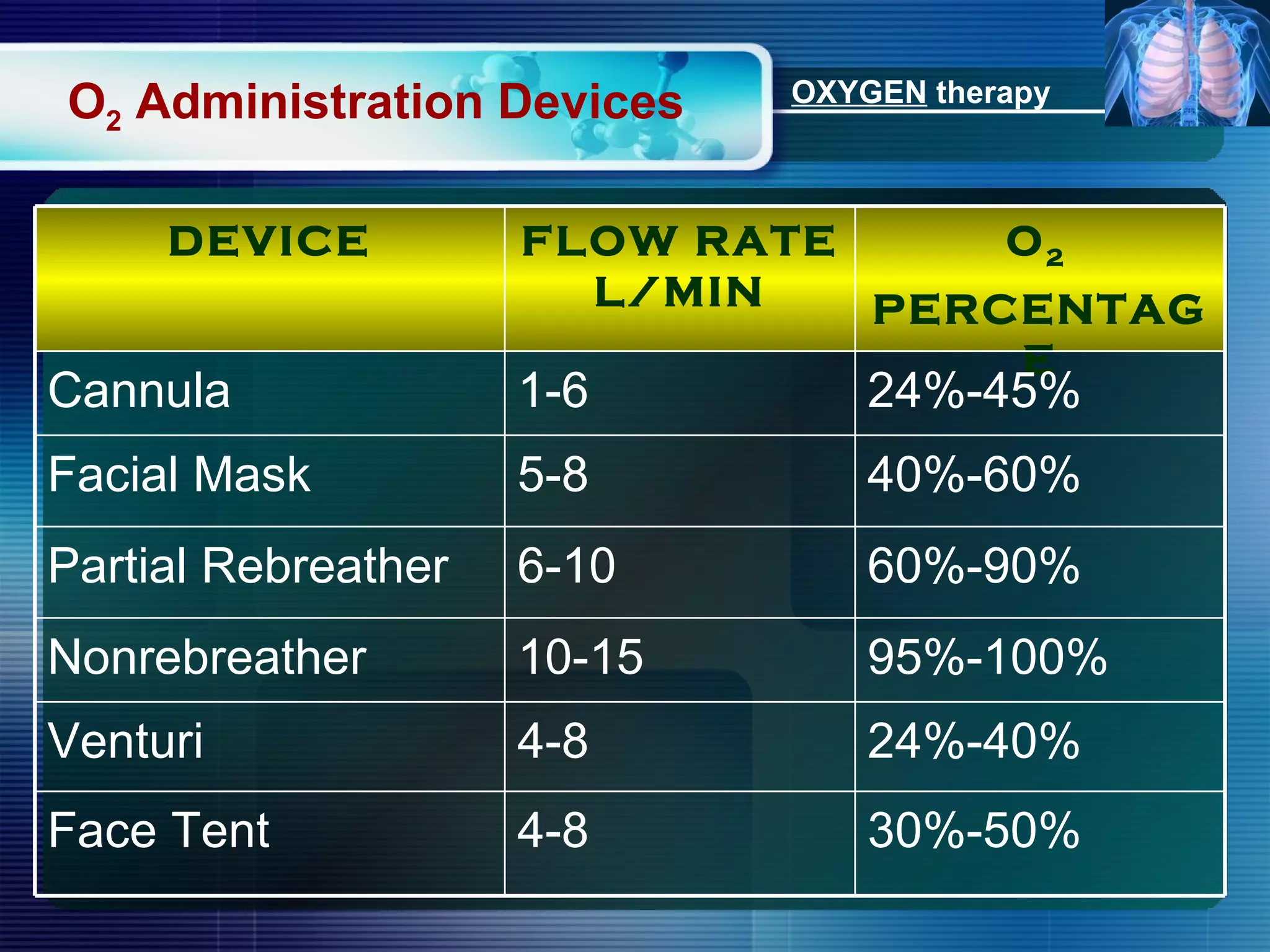
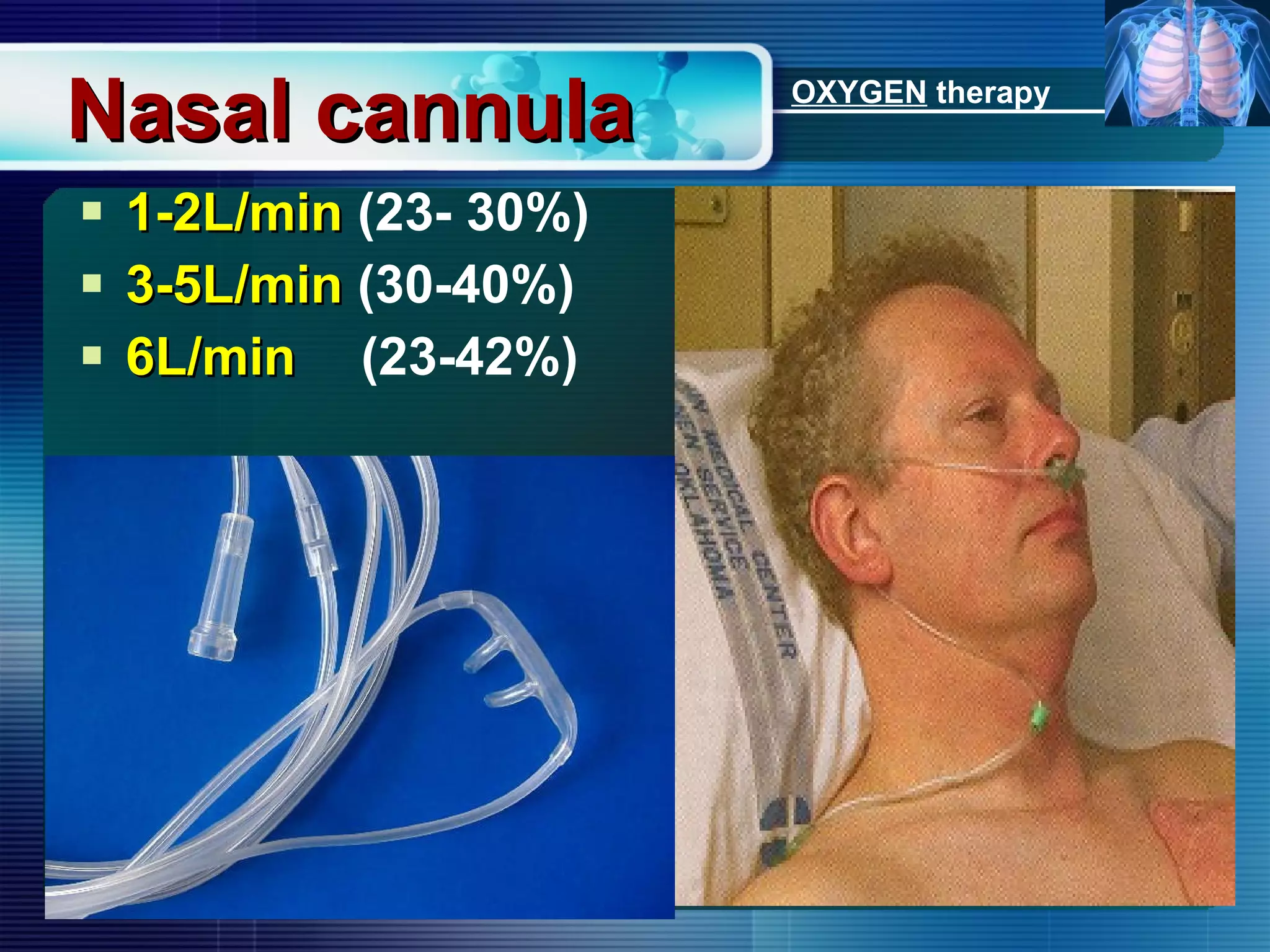
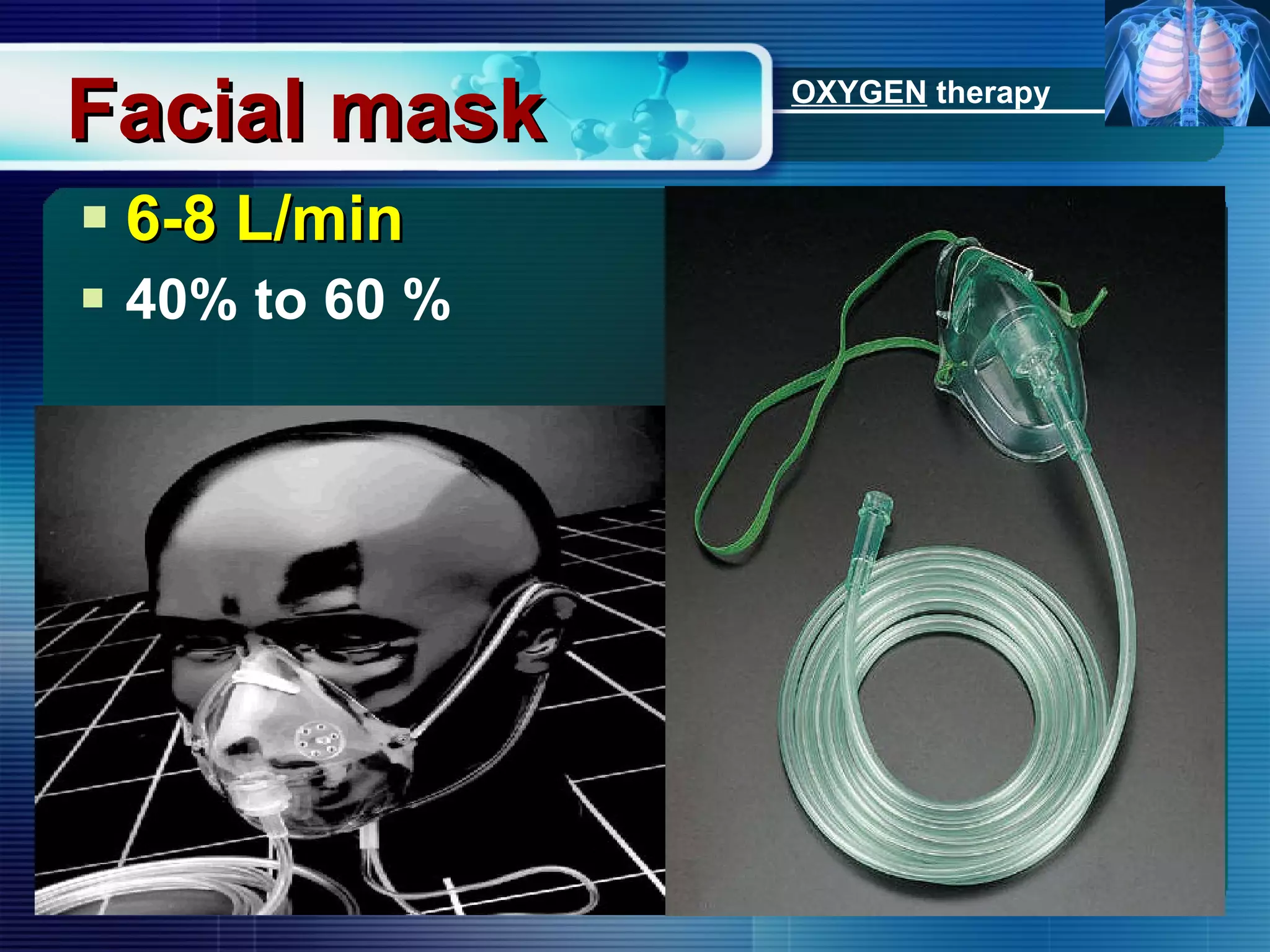
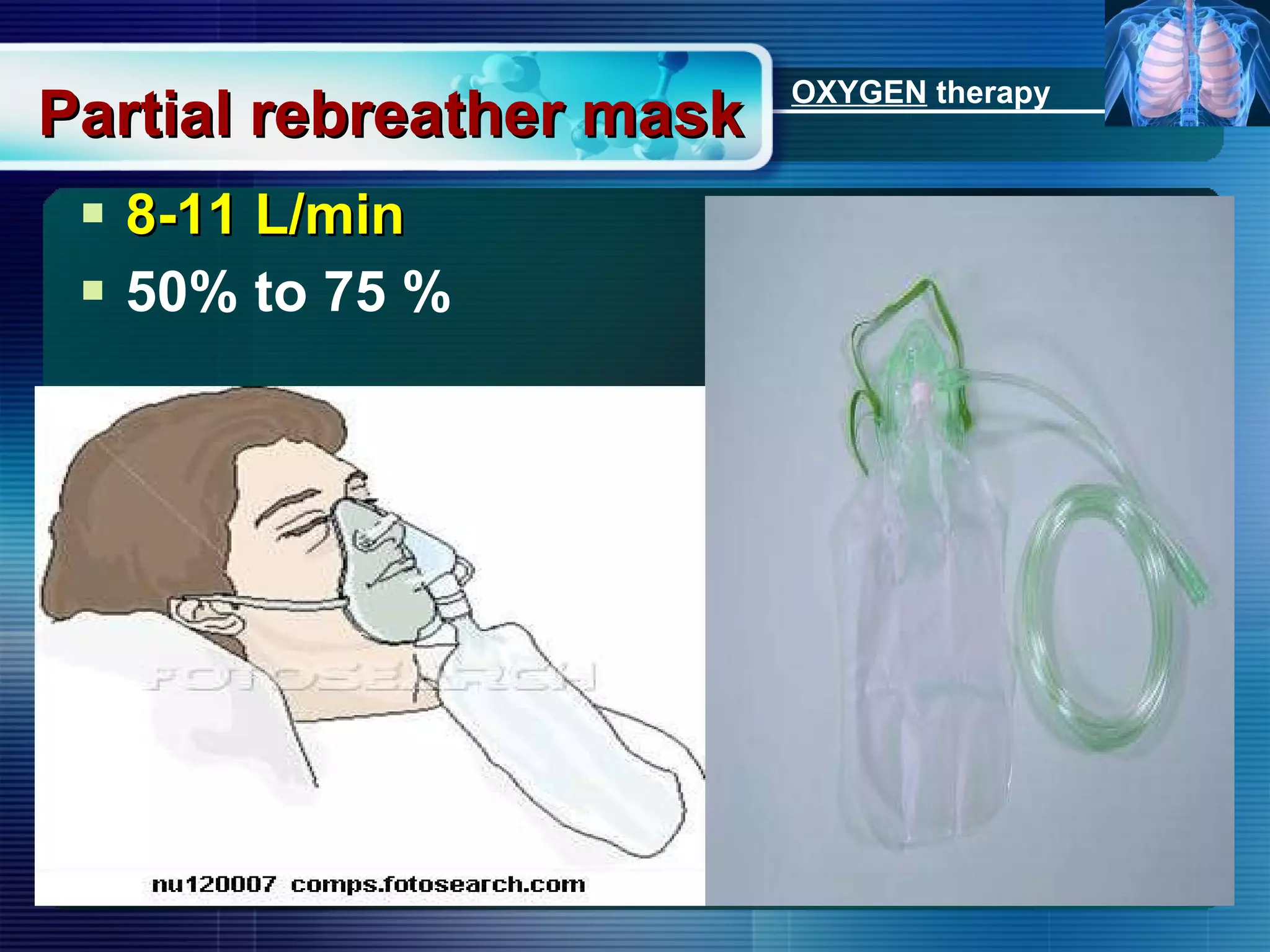
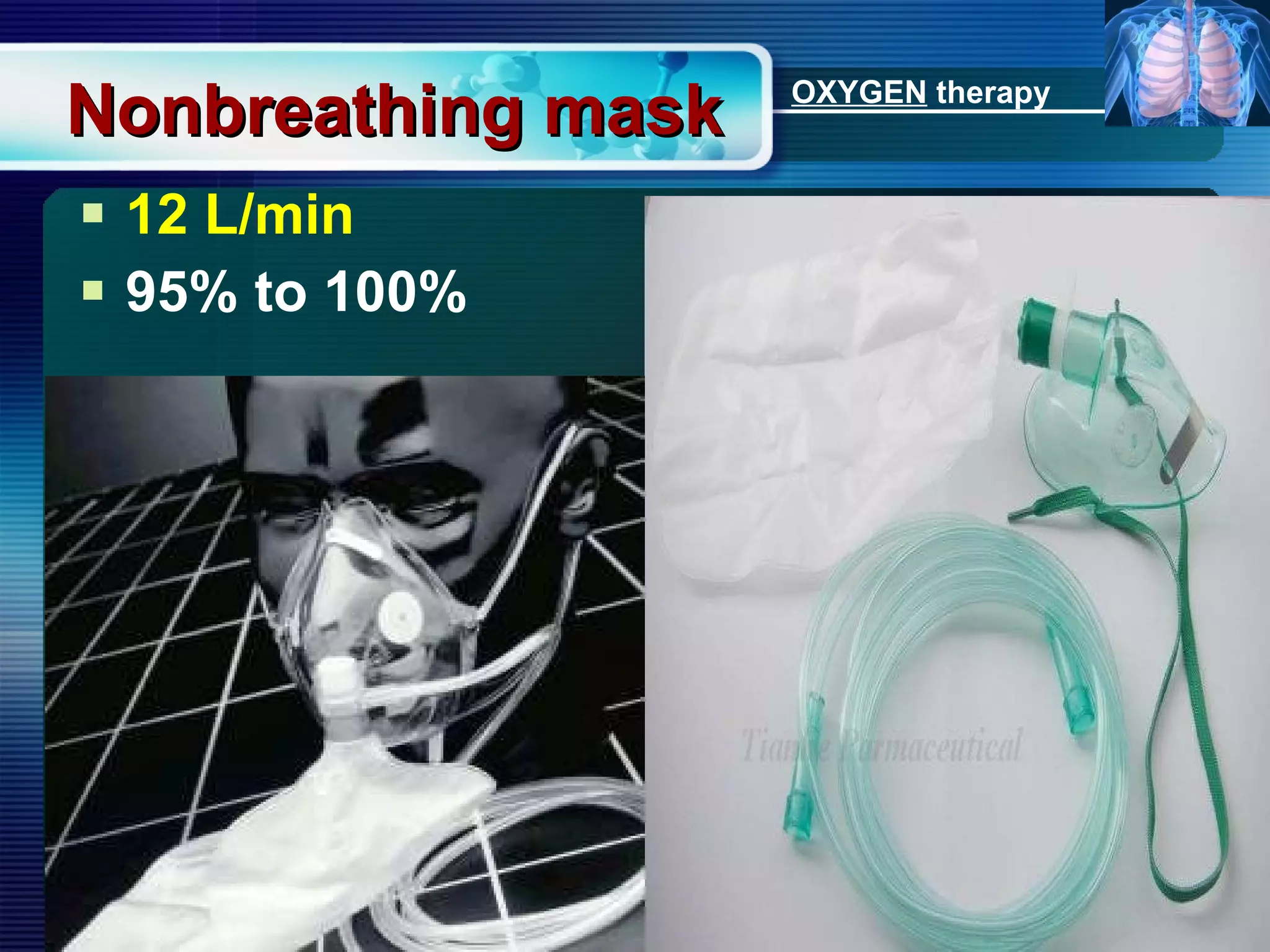
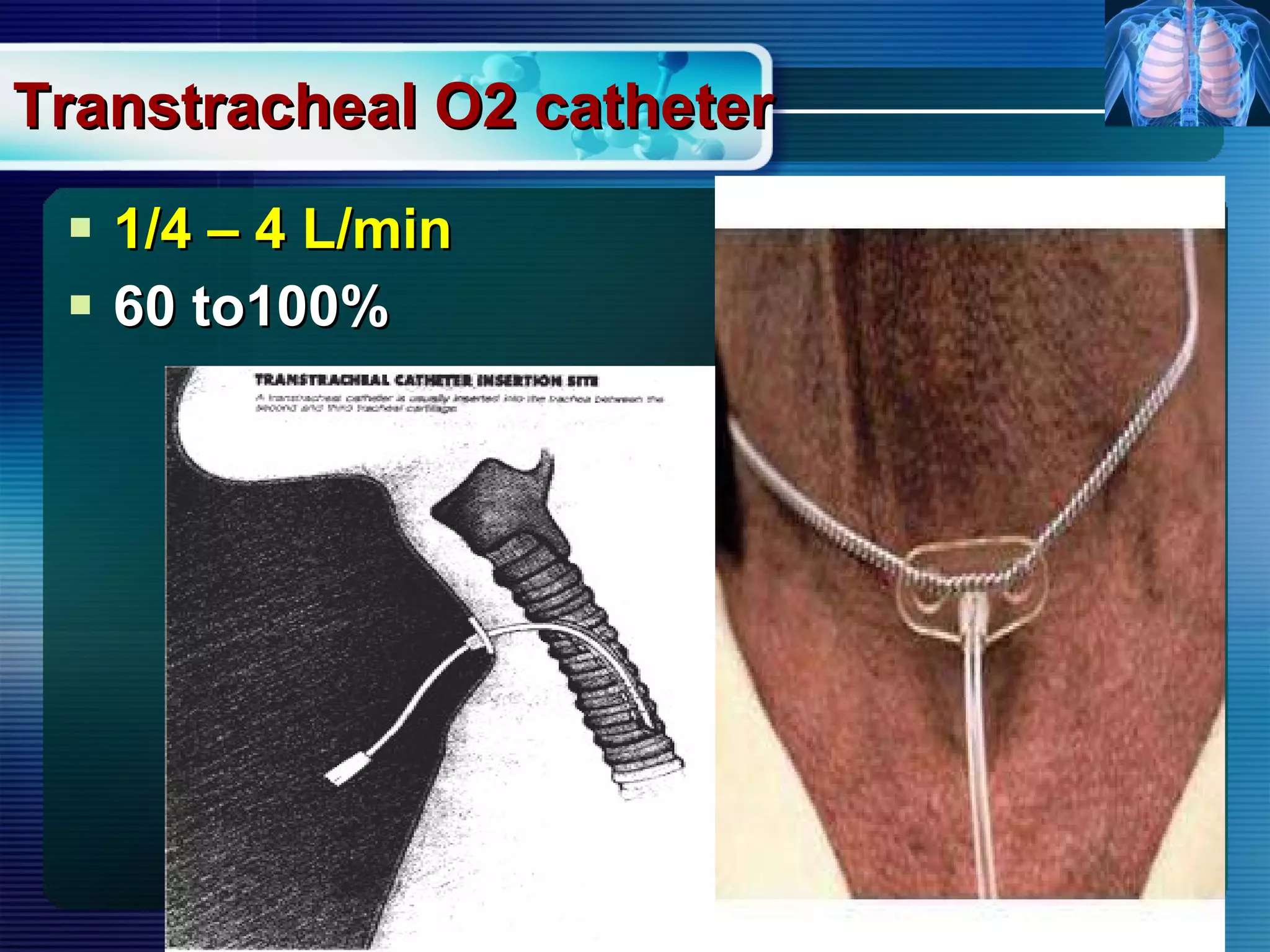
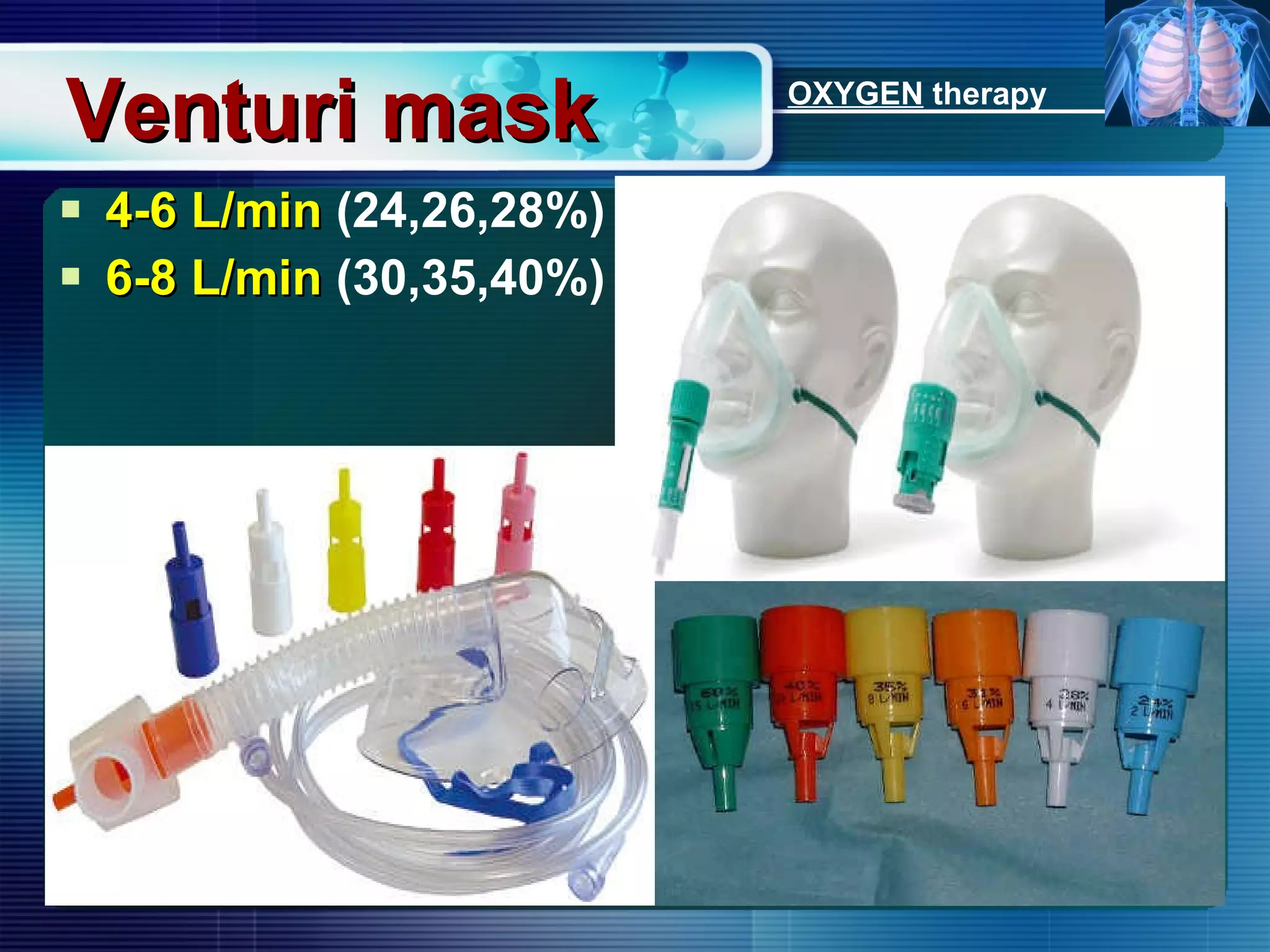
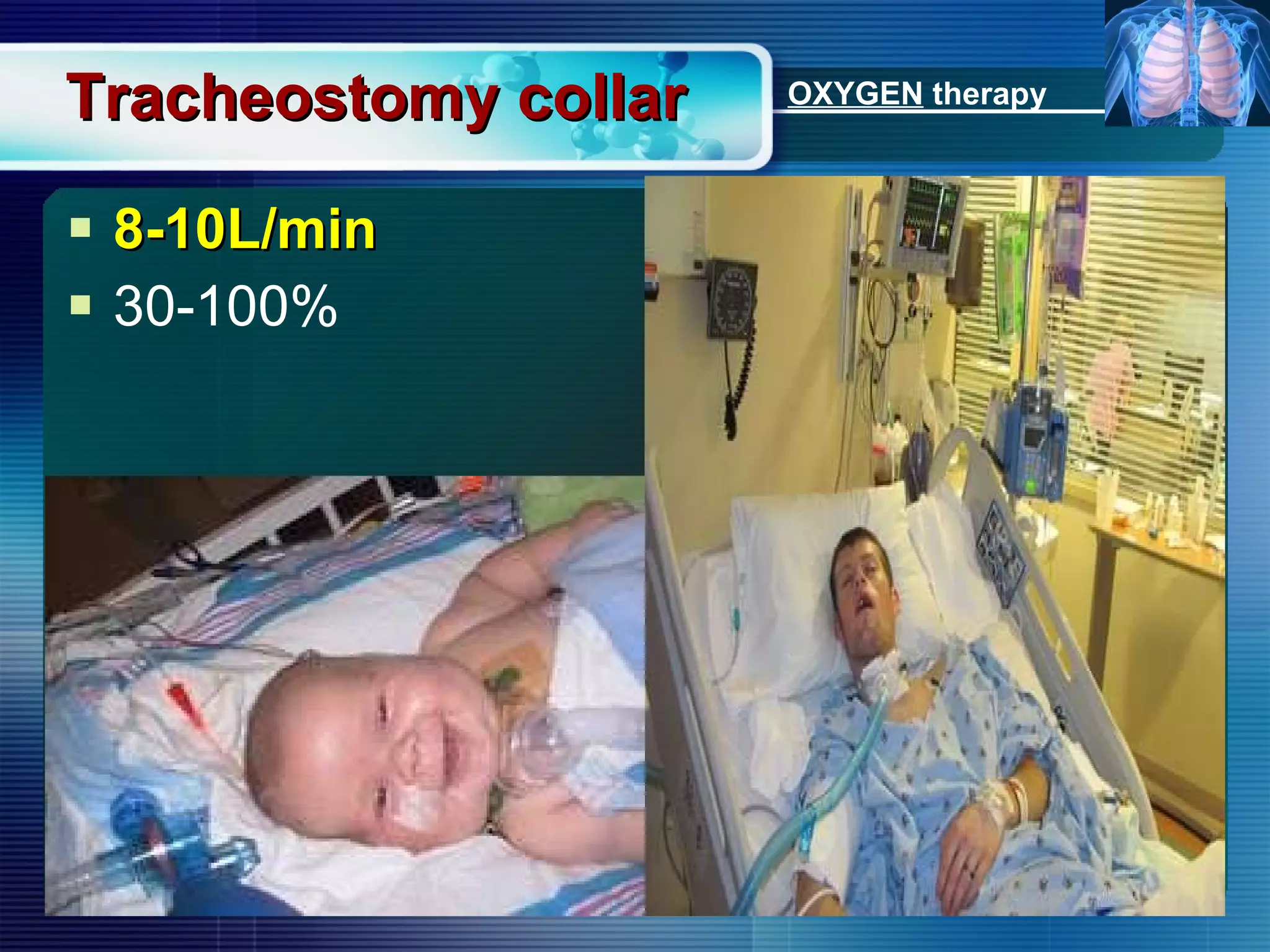
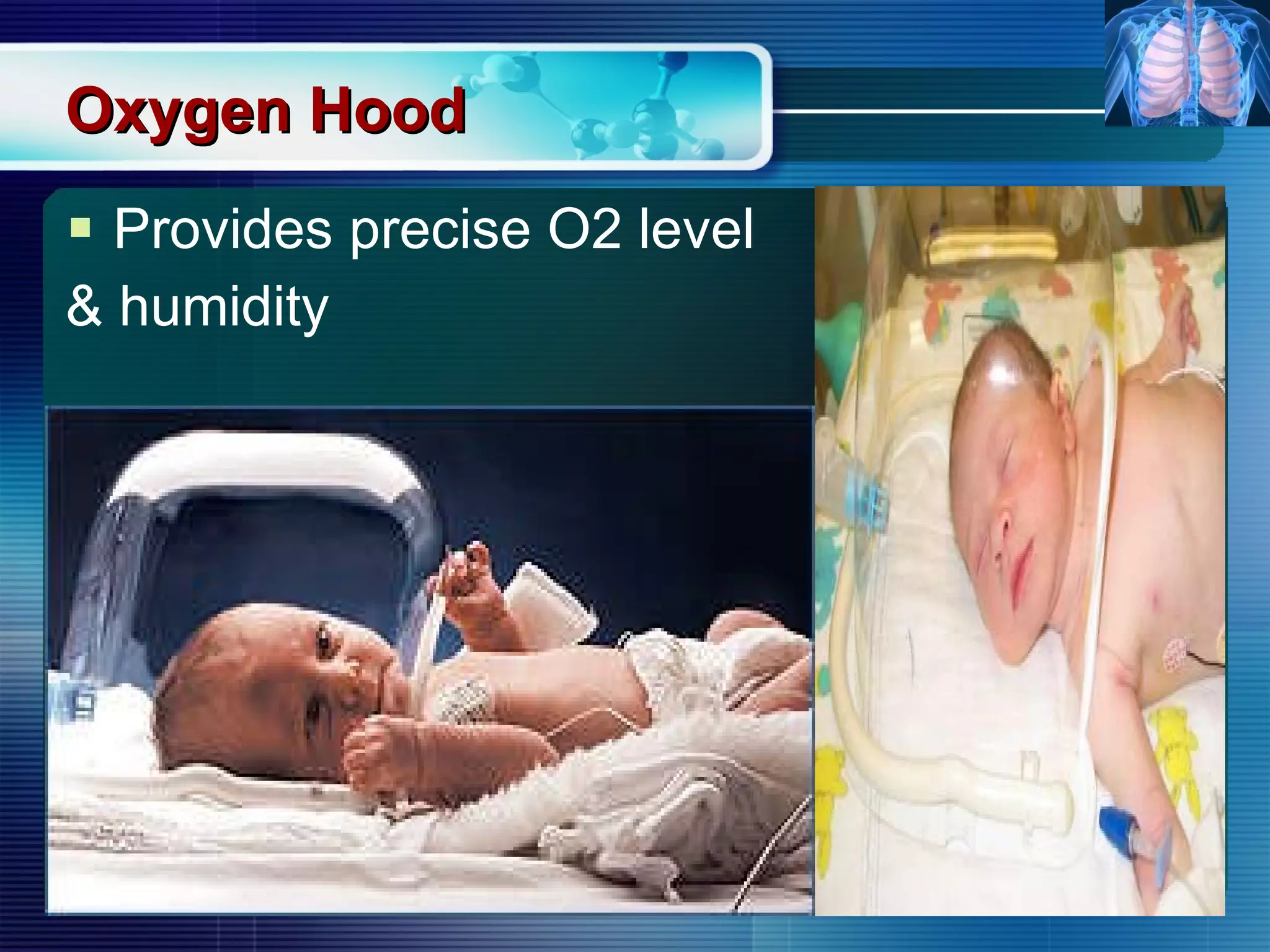
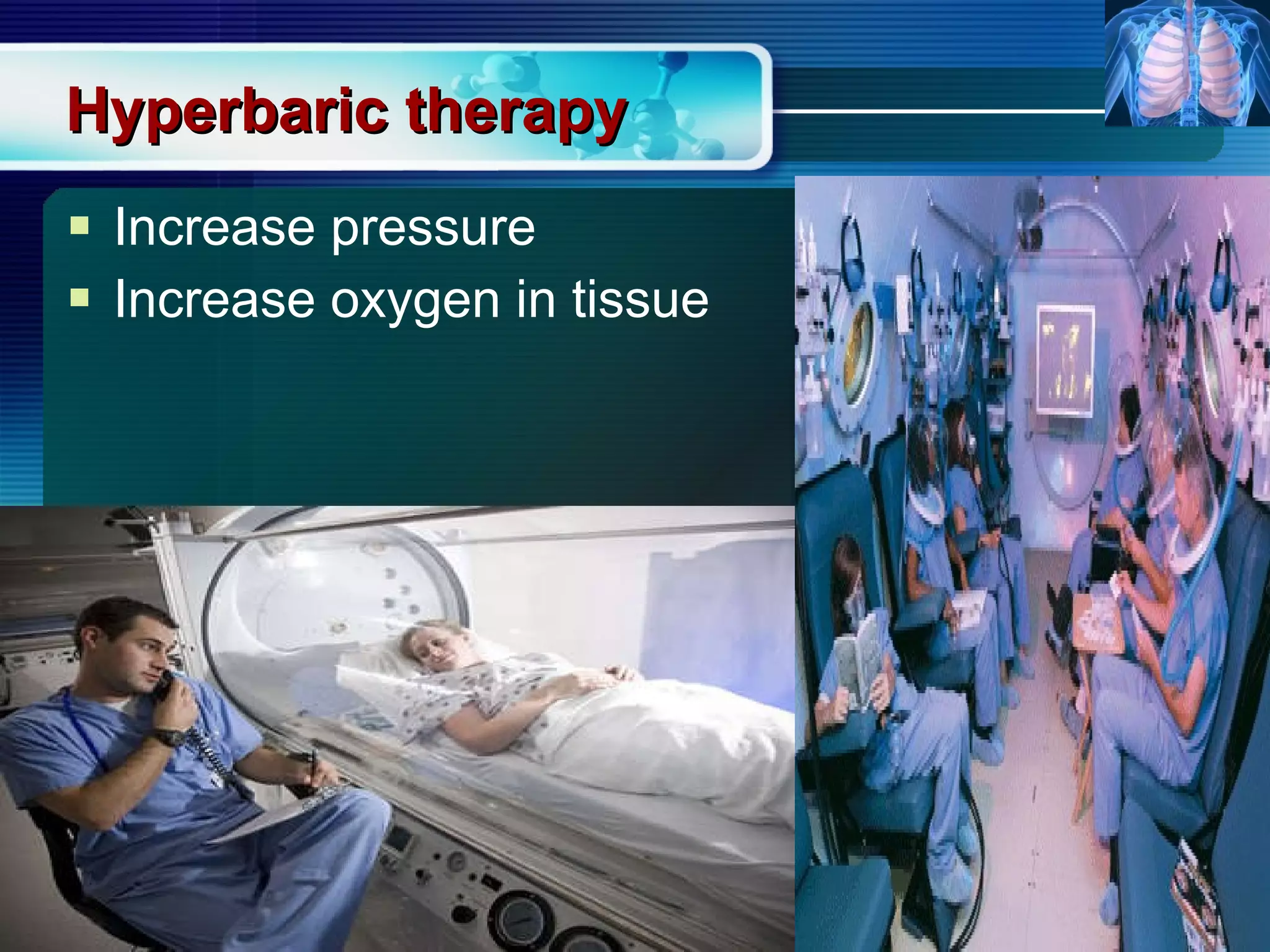
The document outlines the history and definition of oxygen therapy, emphasizing its role in treating hypoxemia by administering oxygen at higher concentrations than found in room air. It discusses various types of hypoxia, signs and symptoms, indications for oxygen therapy, and different delivery devices with their respective flow rates and oxygen percentages. Additionally, it highlights nursing responsibilities in monitoring patients receiving oxygen therapy and reinforces the critical principle of never withholding oxygen from those in need.