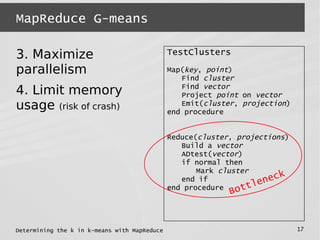
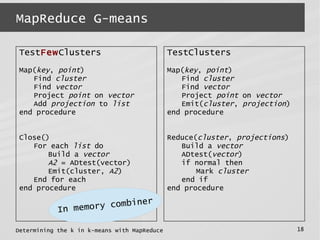
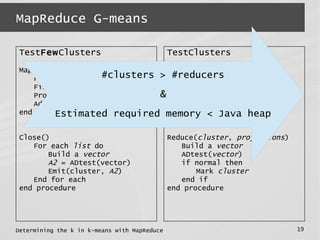
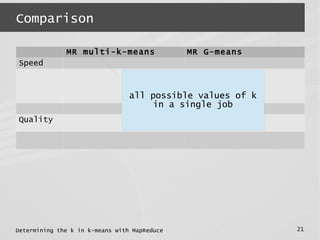
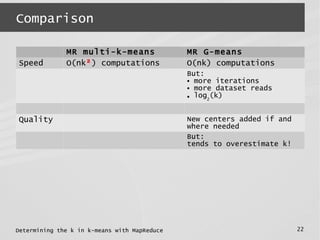
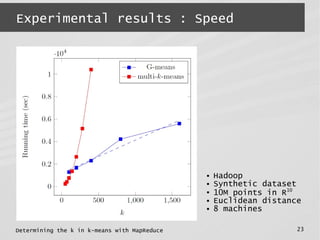
This document describes a MapReduce algorithm for determining the optimal k value in k-means clustering. It presents the G-means algorithm, which uses recursive k-means clustering and normality testing to split clusters until all points are normally distributed around cluster centers. The document outlines challenges in implementing G-means in MapReduce, and describes solutions to reduce I/O, jobs, maximize parallelism and limit memory usage. It compares the proposed MapReduce G-means approach to existing multi-k-means methods, finding it has better quality and comparable speed on synthetic datasets.

![Determining the k in k-means with MapReduce 2
Clustering & k-means
● Clustering
● K-means
[Stuart P. Lloyd. Least squares quantization in pcm. IEEE
Transactions on Information Theory, 28:129–137, 1982.]
– 1982 (a great year!)
– But still largely used
– Drawbacks (amongst others):
● Local minimum
● K is a parameter!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrbeyond2014-140328064623-phpapp01/85/Determining-the-k-in-k-means-with-MapReduce-2-320.jpg)
![Determining the k in k-means with MapReduce 3
Clustering & k-means
● Determine k:
– VERY difficult
[Anil K Jain. Data Clustering : 50 Years Beyond K-Means.
Pattern Recognition Letters, 2009]
– Using cluster evaluation metrics:
Dunn's index, Elbow, Silhouette, “jump method” (based on
information theory), “Gap statistic”,...
O(k²)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrbeyond2014-140328064623-phpapp01/85/Determining-the-k-in-k-means-with-MapReduce-3-320.jpg)
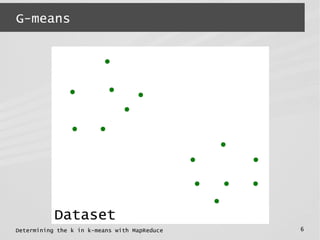
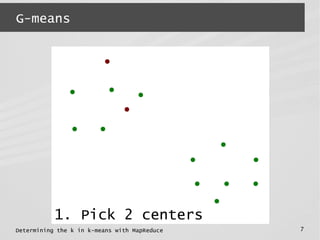
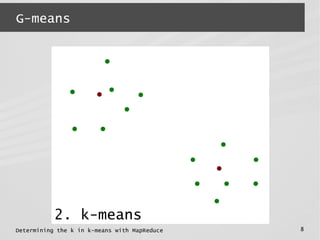
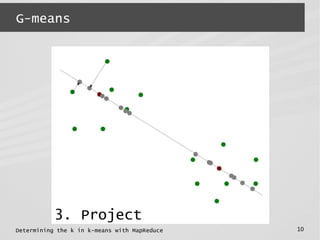
![Determining the k in k-means with MapReduce 4
G-means
● G-means
[Greg Hamerly and Charles Elkan. Learning the k in k-
means. In Neural Information Processing Systems. MIT
Press, 2003]
● K-means : points in each cluster are
spherically distributed around the center
Source:scikit-learn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrbeyond2014-140328064623-phpapp01/85/Determining-the-k-in-k-means-with-MapReduce-4-320.jpg)
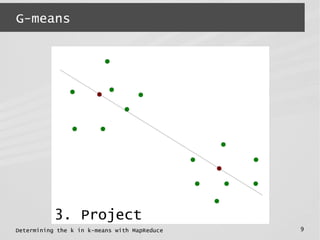
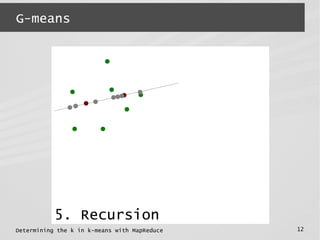
![Determining the k in k-means with MapReduce 5
G-means
● G-means
[Greg Hamerly and Charles Elkan. Learning the k in k-
means. In Neural Information Processing Systems. MIT
Press, 2003]
● K-means : points in each cluster are
spherically distributed around the center
normality test &
recursion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrbeyond2014-140328064623-phpapp01/85/Determining-the-k-in-k-means-with-MapReduce-5-320.jpg)