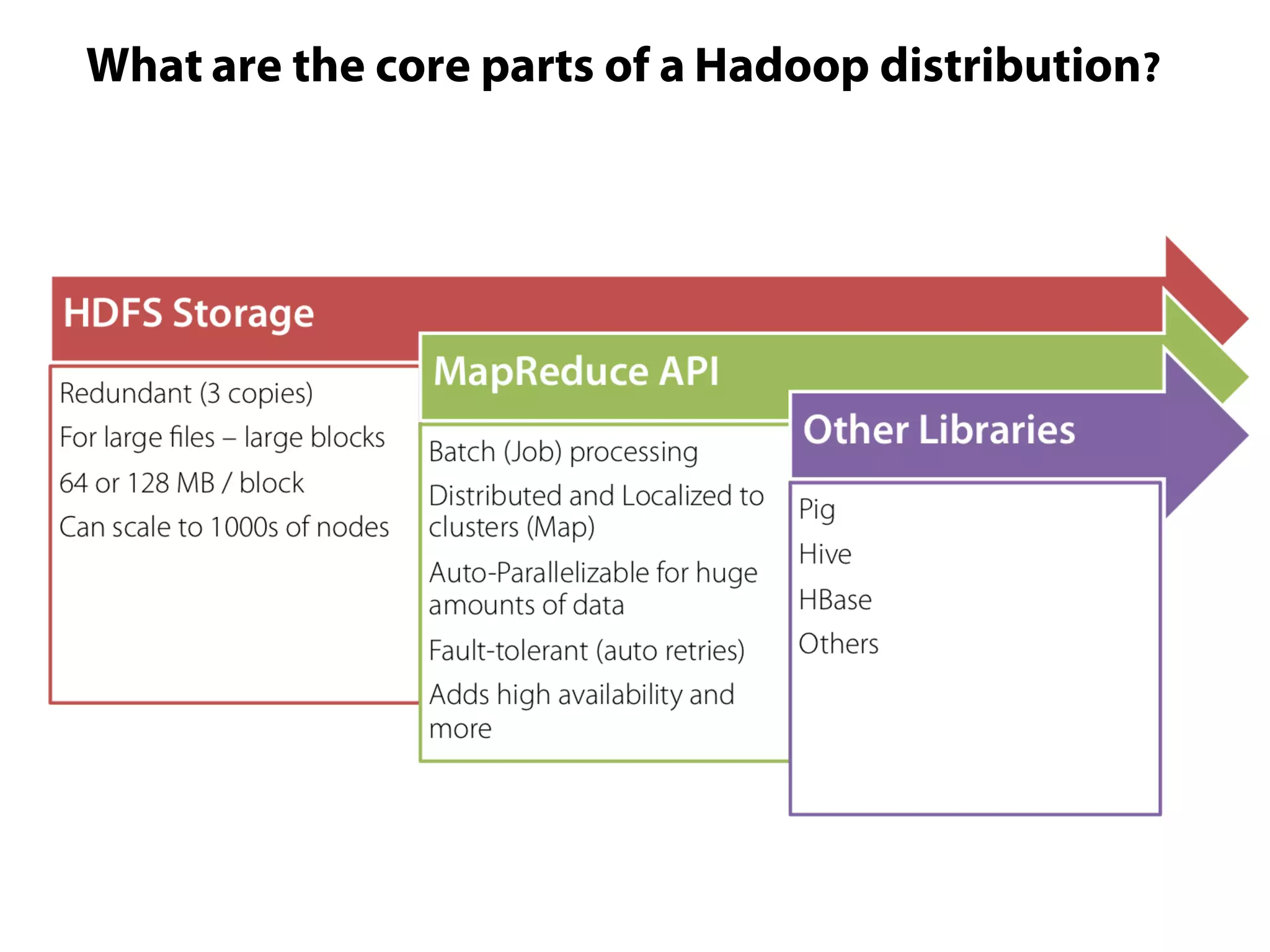
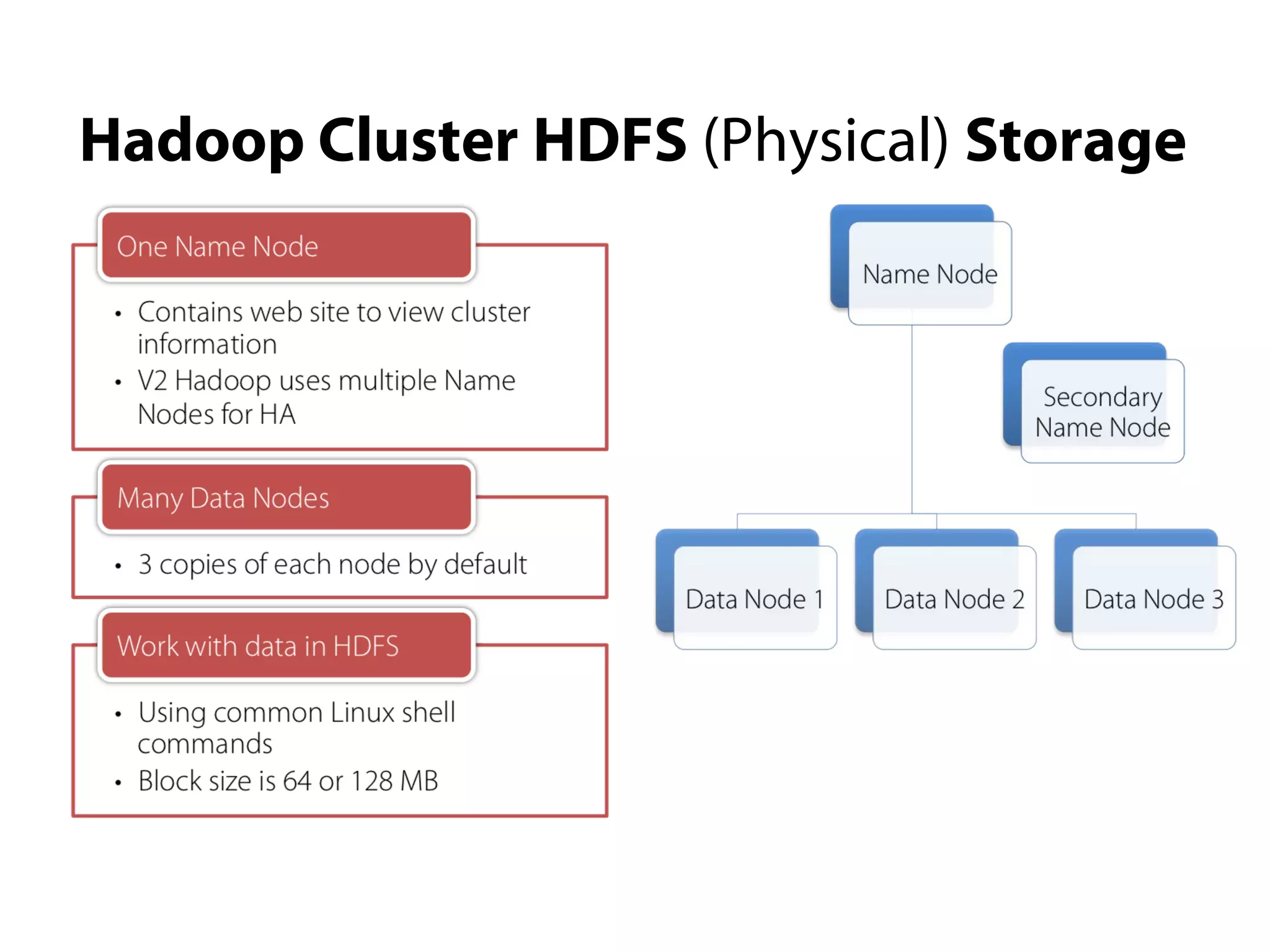
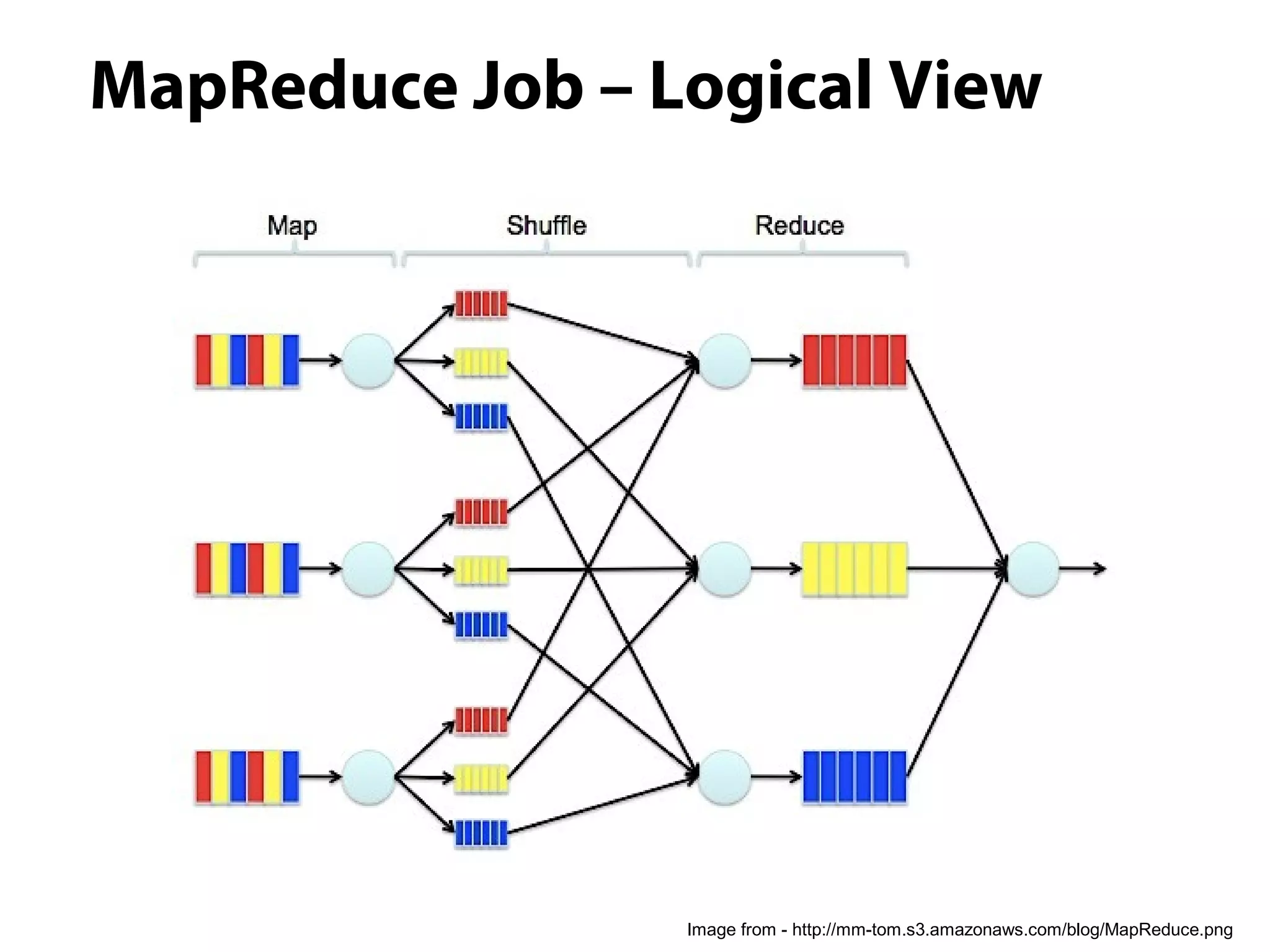
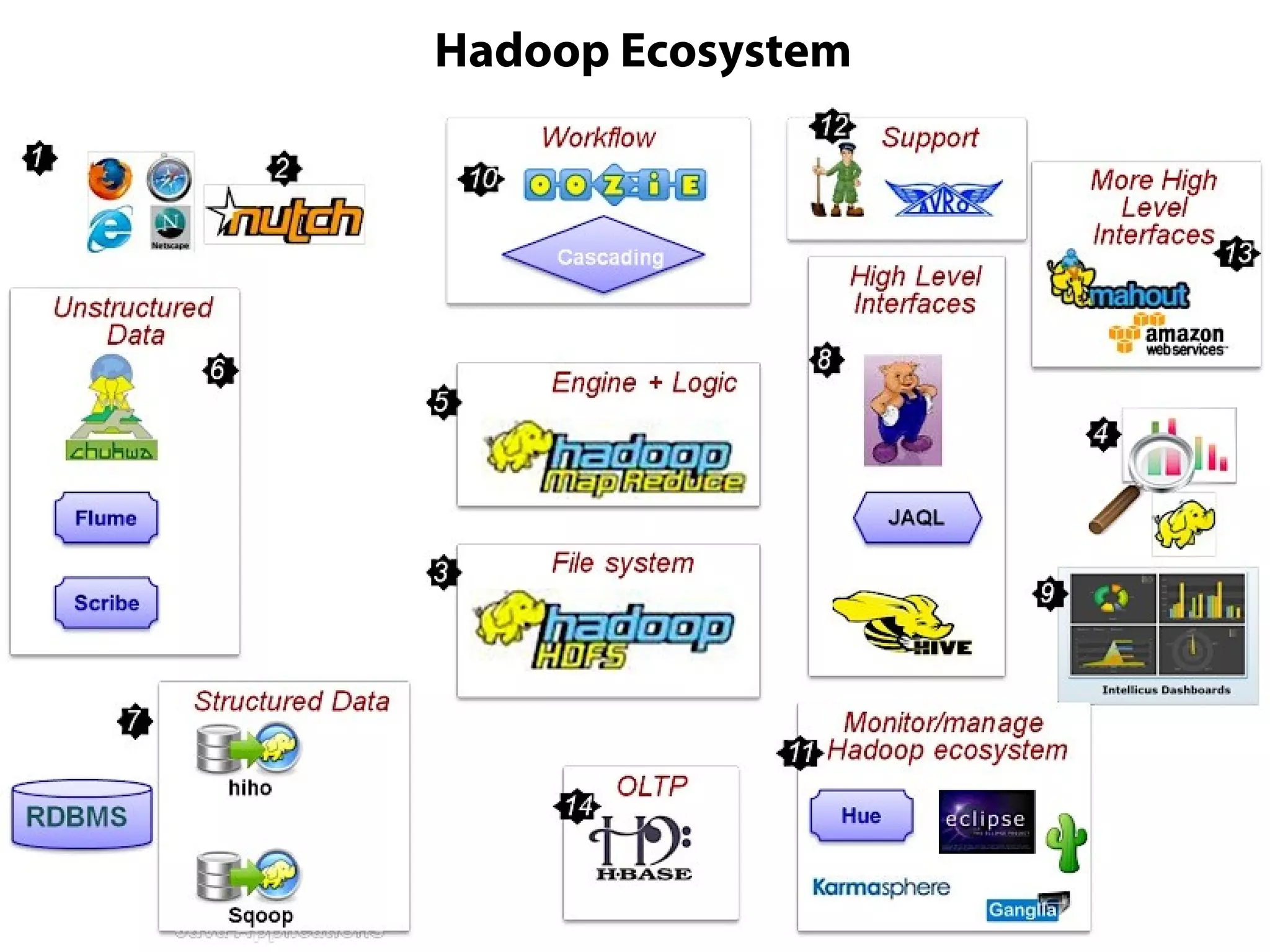
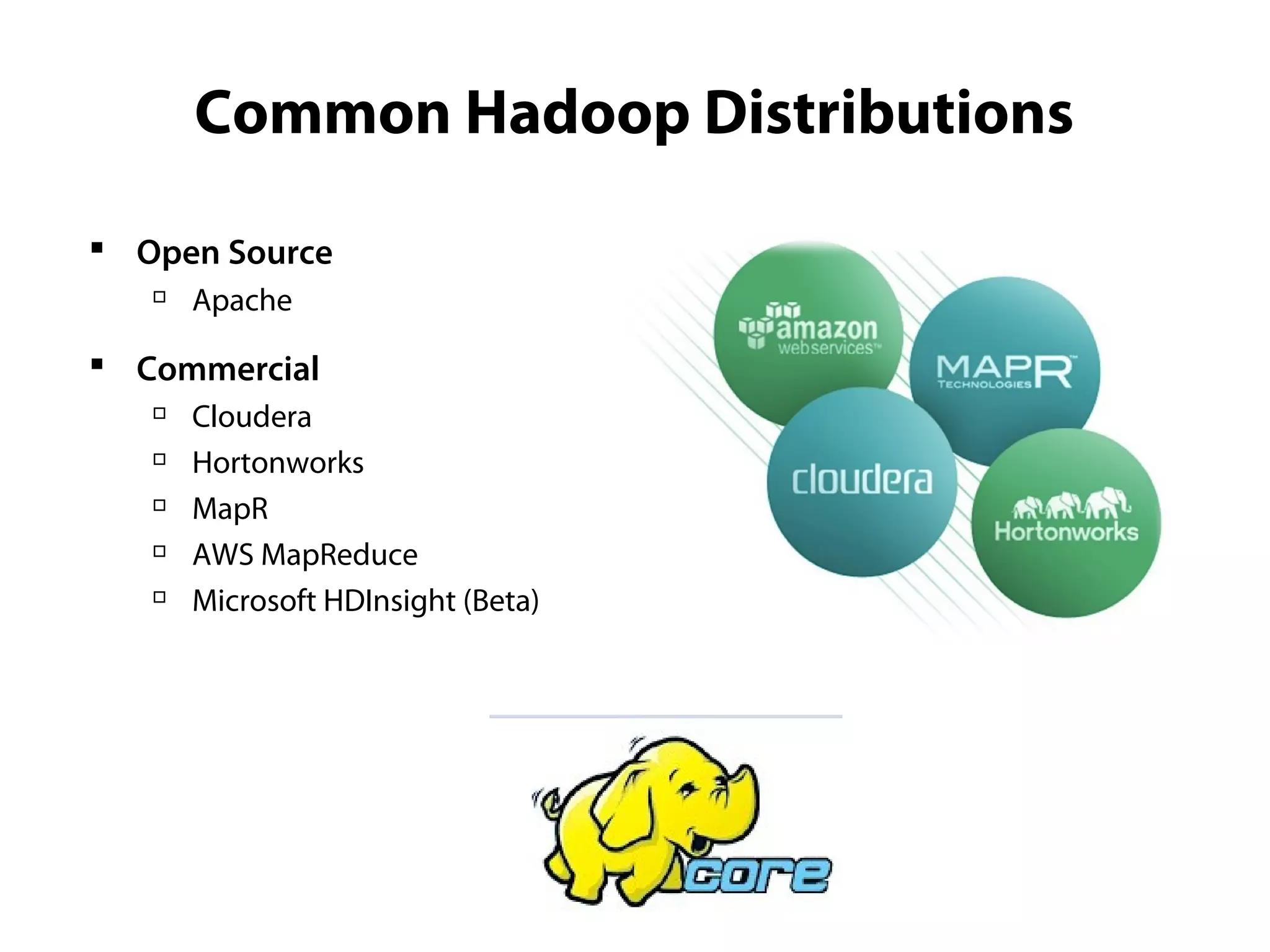
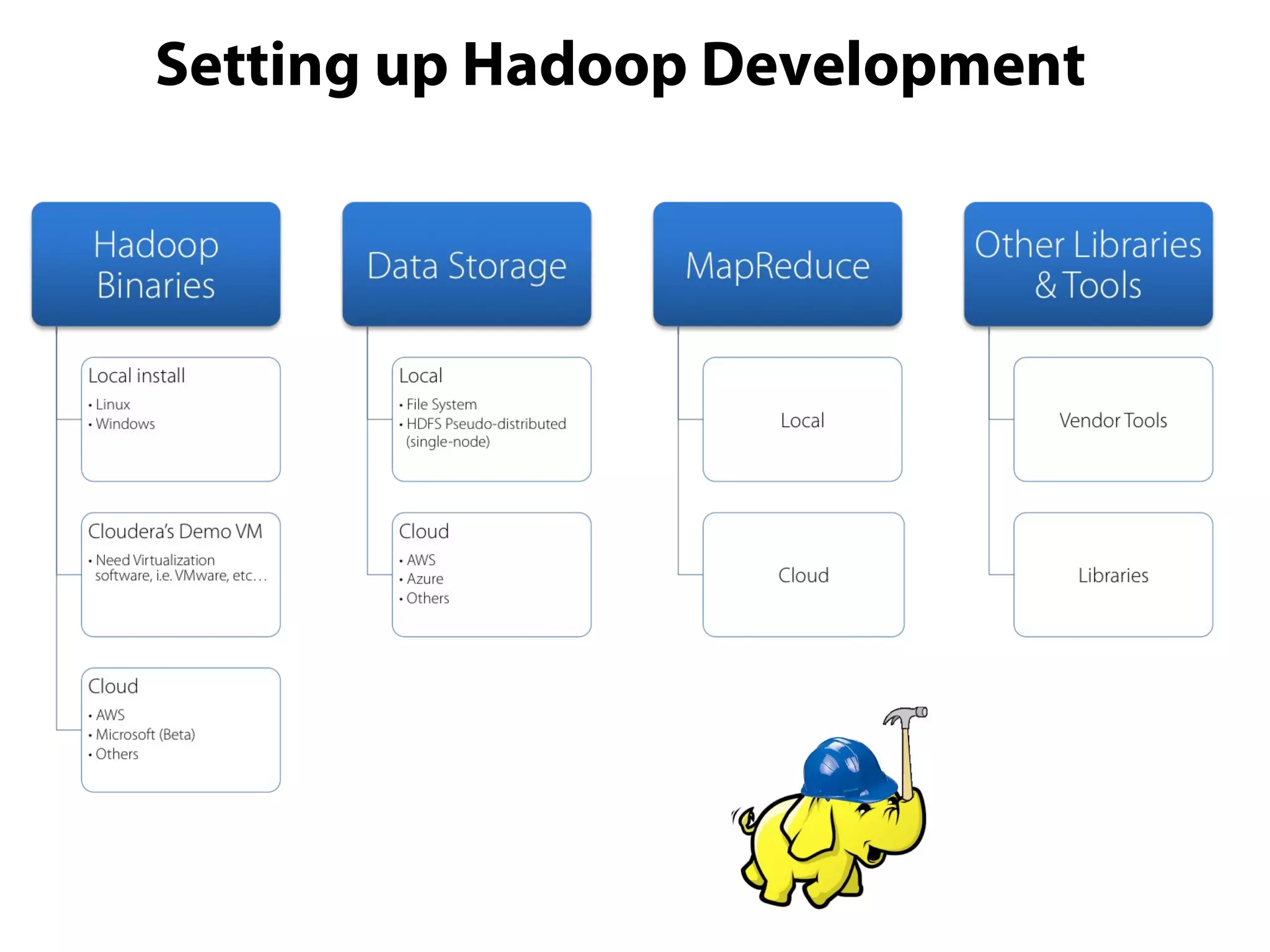
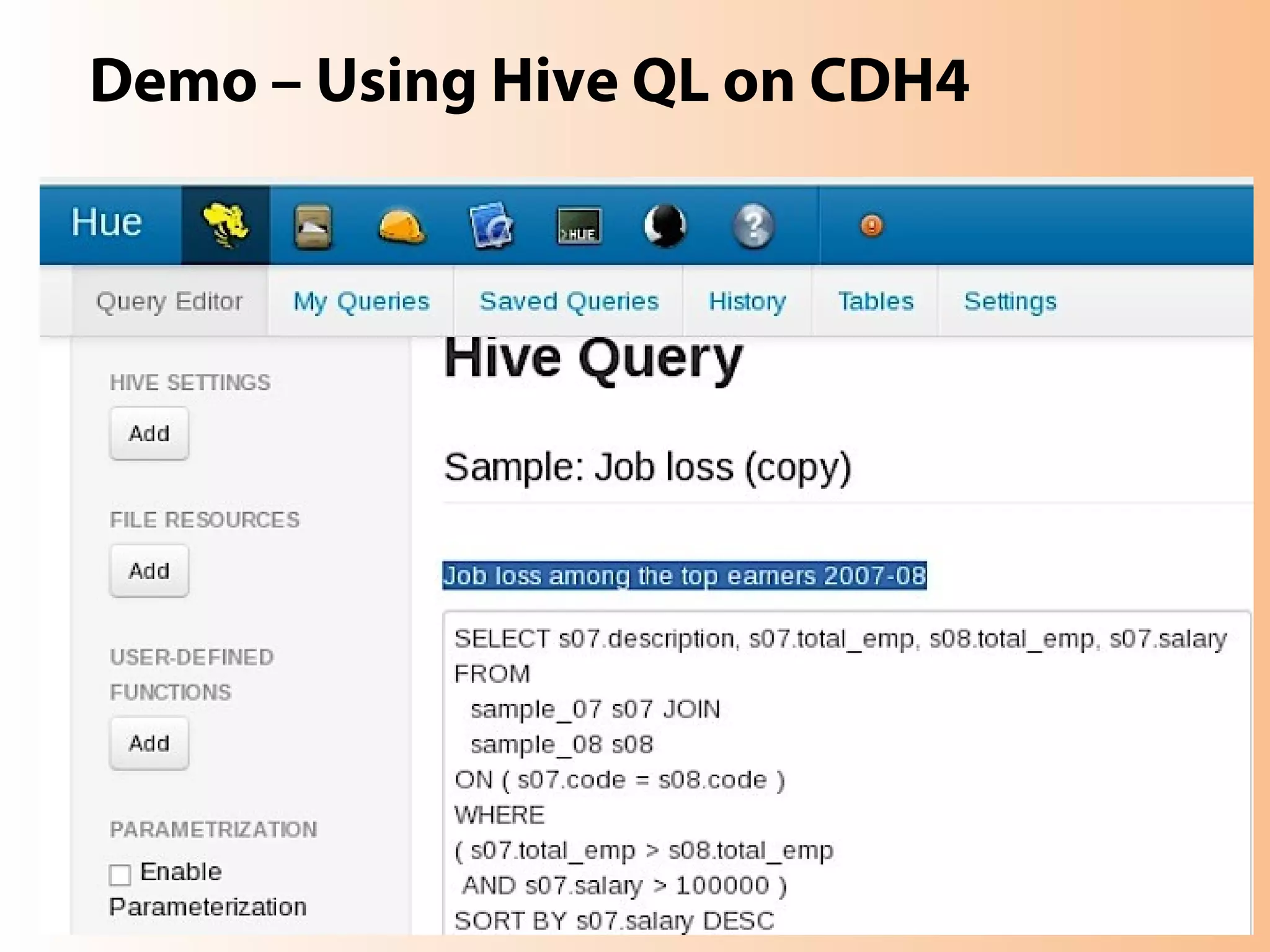
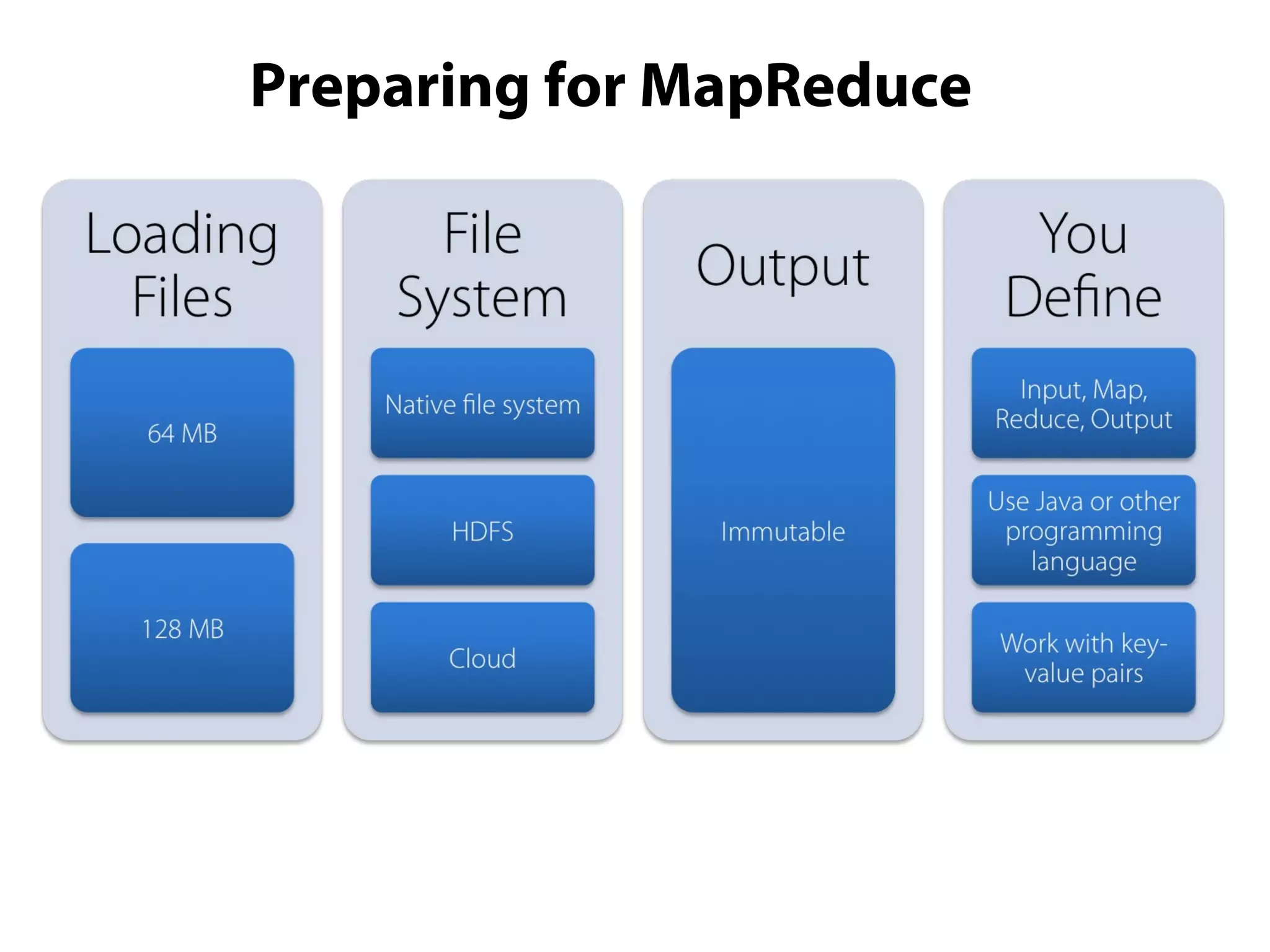
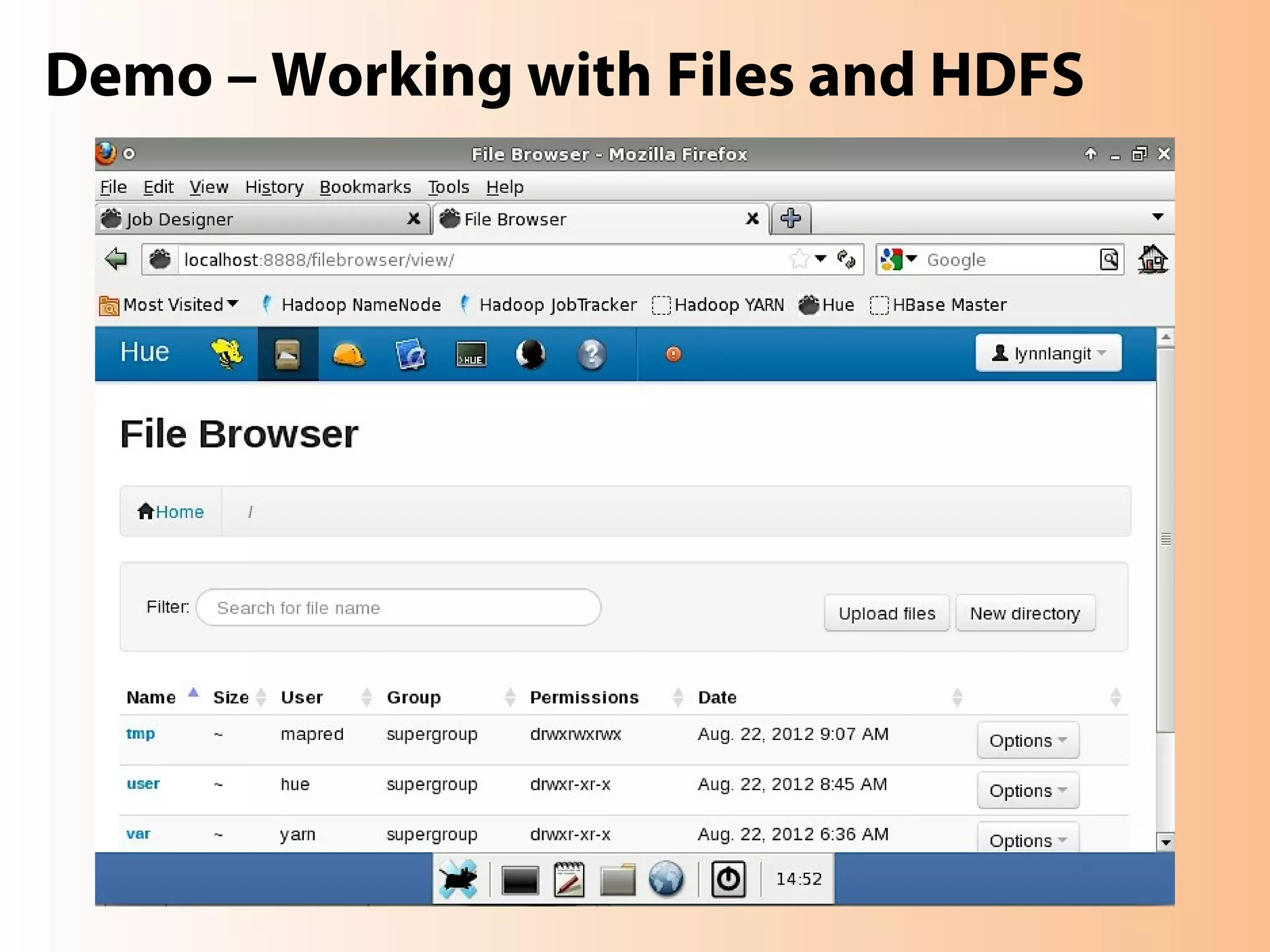
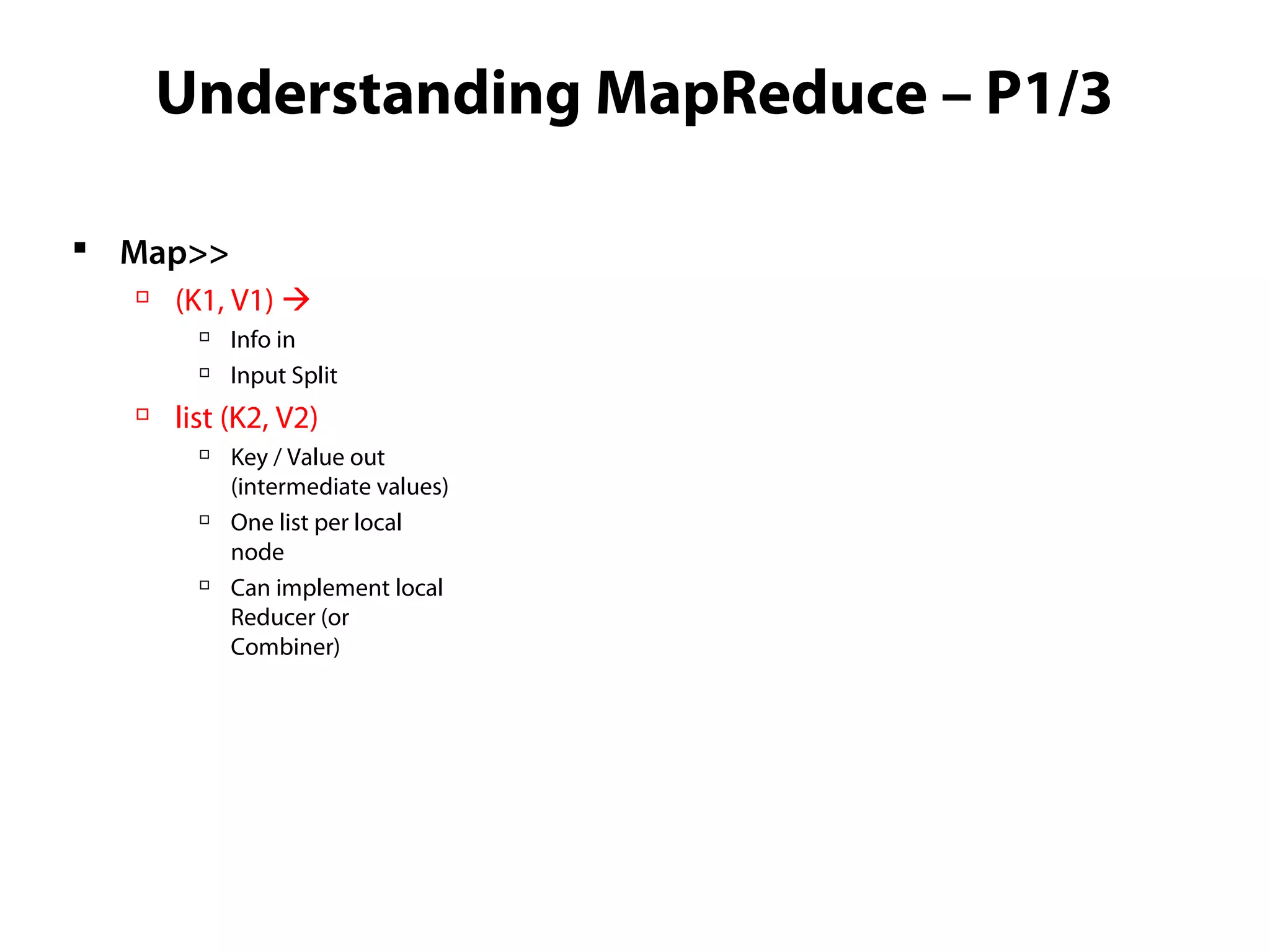
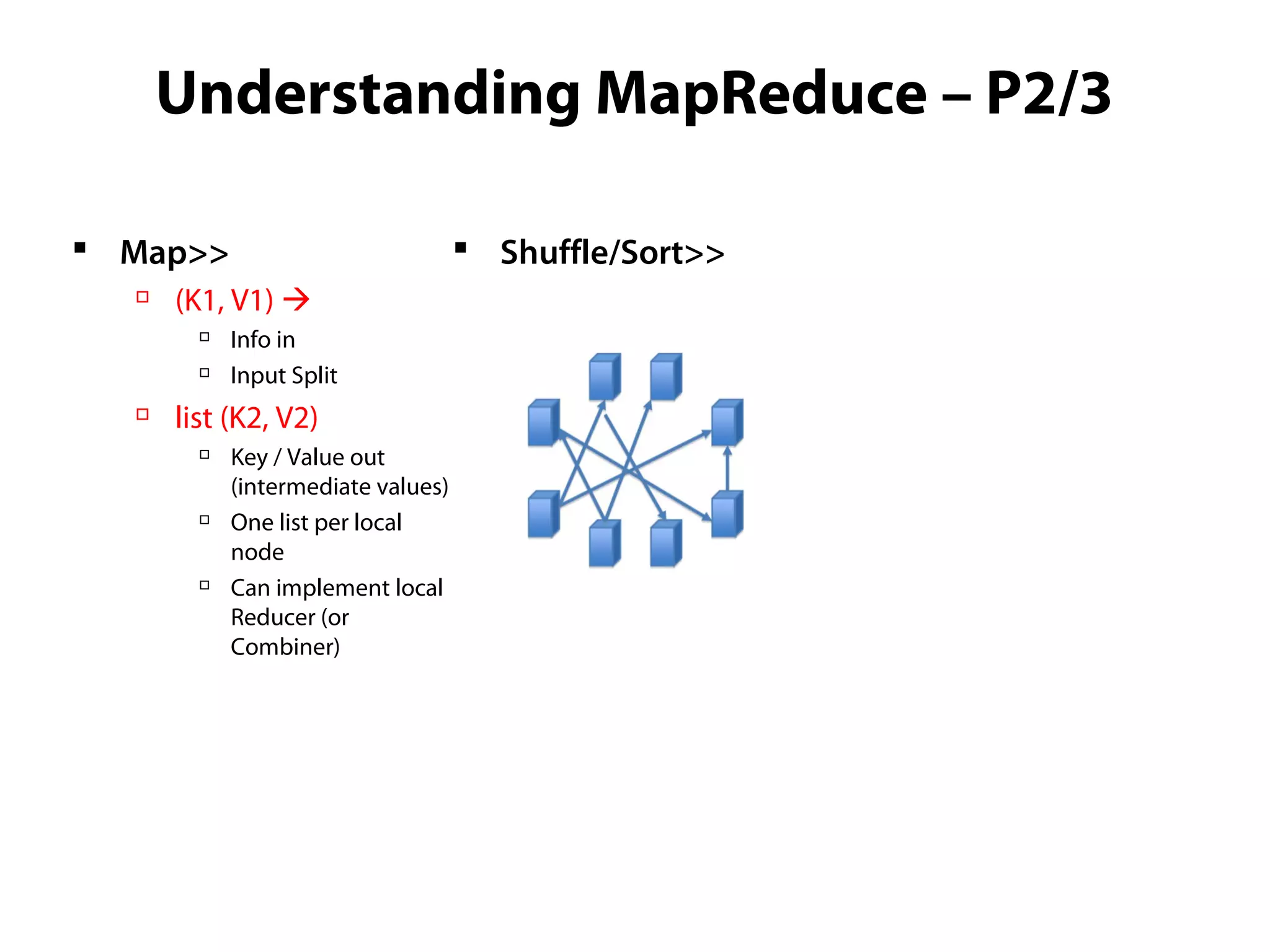
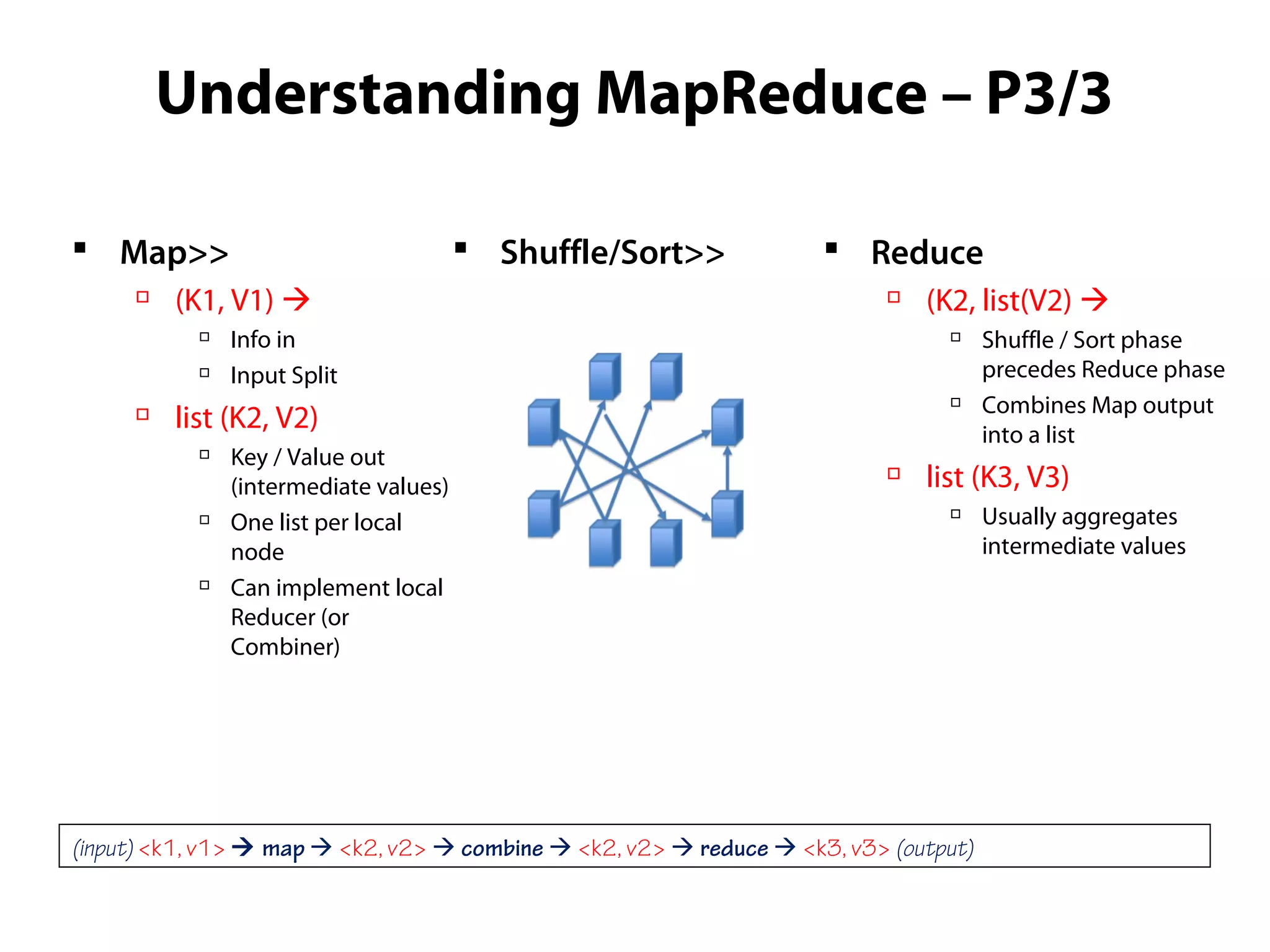
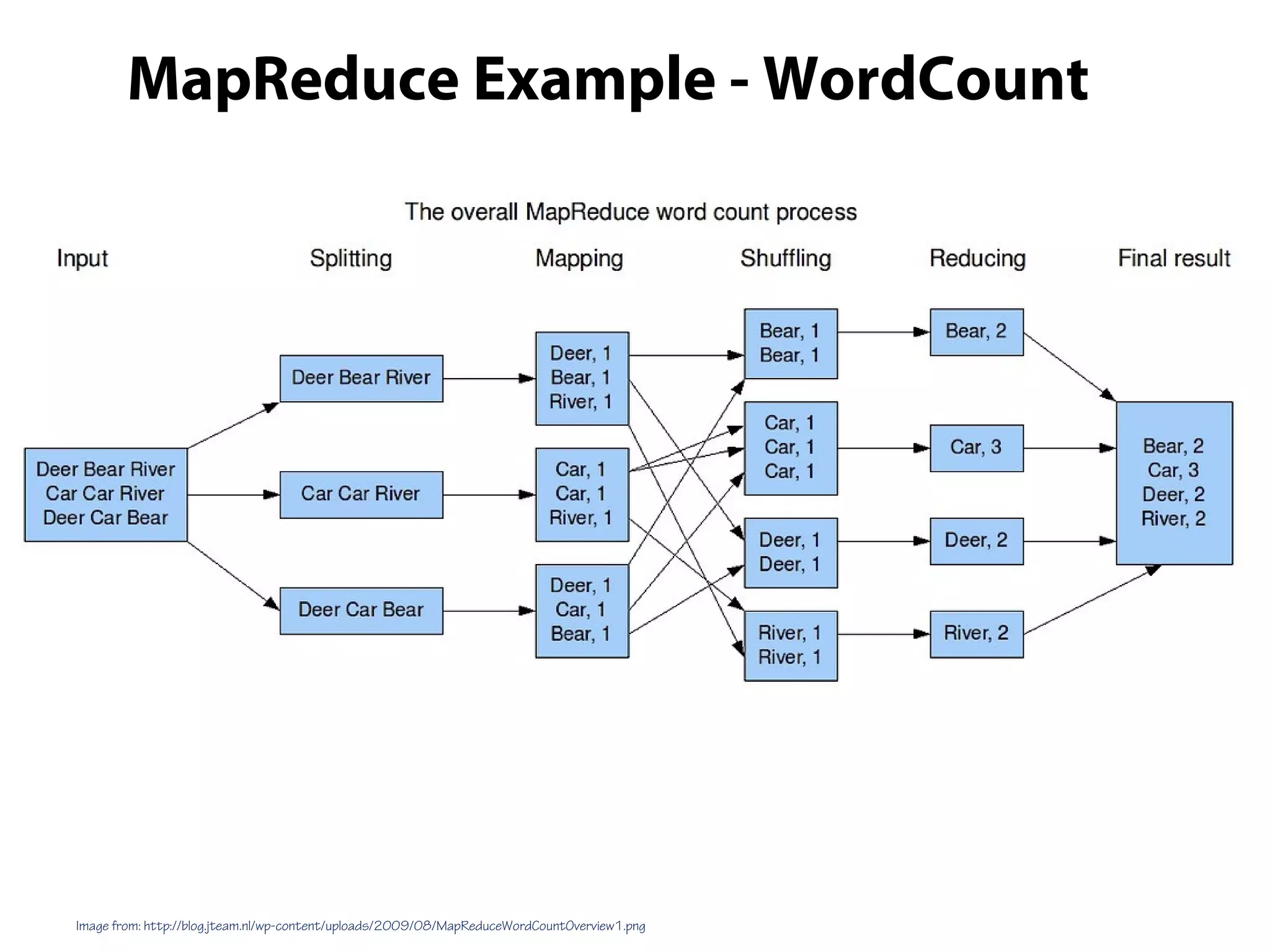
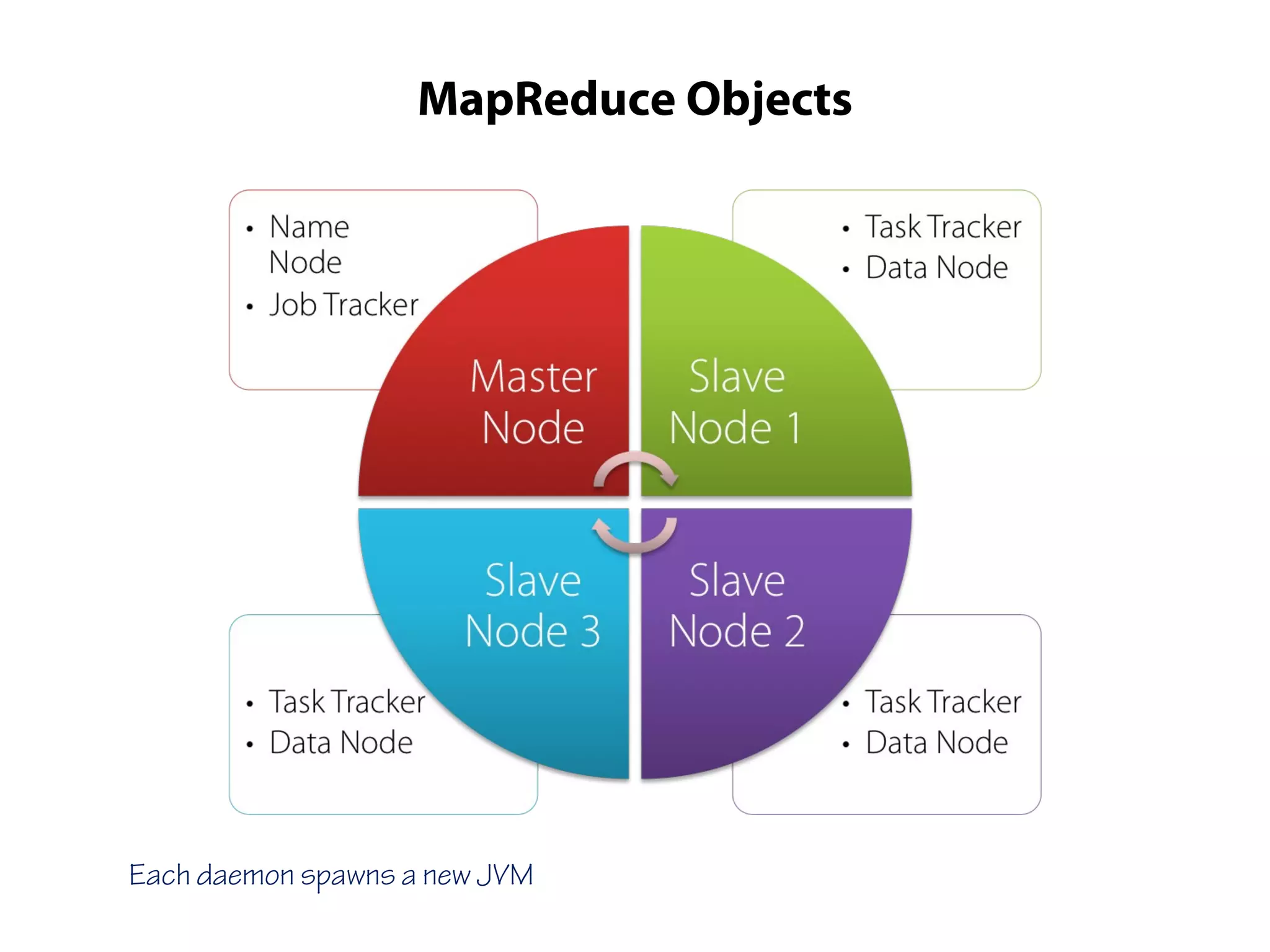
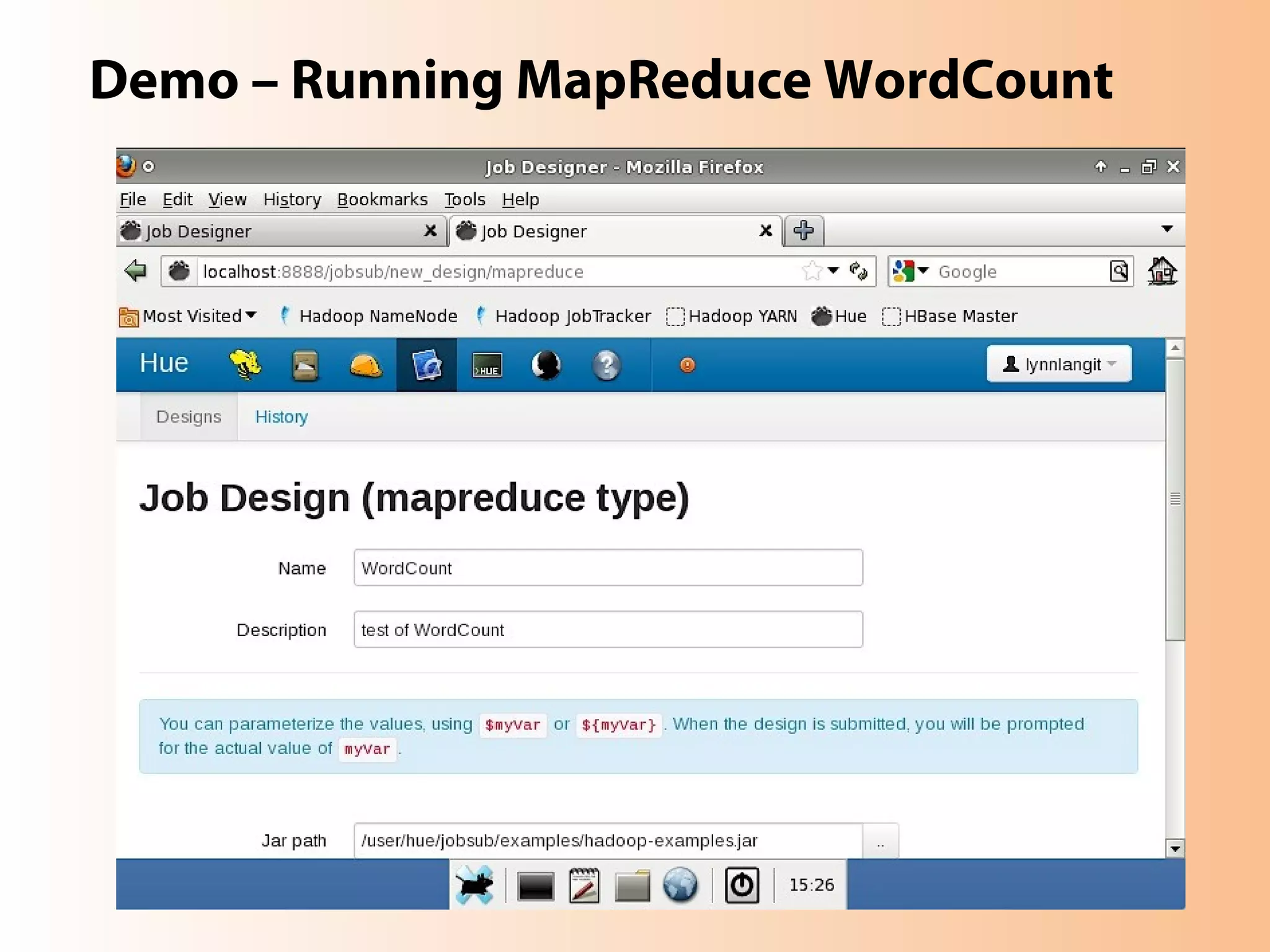
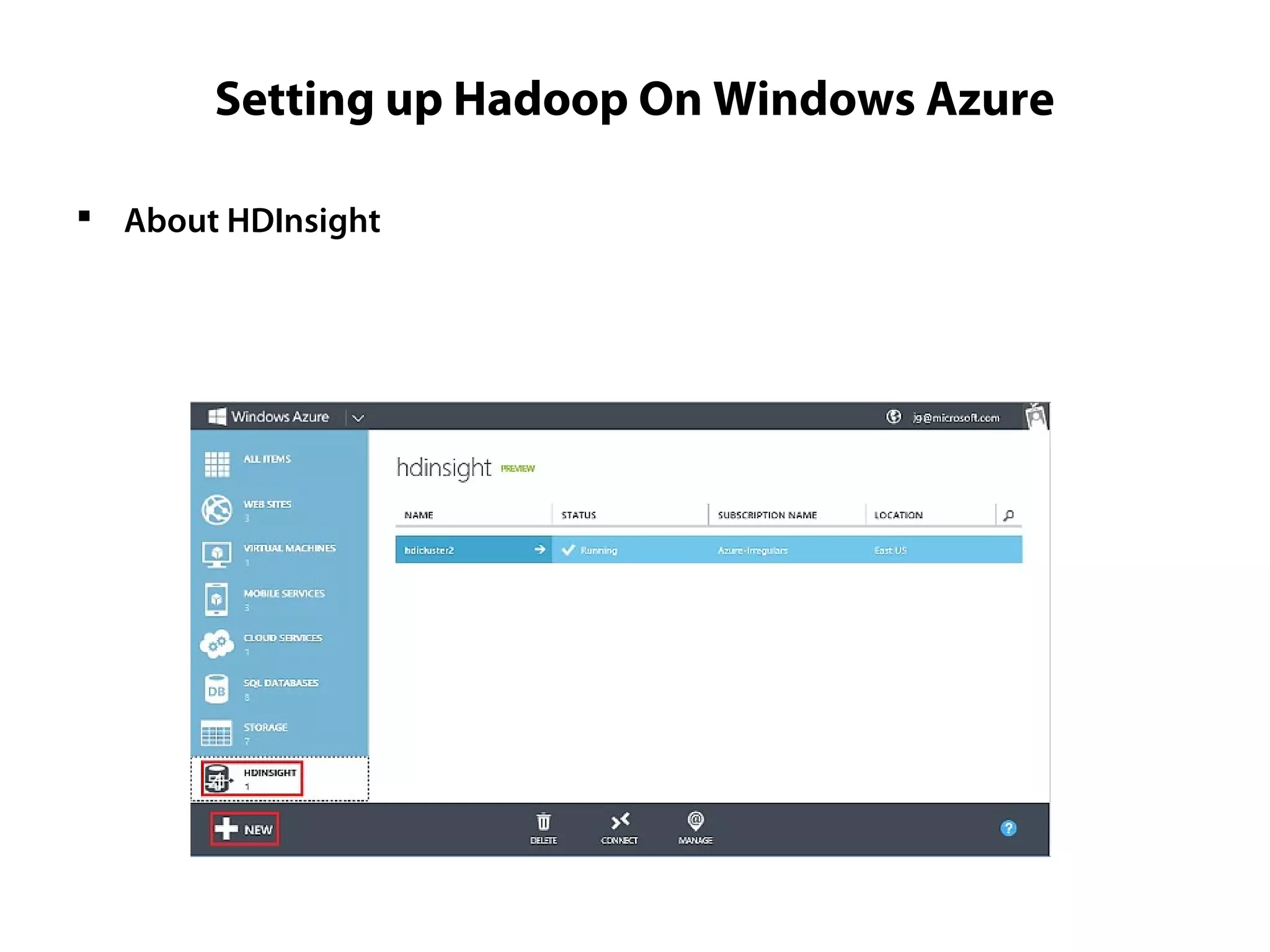
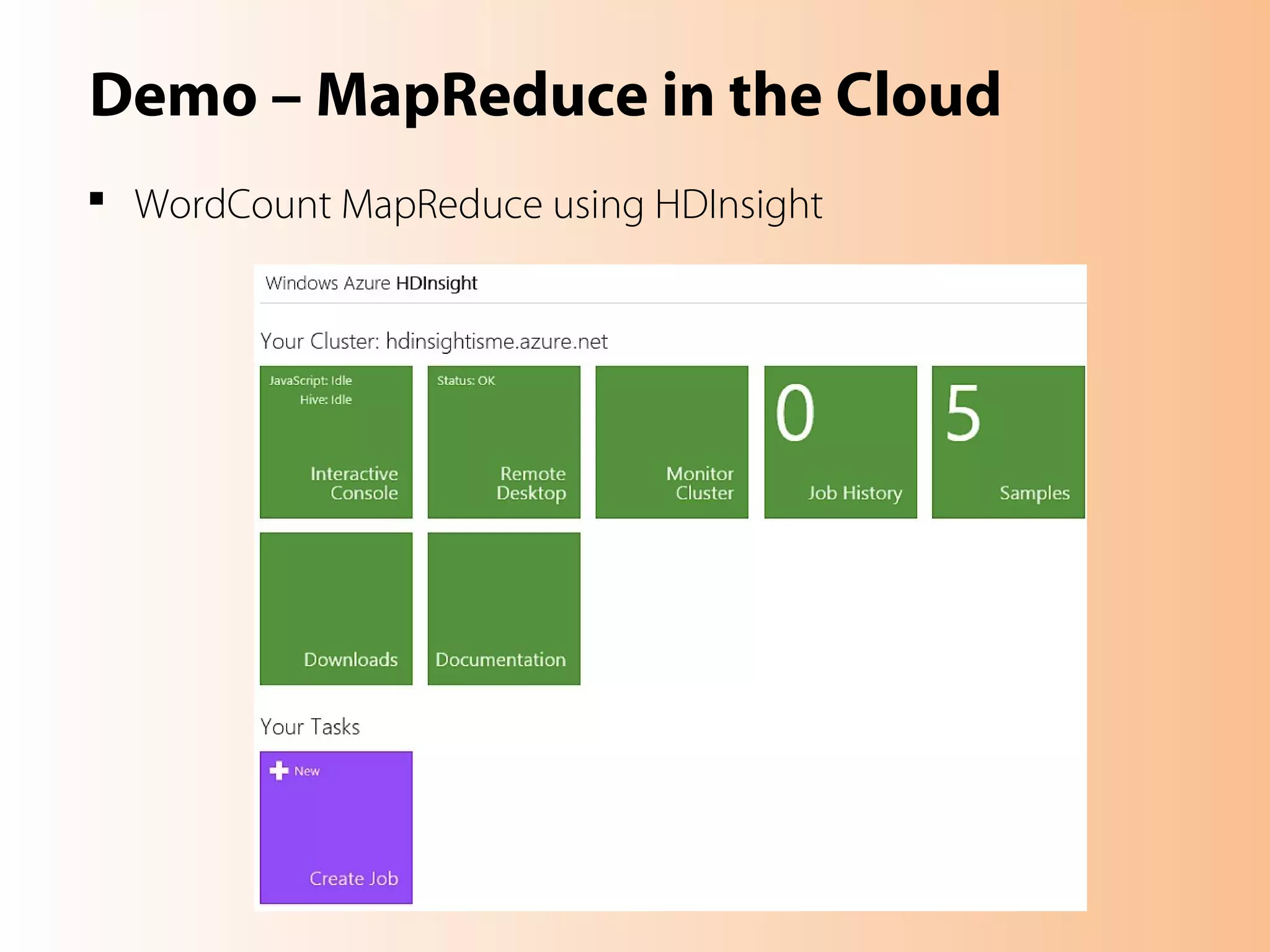
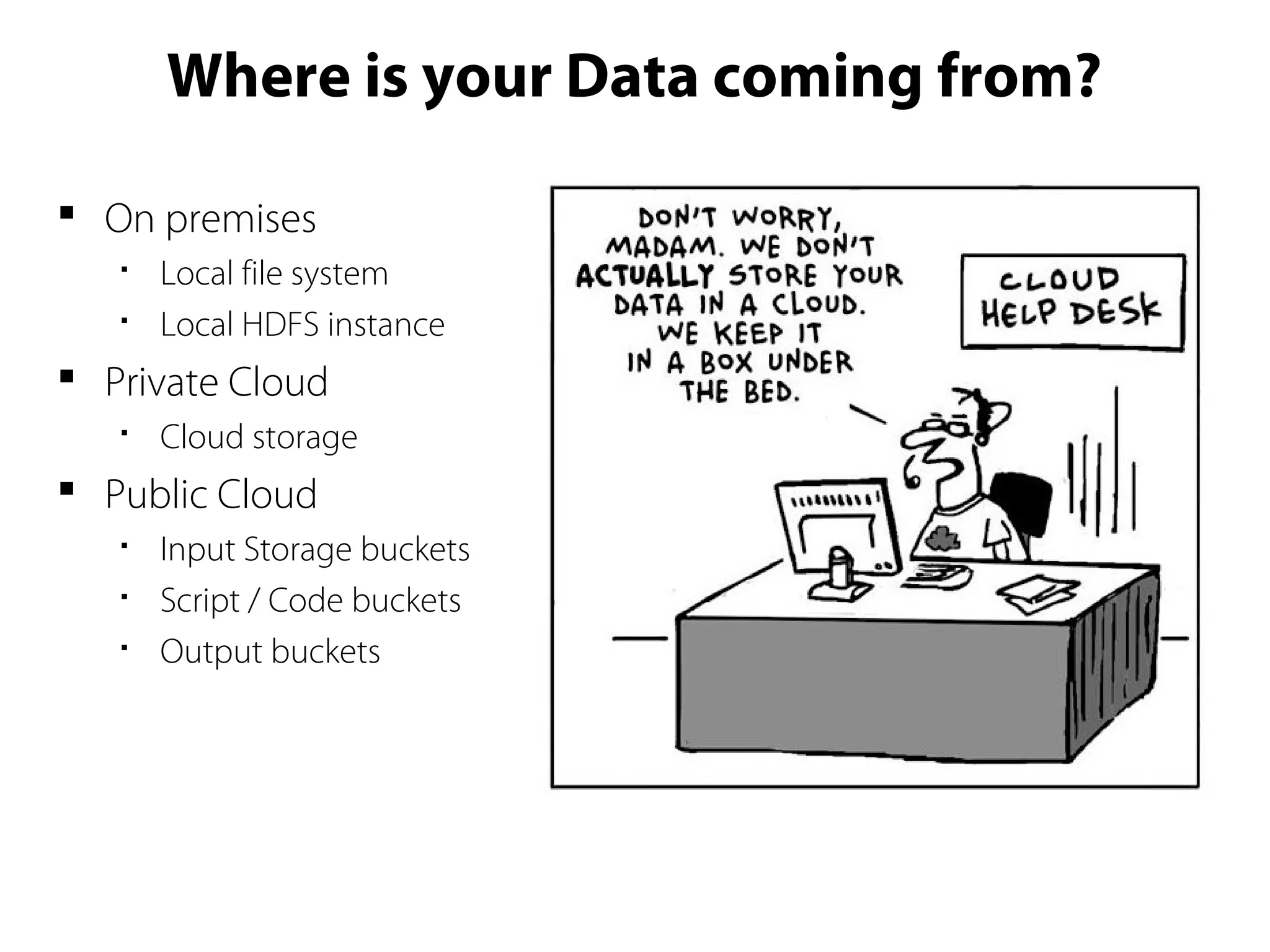
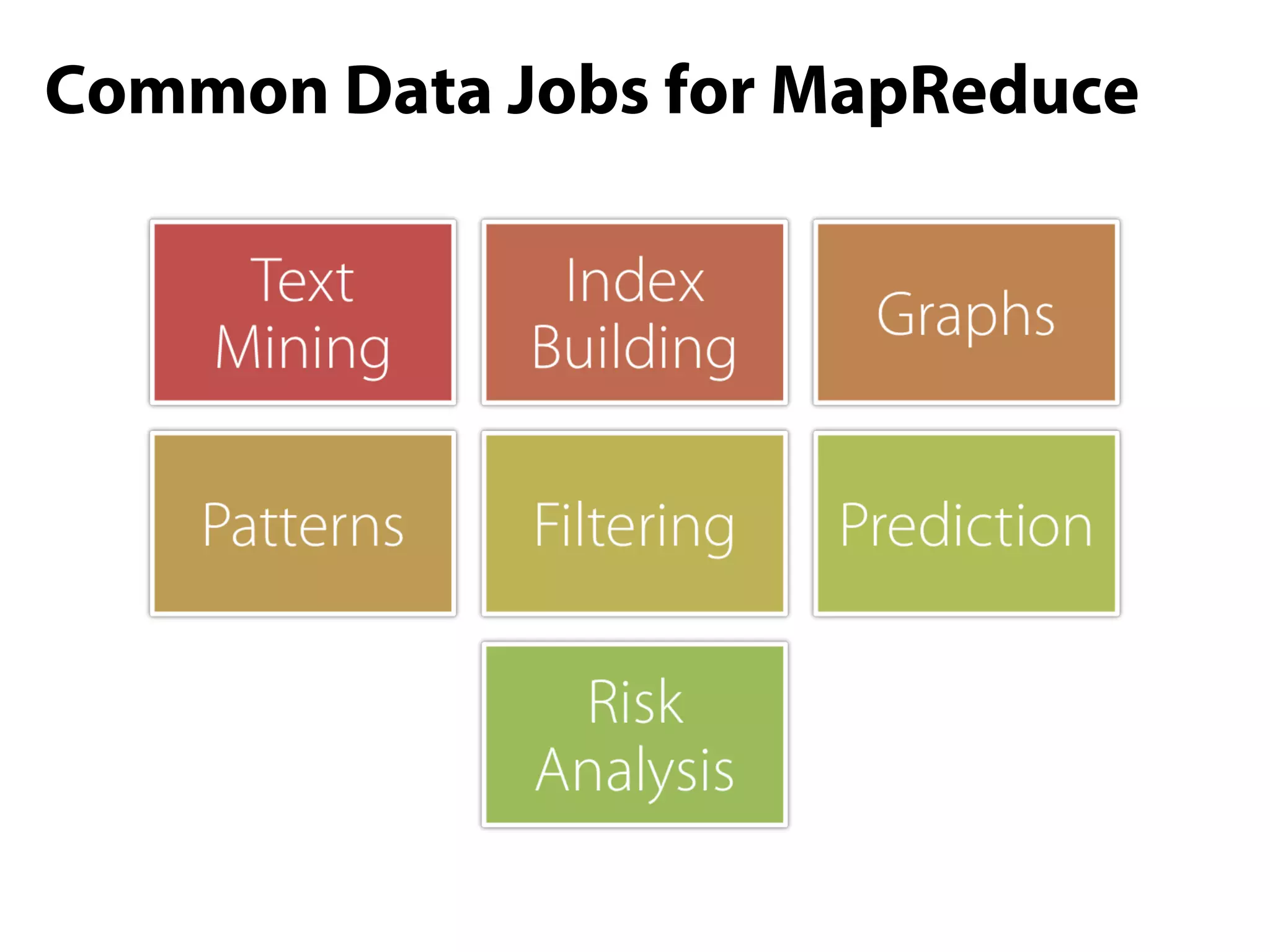
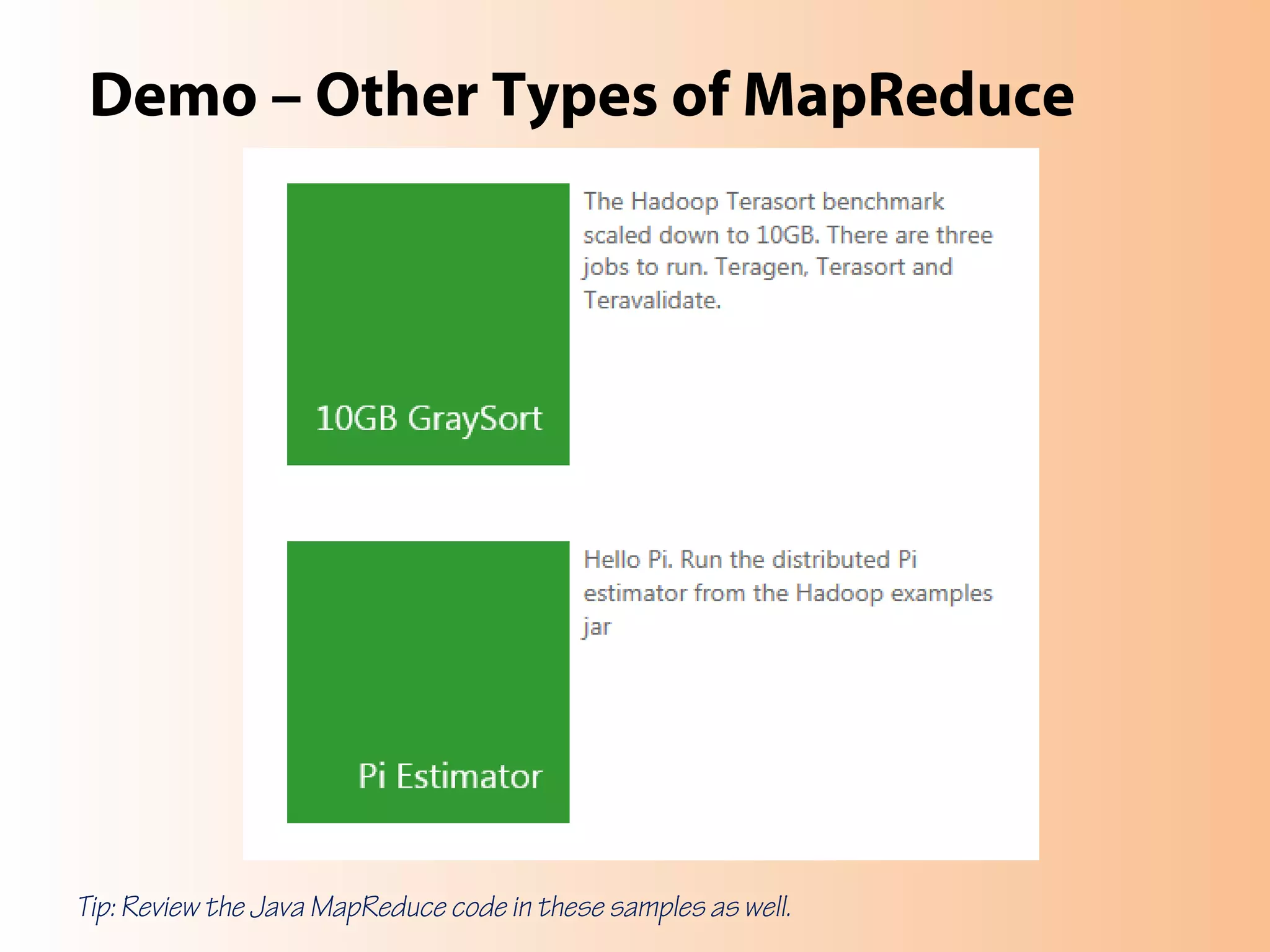
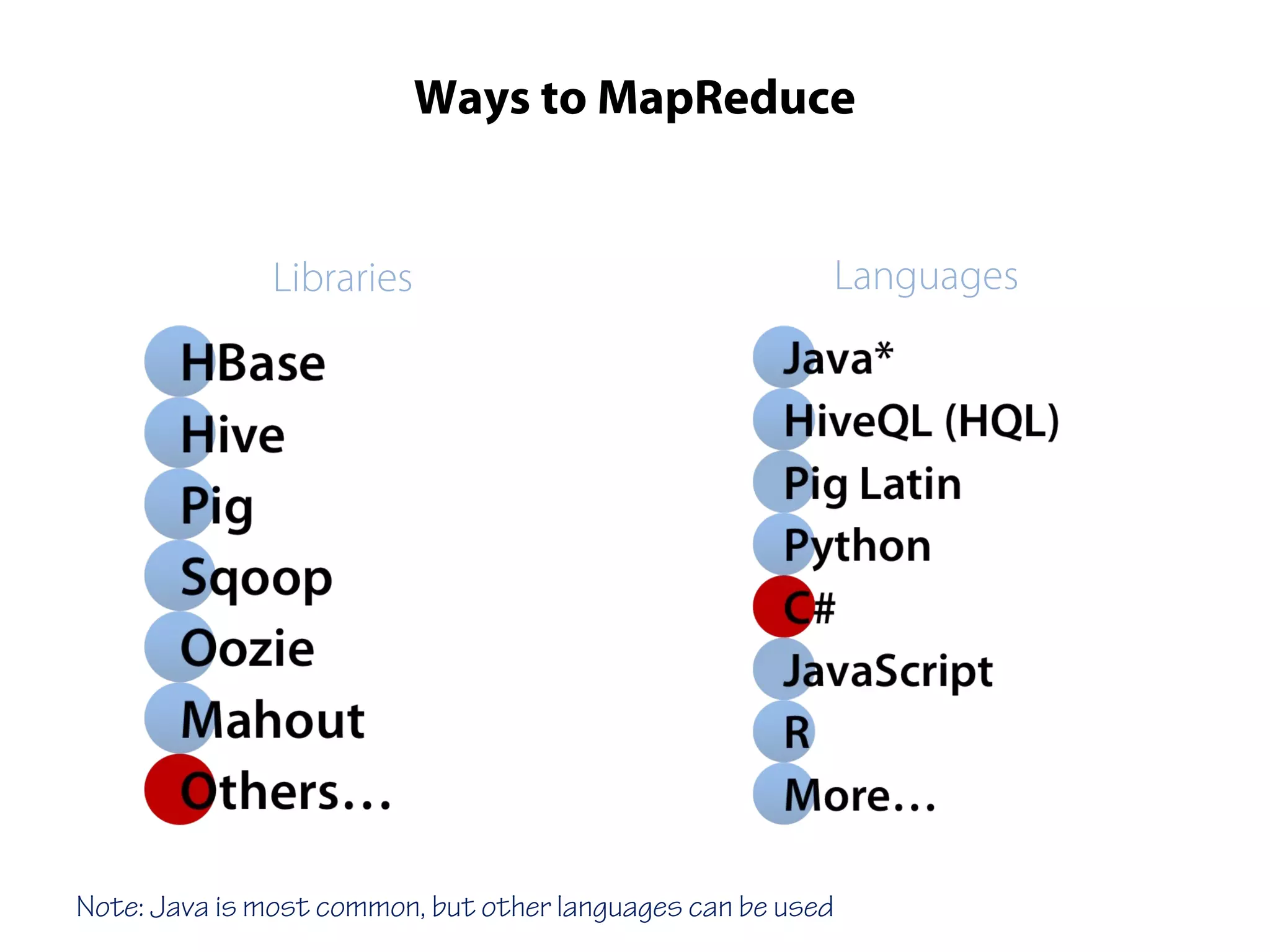
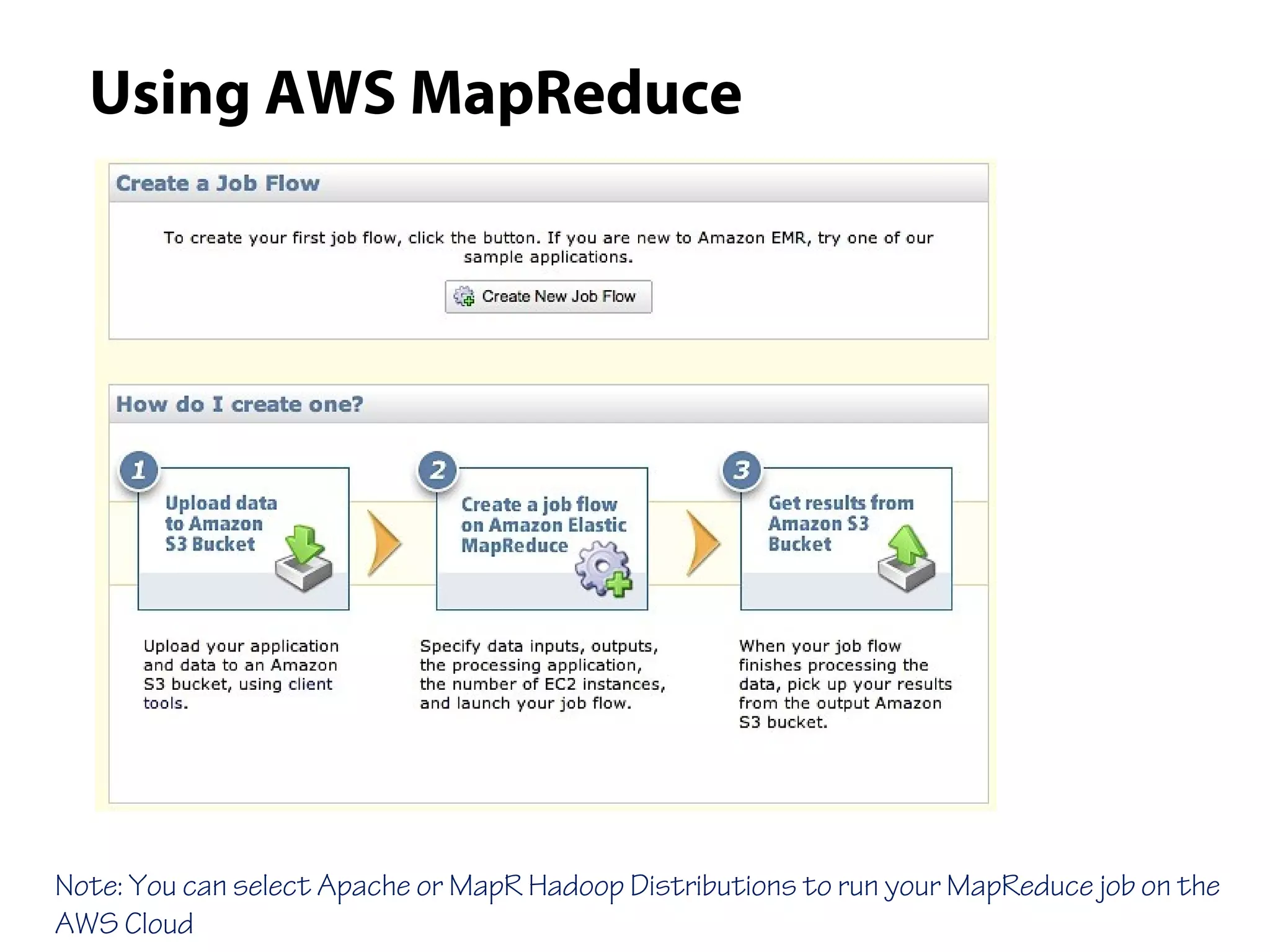
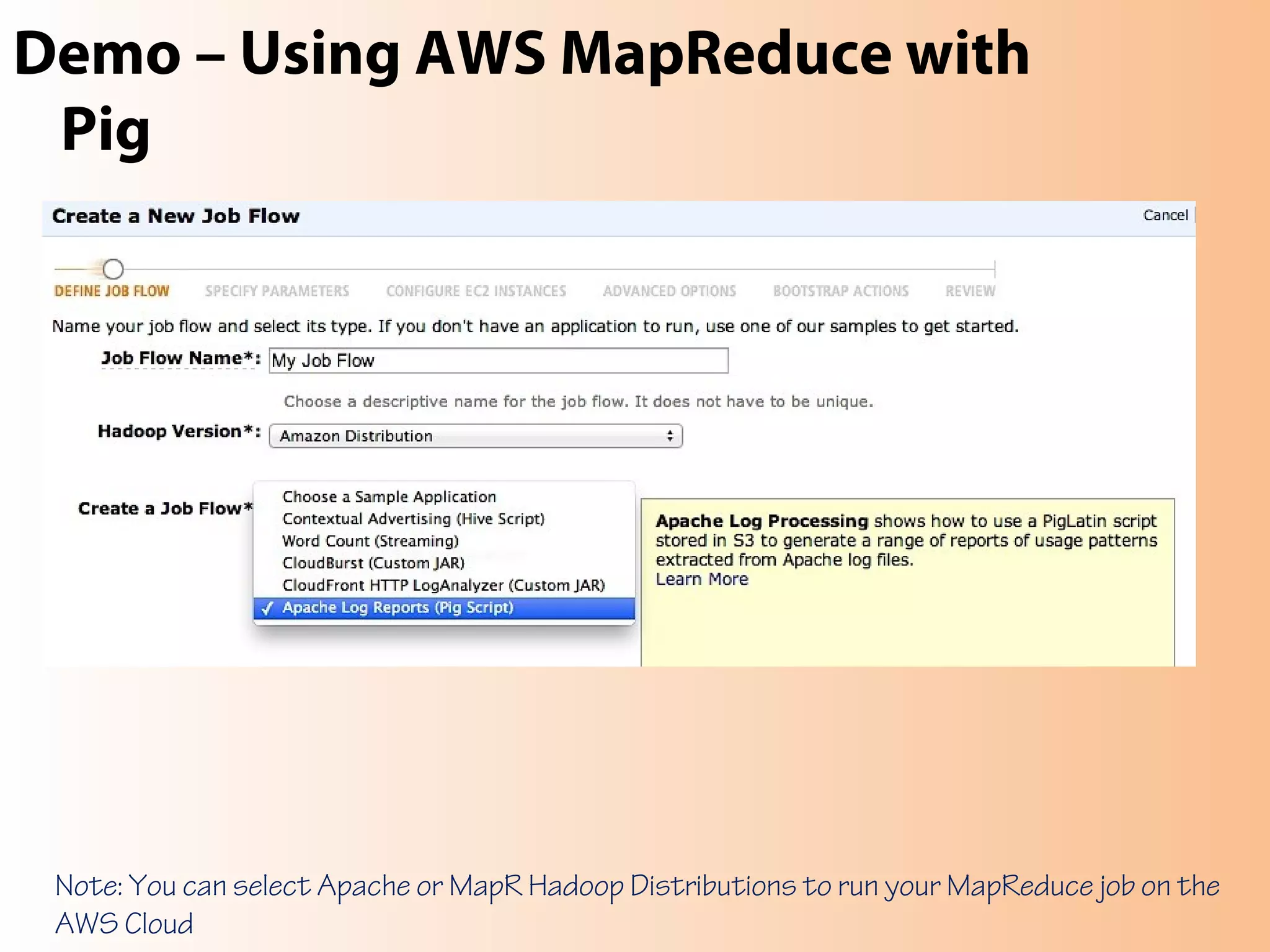
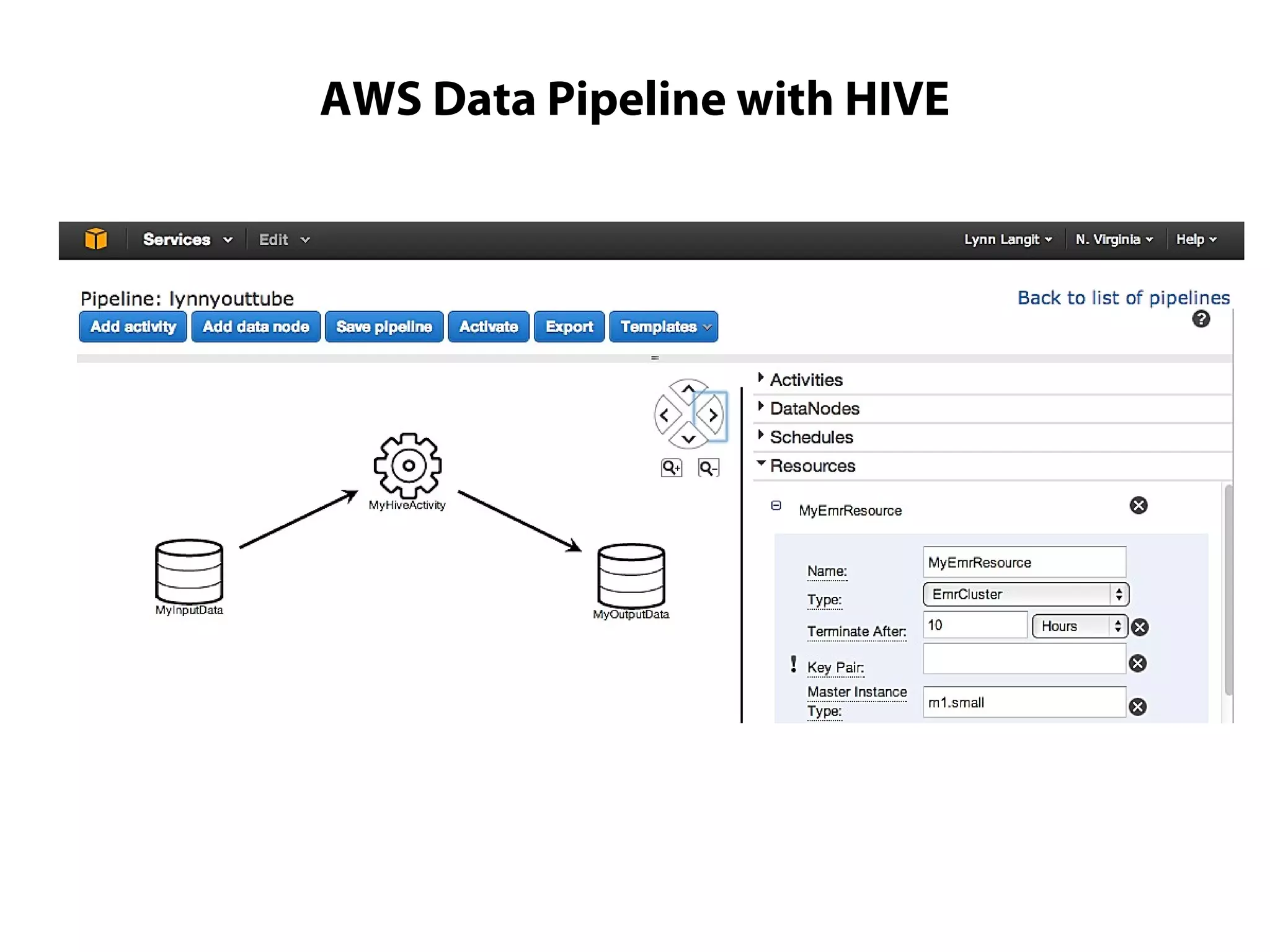
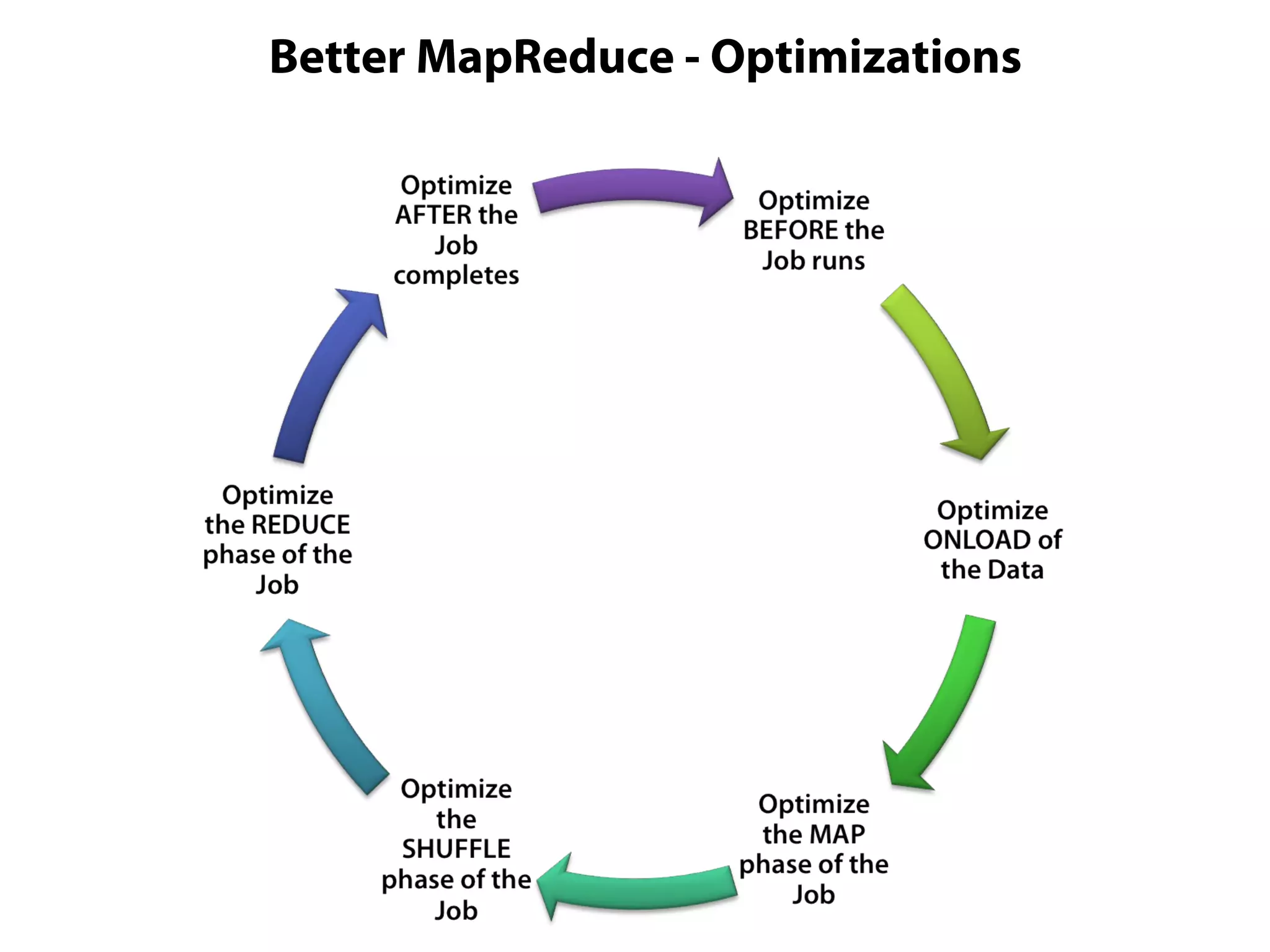
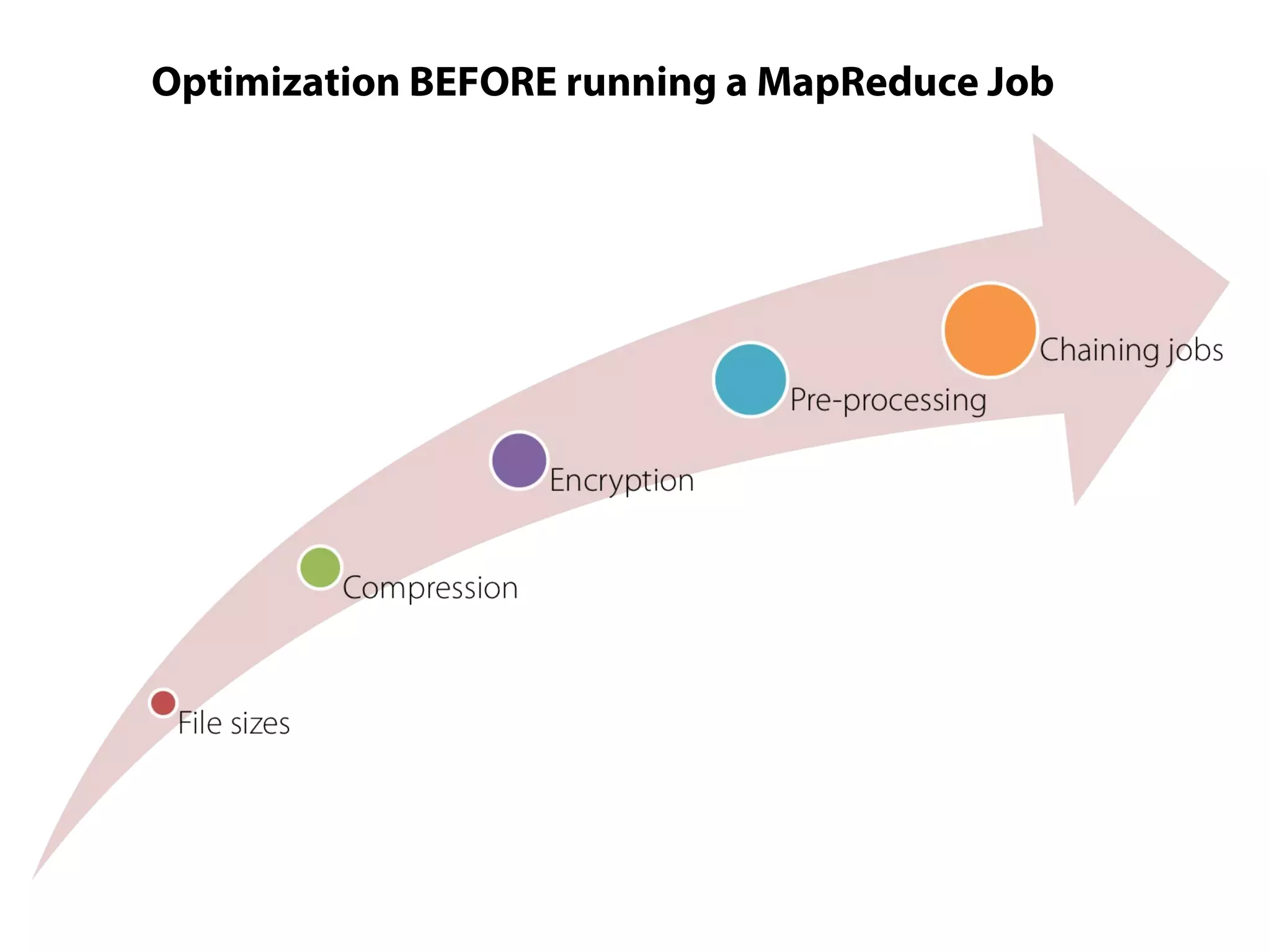
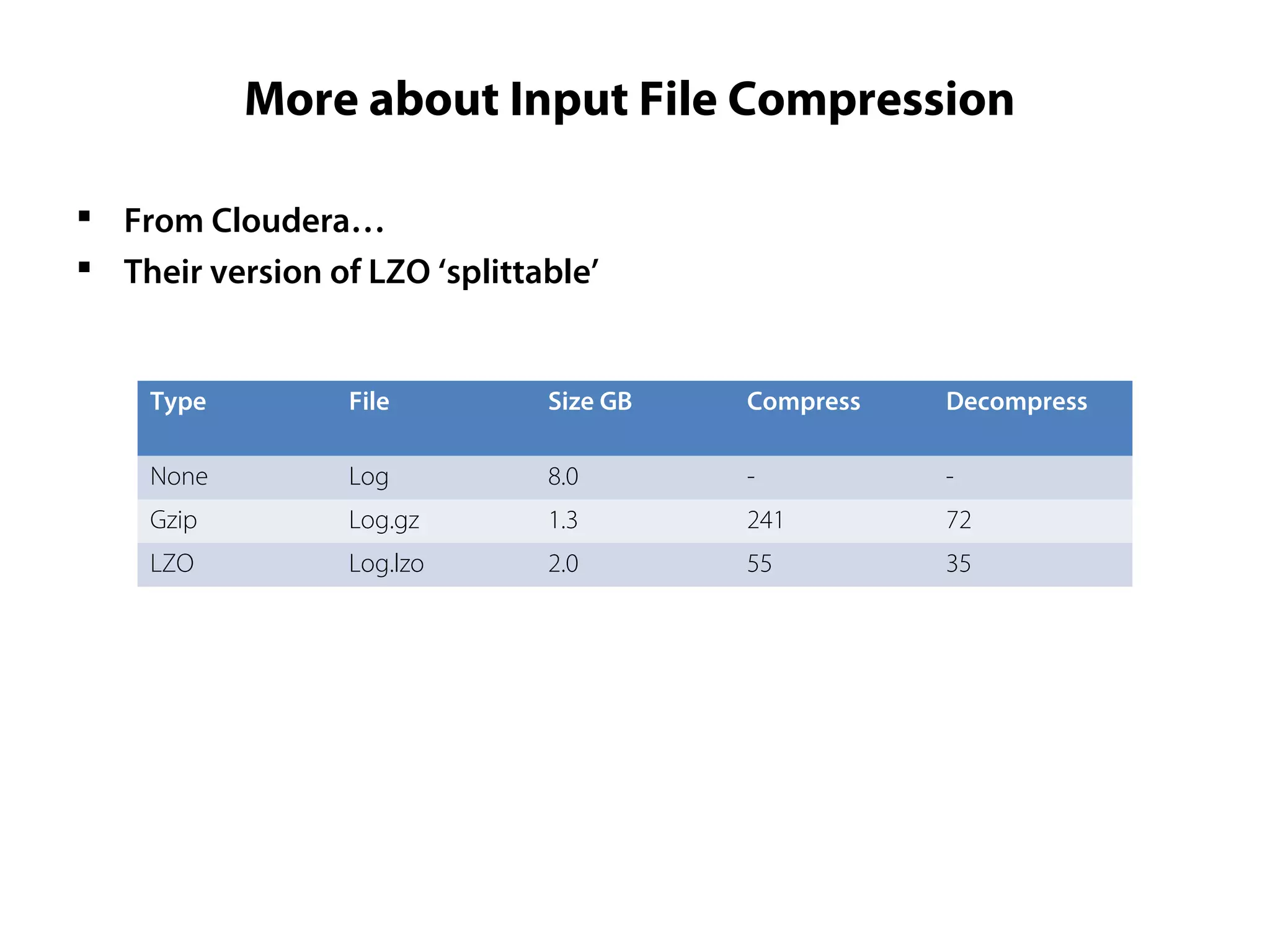
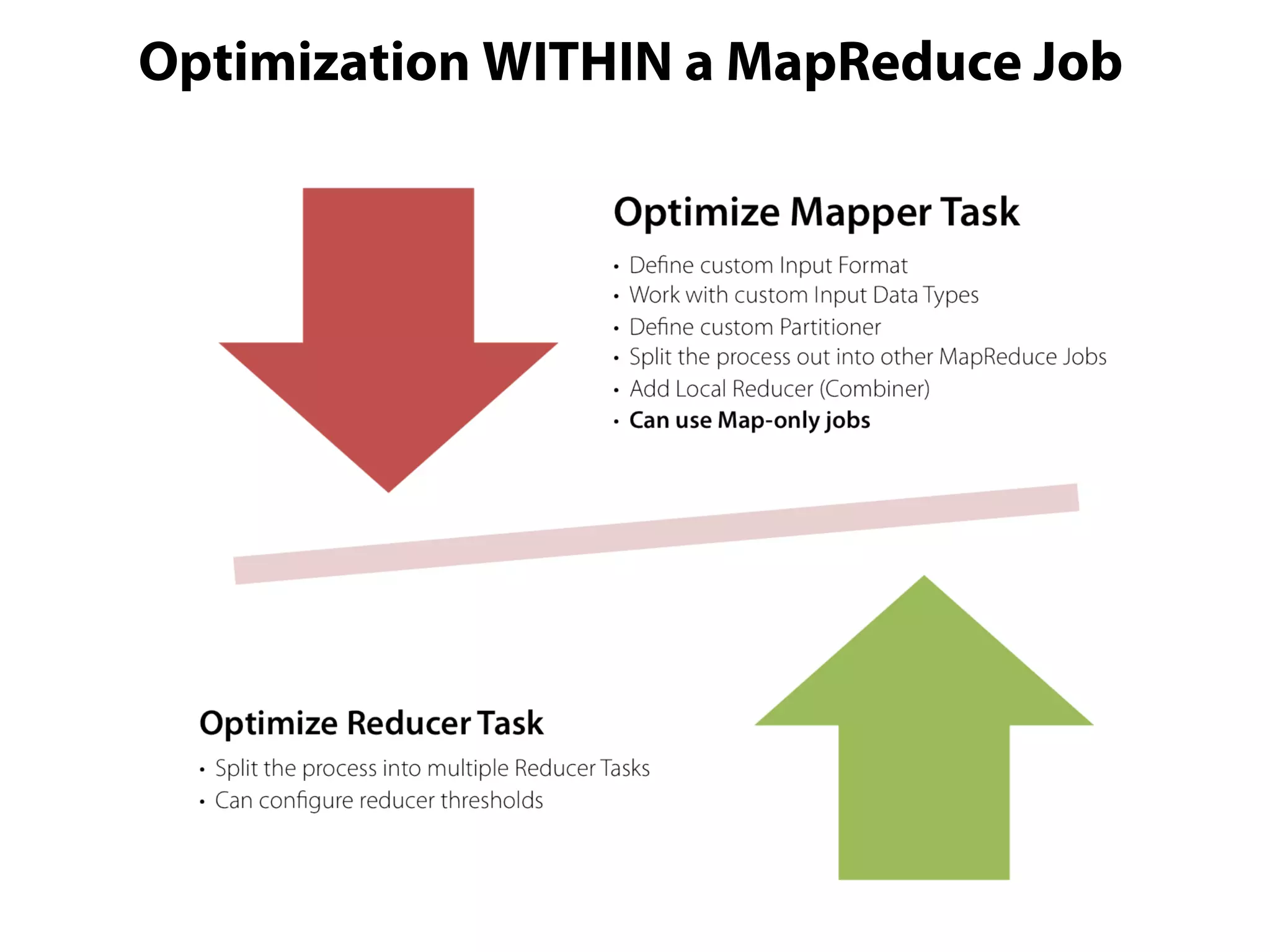
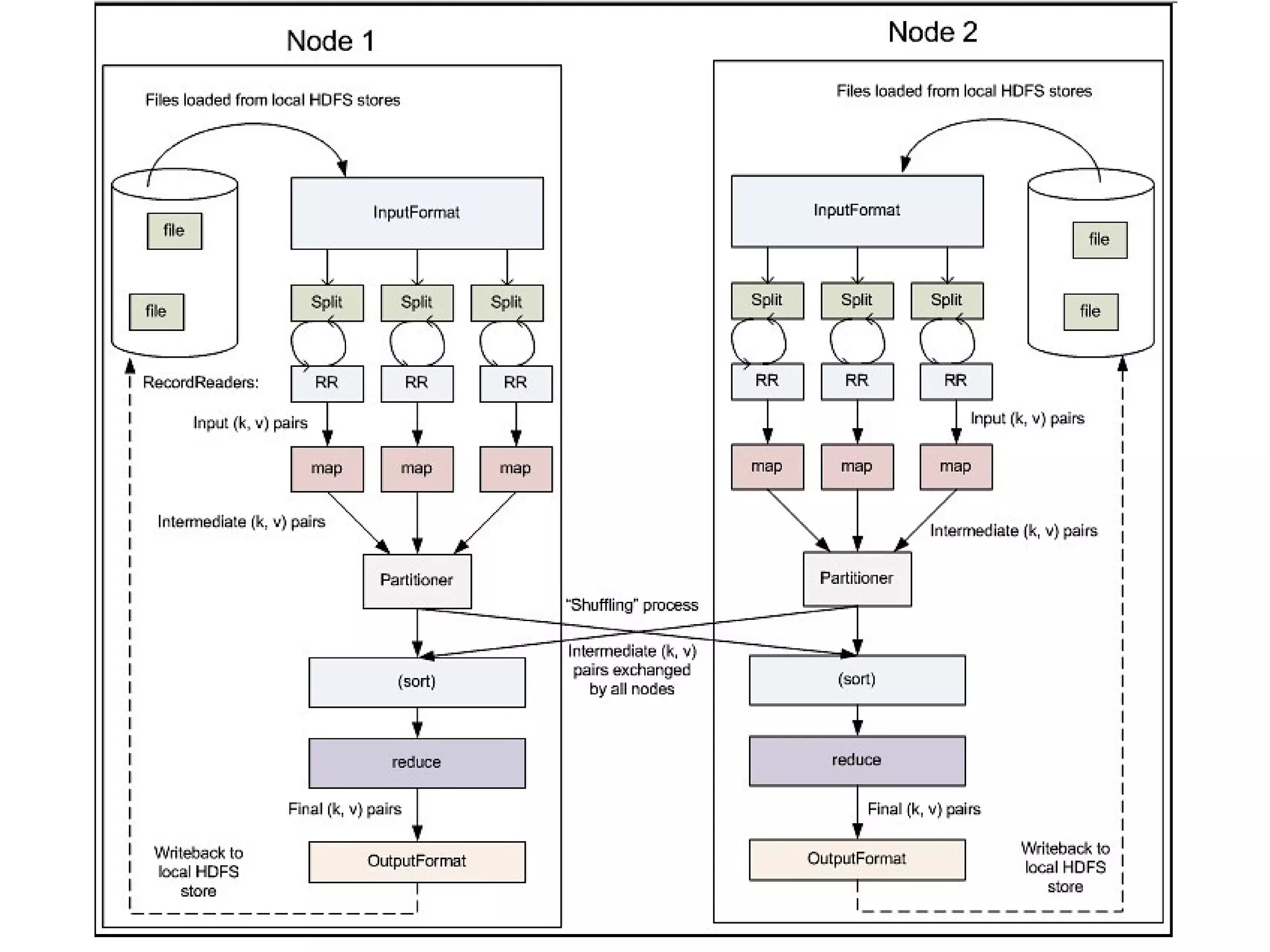
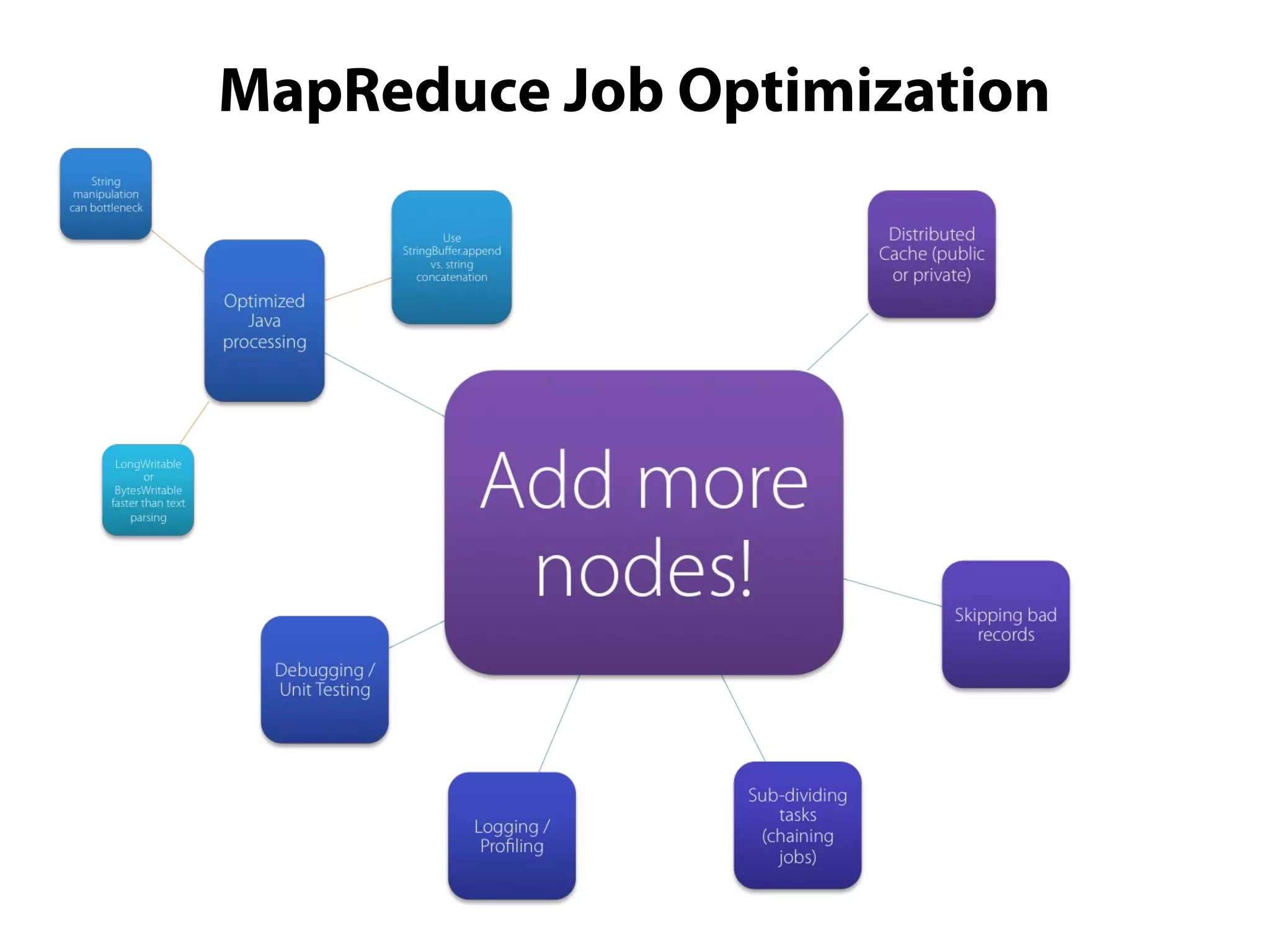
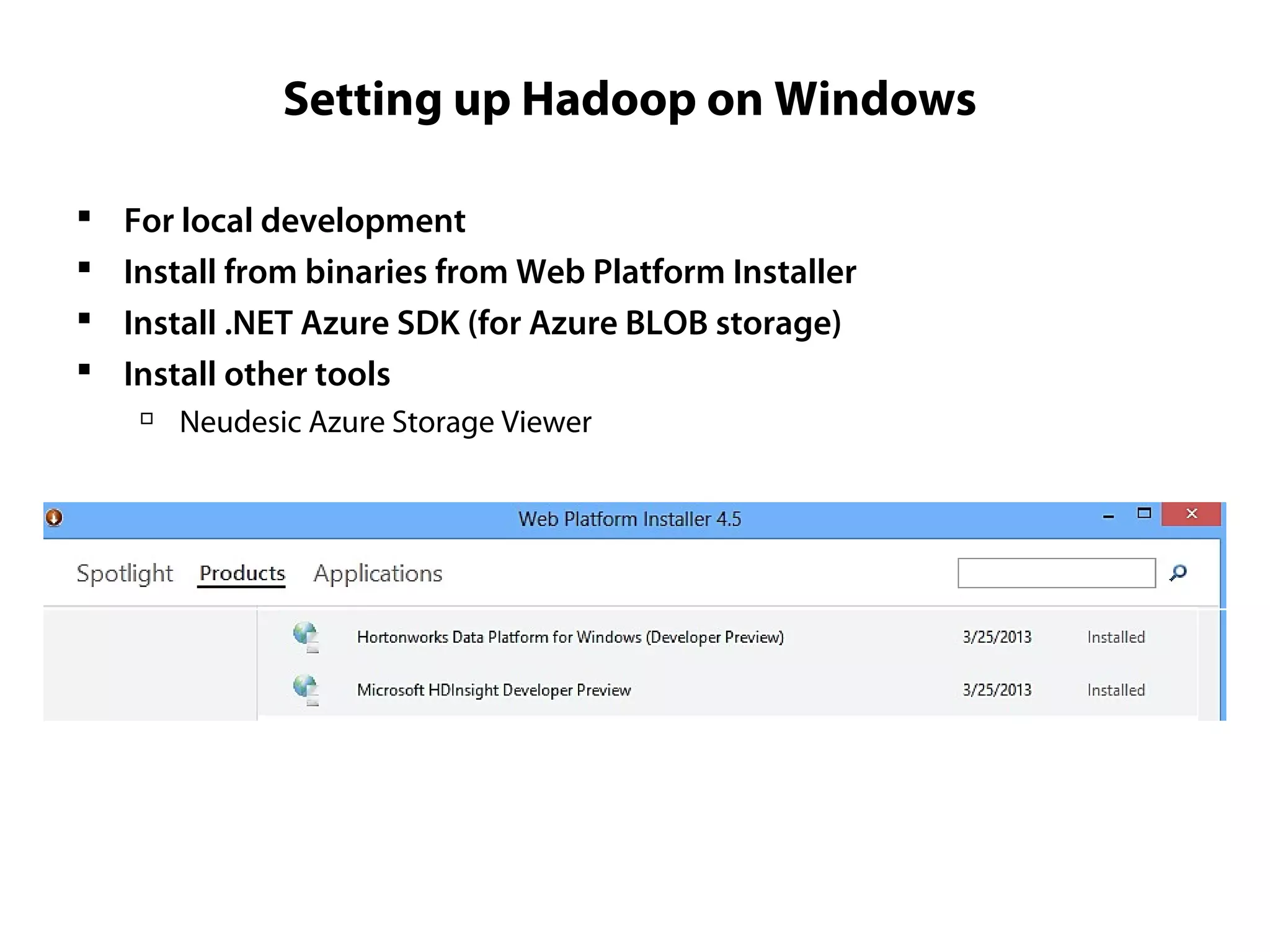
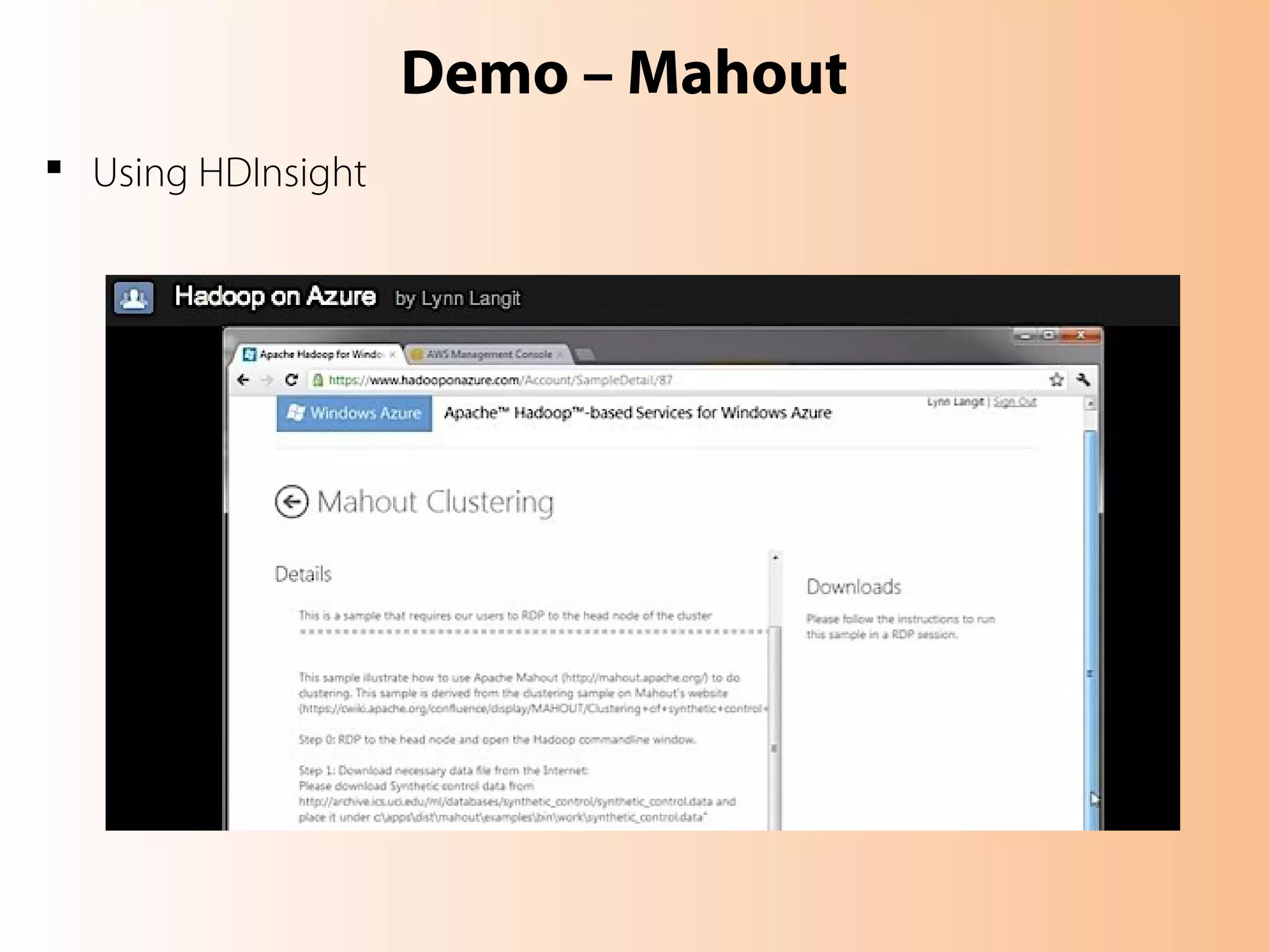
This document provides an overview of the Hadoop MapReduce Fundamentals course. It discusses what Hadoop is, why it is used, common business problems it can address, and companies that use Hadoop. It also outlines the core parts of Hadoop distributions and the Hadoop ecosystem. Additionally, it covers common MapReduce concepts like HDFS, the MapReduce programming model, and Hadoop distributions. The document includes several code examples and screenshots related to Hadoop and MapReduce.