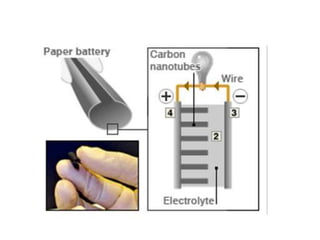
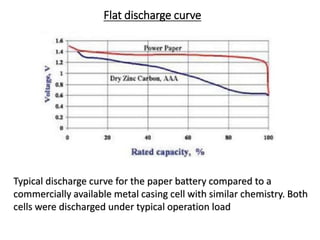
Paper batteries provide a flexible, lightweight alternative to conventional batteries. They are constructed by combining carbon nanotubes with cellulose-based paper to form electrodes. During use, an oxidation reaction occurs at the anode while a reduction reaction occurs at the cathode, generating a flow of electrons. Paper batteries have advantages over conventional batteries like being bendable, biodegradable, and able to charge within 10 seconds. However, they also have disadvantages such as higher cost and challenges related to scaling up. Potential applications include use in electronics like watches, calculators, and laptops.