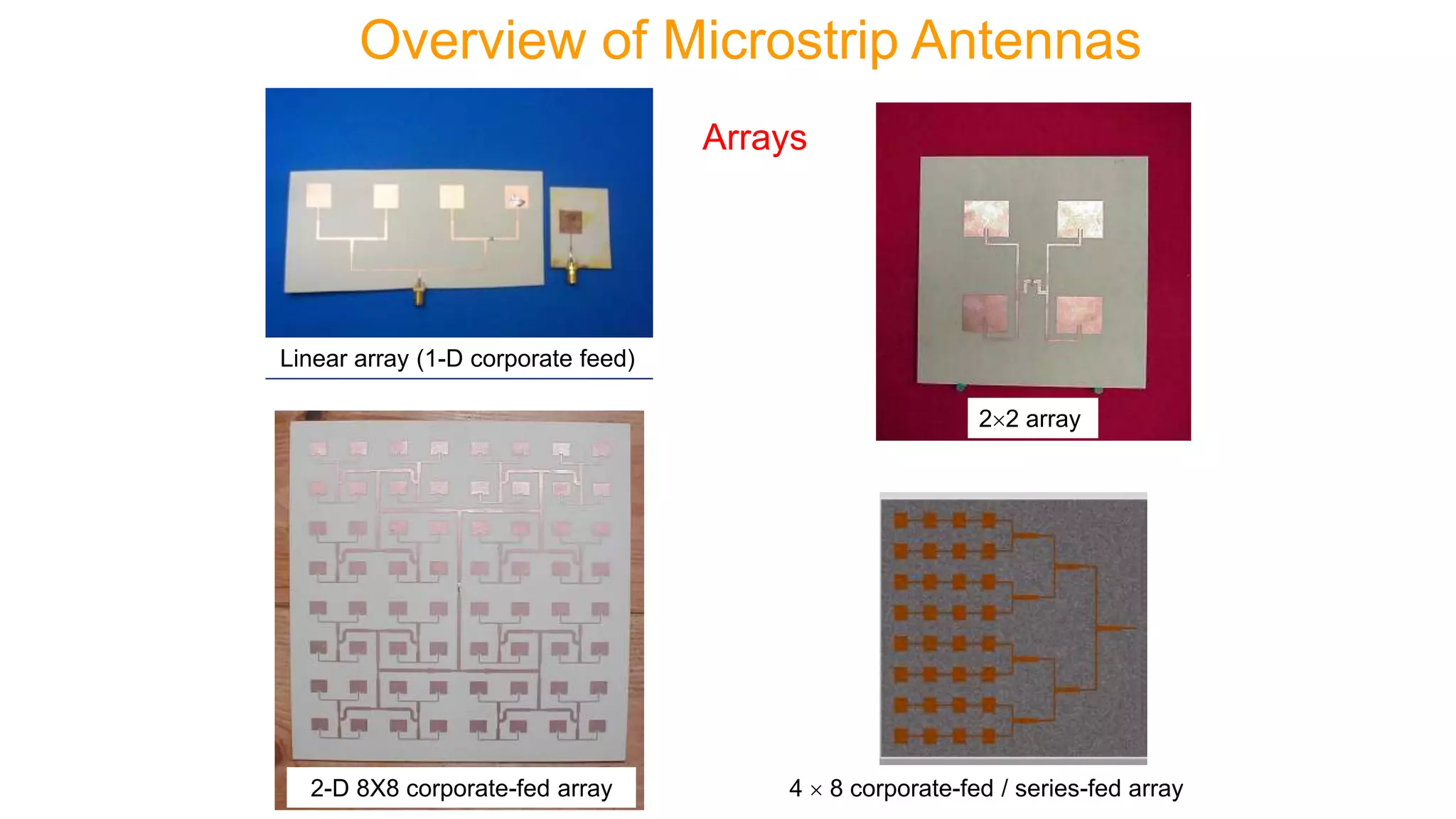
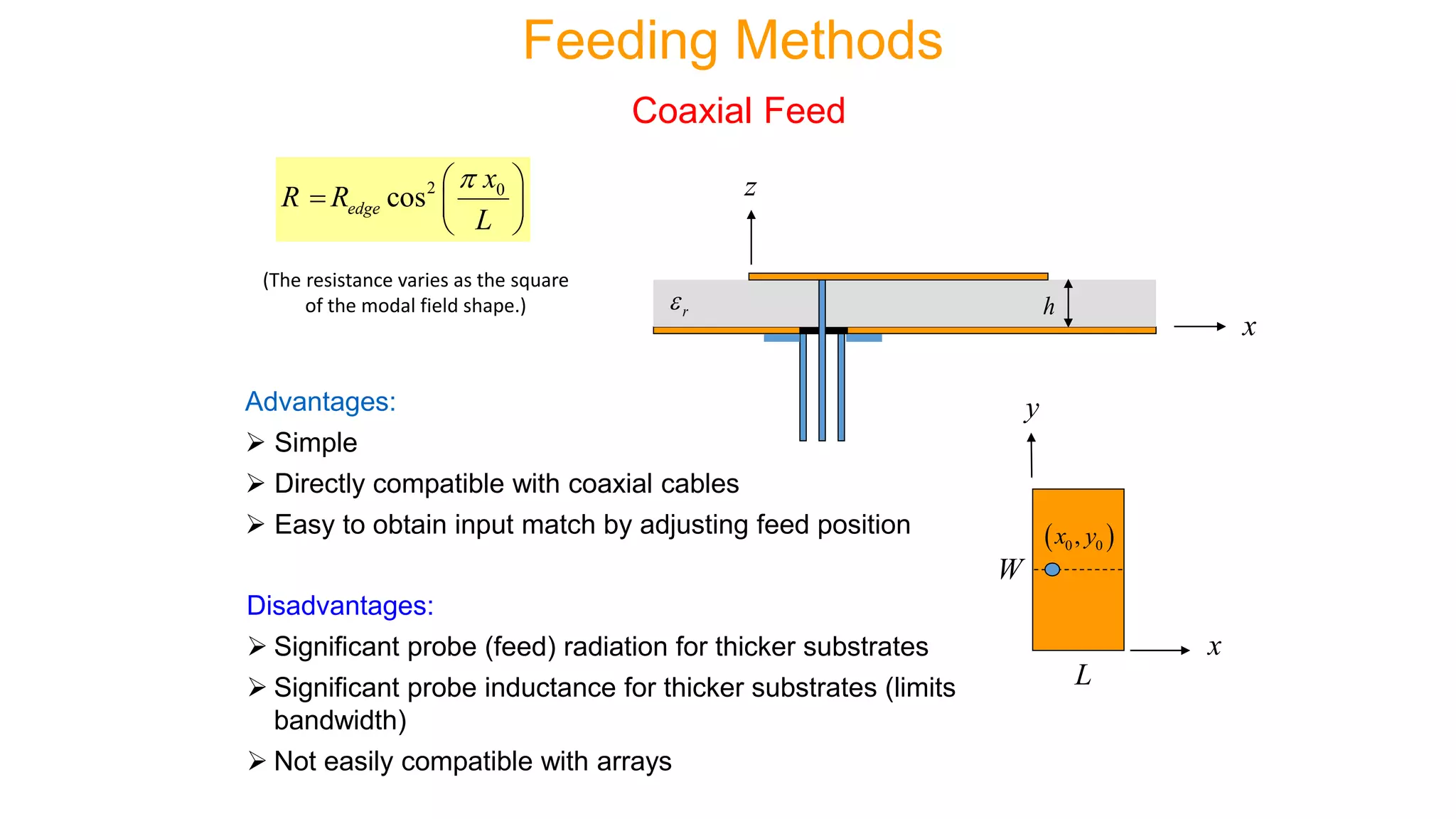
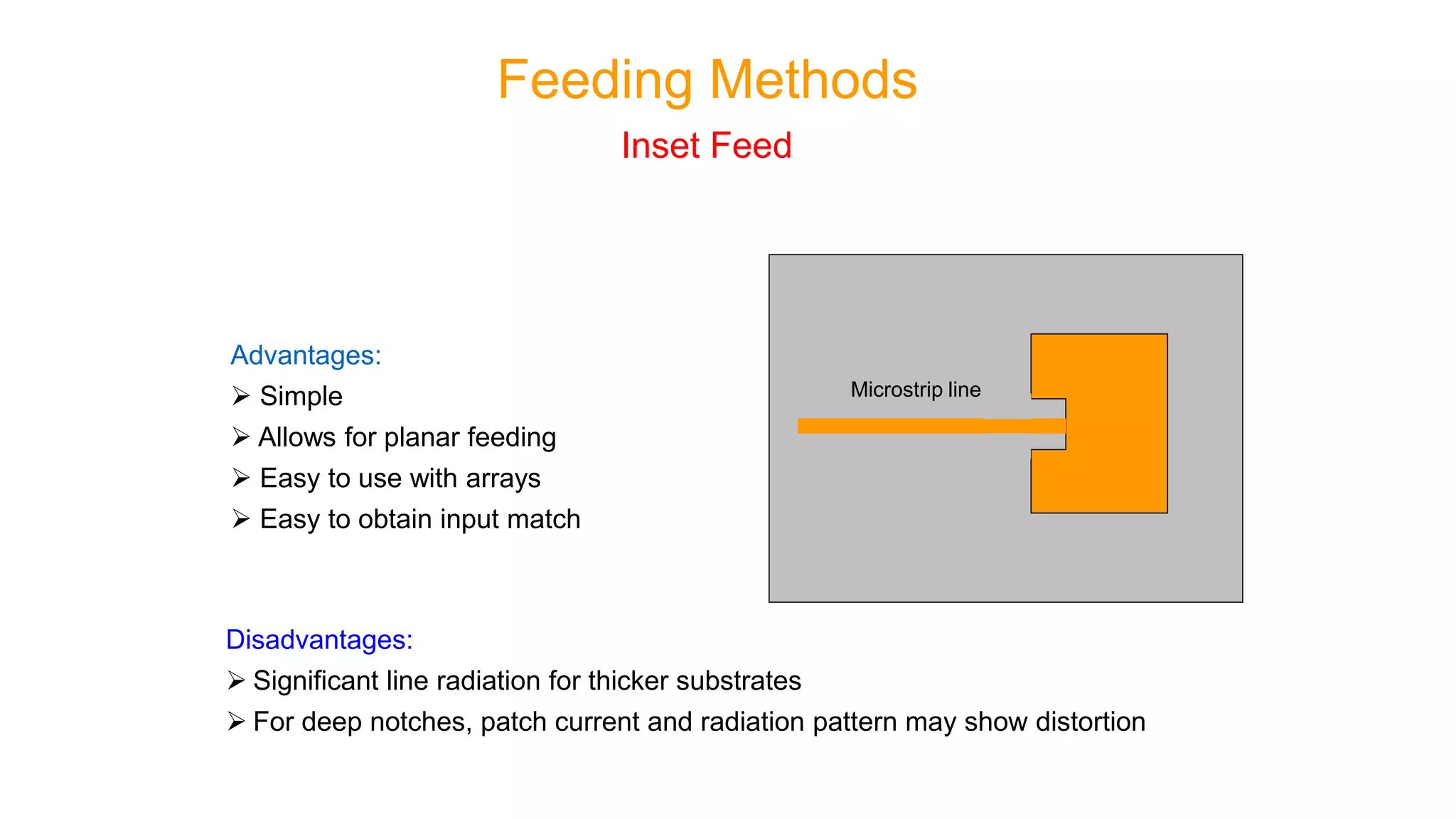
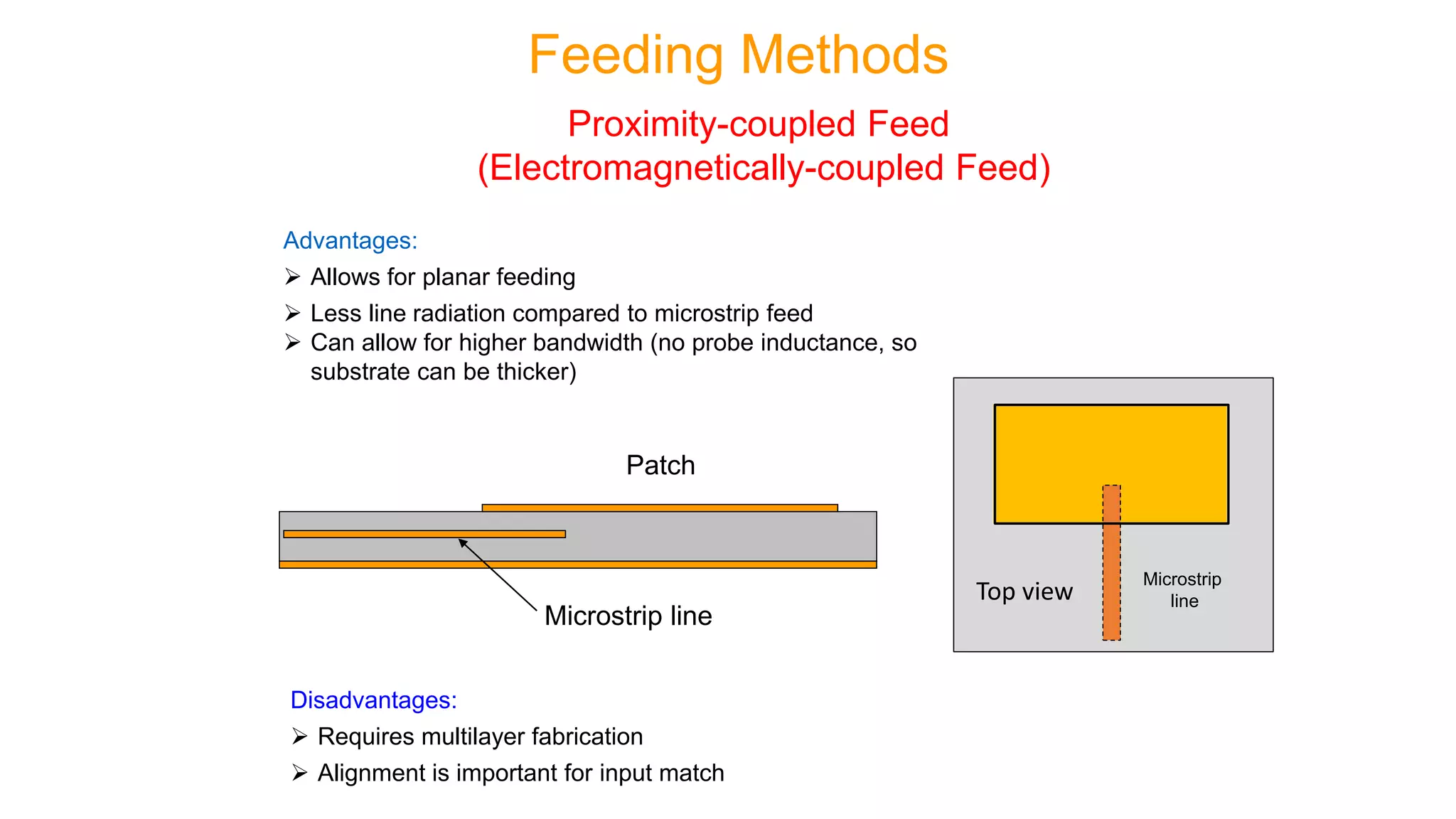
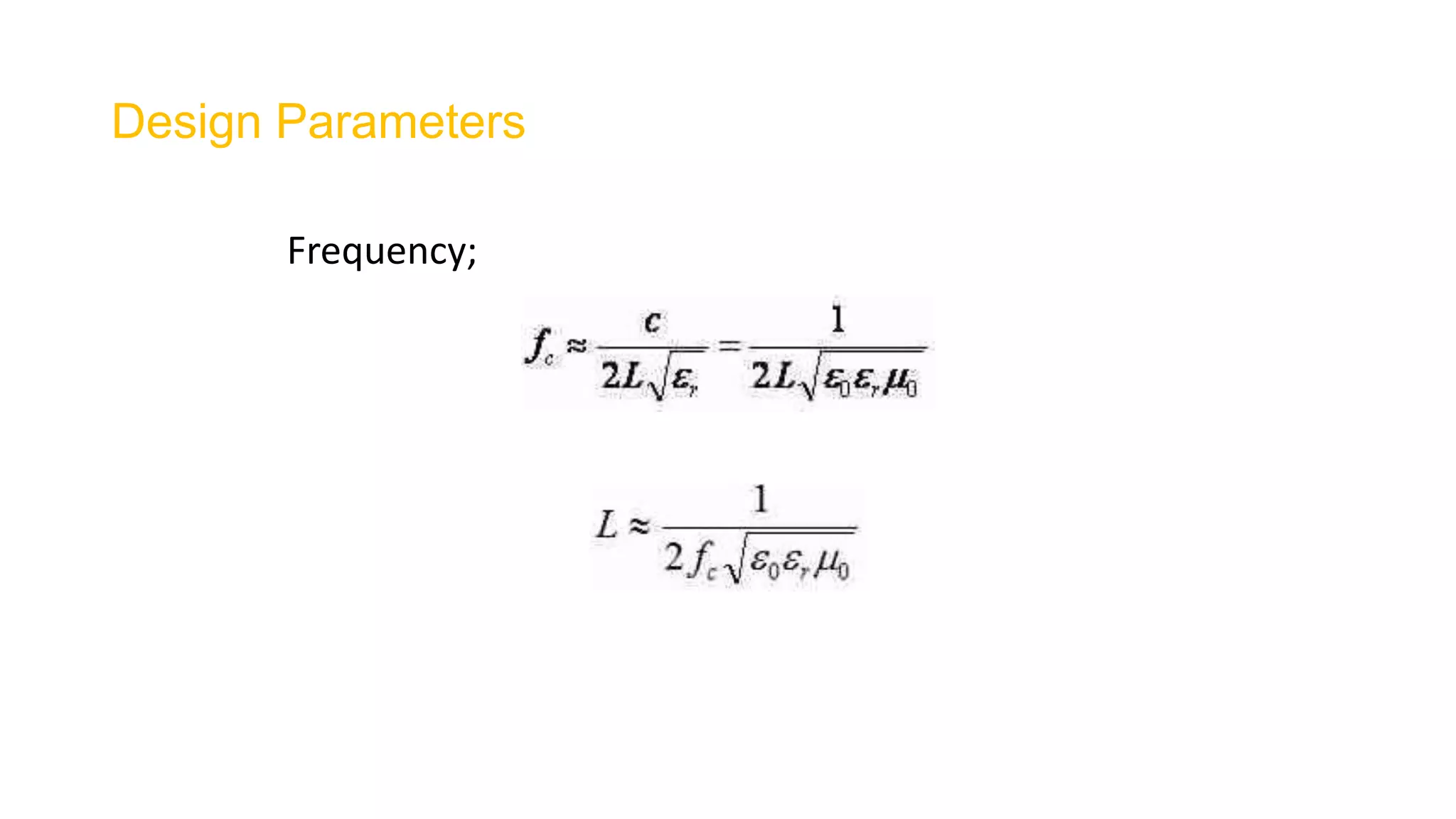
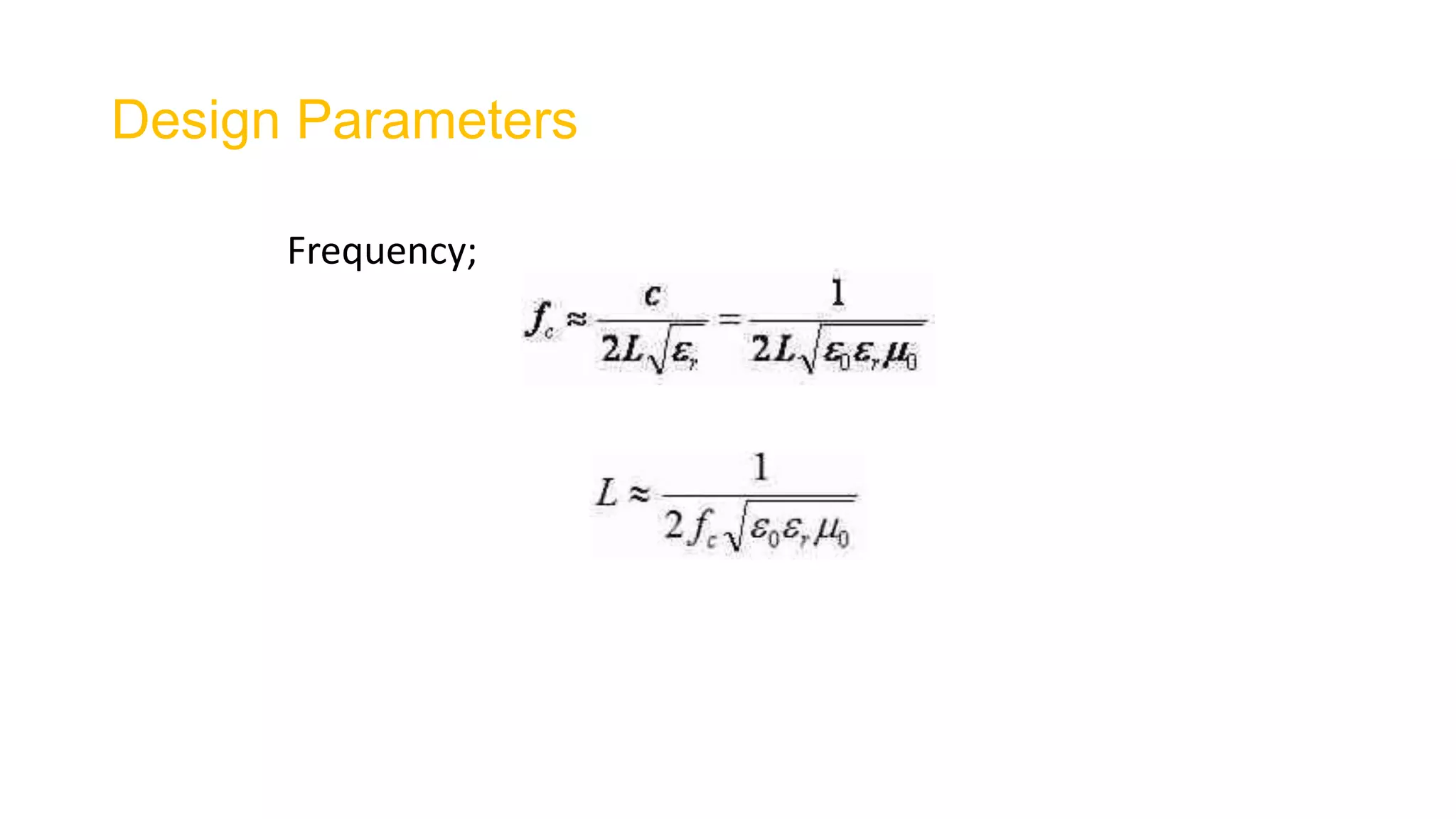
Microstrip antennas, also known as patch antennas, are low-profile antennas commonly used in microwave frequencies, typically consisting of a metal patch on a grounded dielectric substrate. Despite their advantages such as ease of fabrication, straightforward feeding methods, and moderate directivity, they have limitations including low bandwidth and efficiency, and are solely applicable at microwave frequencies and above. Common applications include satellite and microwave communications, cell phone antennas, and GPS antennas, with various feeding methods that influence performance and design.