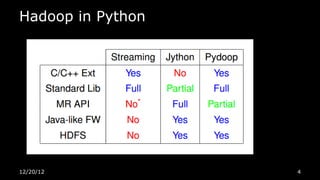
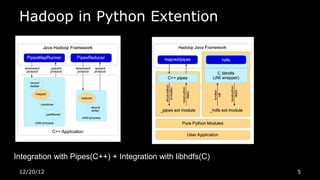
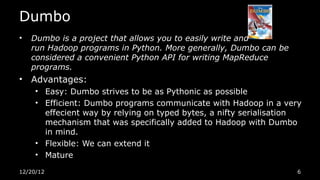
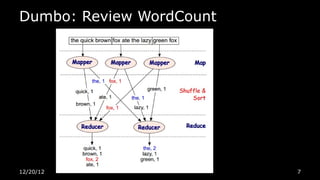
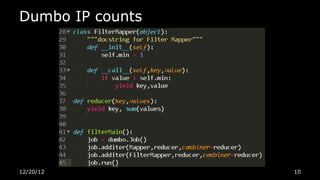
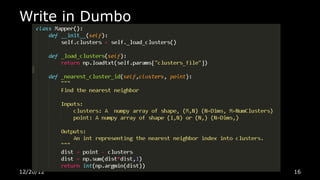
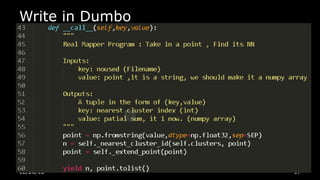
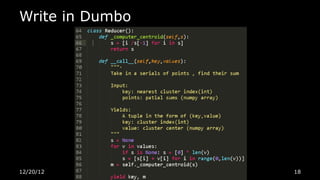
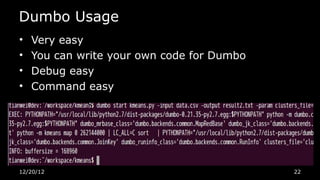
This document discusses using Python for Hadoop and data mining. It introduces Dumbo, which allows writing Hadoop programs in Python. K-means clustering in MapReduce is also covered. Dumbo provides a Pythonic API for MapReduce and allows extending Hadoop functionality. Examples demonstrate implementing K-means in Dumbo and optimizing it by computing partial centroids locally in mappers. The document also lists Python books and tools for data mining and scientific computing.