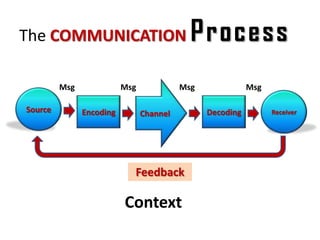
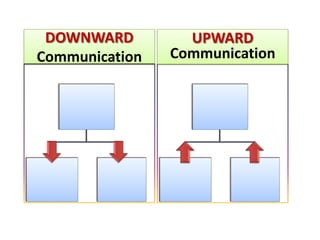
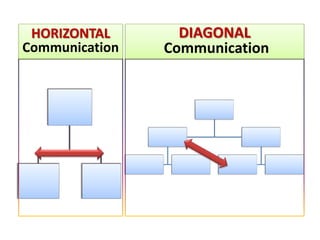
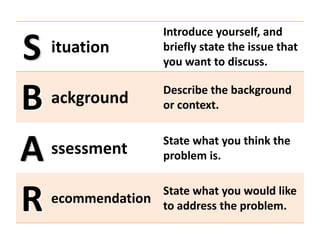
Communication is essential for successful healthcare management. It is defined as the exchange of thoughts, messages, or information through various modes like verbal, non-verbal, written, and electronic. There are different types of communication like interpersonal and organizational. Effective communication requires understanding potential barriers and utilizing strategies like active listening. In healthcare, communication must be timely, accurate, unambiguous and understood to prevent errors and ensure patient safety. Managers should assess communication and use clear, simple messaging through multiple channels.