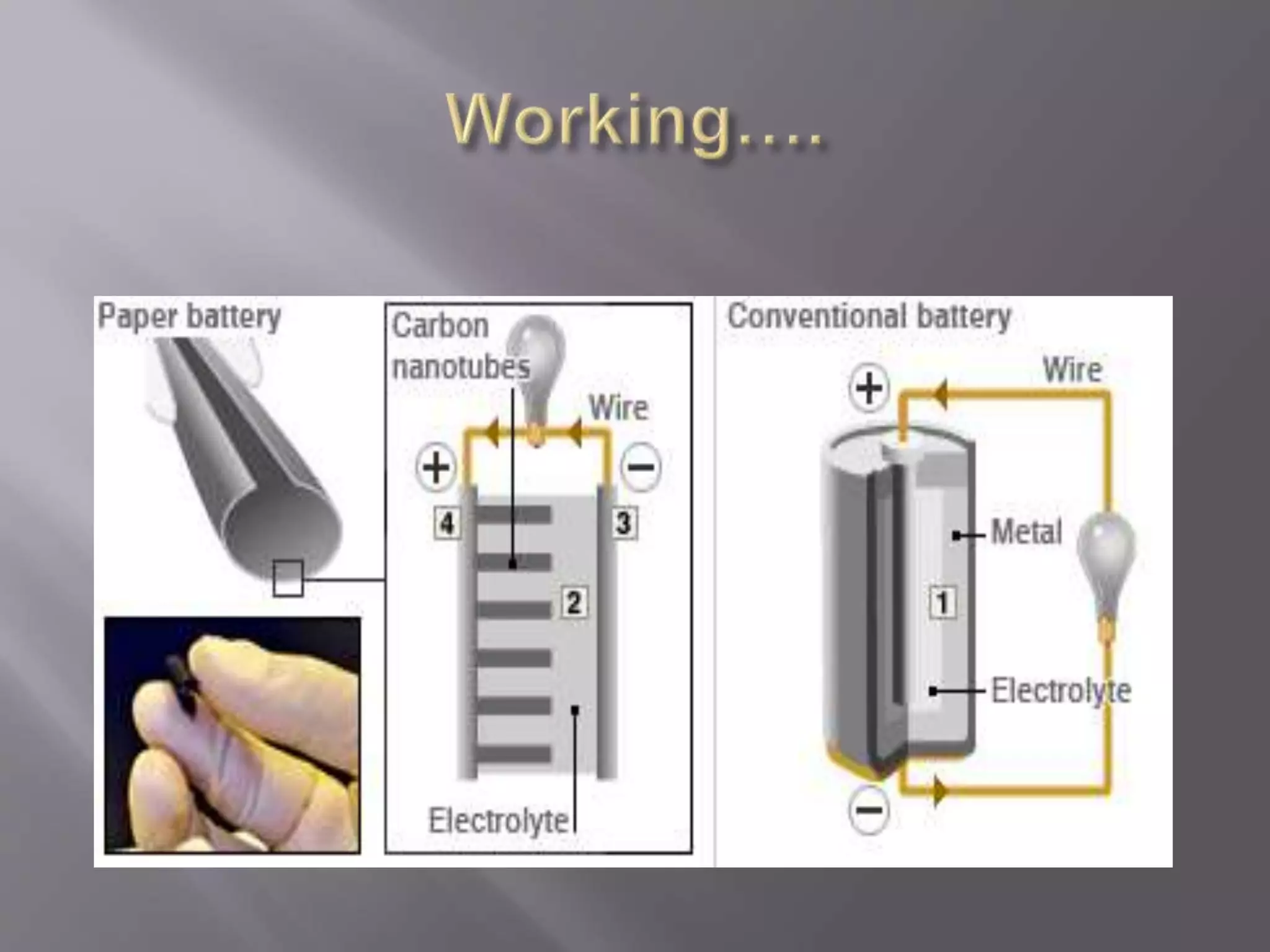
A paper battery is a flexible energy storage device formed by infusing carbon nanotubes into cellulose-based paper. It acts as both a battery and supercapacitor, providing steady power and bursts of energy. The carbon nanotubes serve as electrodes, allowing the battery to conduct electricity through a chemical reaction with an electrolyte. Paper batteries have advantages of flexibility, thinness, and lack of toxicity, but limitations include low strength and high cost of nanotube production. Future applications could include use in medical devices and consumer electronics.