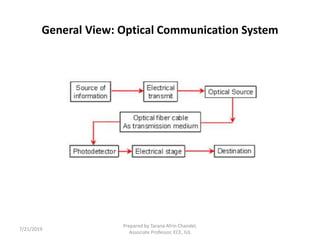
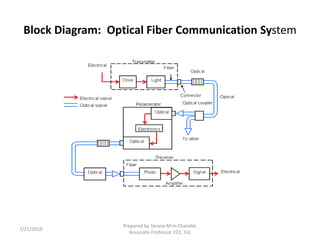
The document provides an introduction to optical fiber communication, detailing its components, structure, and advantages. It outlines the key elements of the optical fiber system including the transmitter, regenerators, and receiver, as well as the characteristics of fiber optic cables. The advantages of using fiber optics include high bandwidth, low transmission loss, and immunity to interference.