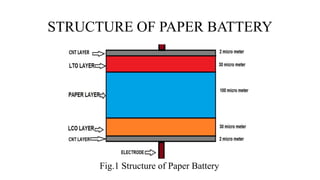
A paper battery is described that combines carbon nanotubes with paper to create a flexible energy storage device. It functions similar to both a battery and supercapacitor. Compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, paper batteries are thinner, lighter, lower cost and can be recharged much faster. They work by facilitating the flow of lithium ions between carbon nanotube electrodes during charging and discharging. Potential applications include powering electronics, medical devices and as a more sustainable battery alternative.

























![REFERENCE
• 1] L. Hu, J. W. Choi, Y. Yang, S. Jeong, F. La Mantia, F. Cui, and Y.
Cui, “Highly conductive paper for energy-storage devices,” Proc. Nat.
Academy Sci., vol. 106, pp. 21490–21494, 2009.
• [2] L.Hu,H.Wu,F. LaMantia,Y.Yang,andY.Cui,“Thin,flexiblesecondary
Li-ion paper batteries,” ACS Nano, vol. 4, pp. 5843–5848, 2010.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperbatterydhikil-190825160001/85/Paper-battery-27-320.jpg)
![• [3]S.Stewart,P.Albertus,V.Srinivasan,I.Plitz,N.Pereira,G.Amatucci,and
J.Newman,“Optimizingthe performance of lithium titanate spinel
paired with activated carbon or iron phosphate,” J. Electrochem. Soc.,
vol. 155, pp. A253–A261, 2008.
• [4] L. Hu, D. S. Hecht, and G. Gruner, “Percolation in transparent and
conducting carbon nanotube networks,” Nano Lett., vol. 4, pp. 2513–
2517, 2004.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperbatterydhikil-190825160001/85/Paper-battery-28-320.jpg)
