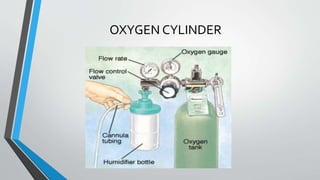
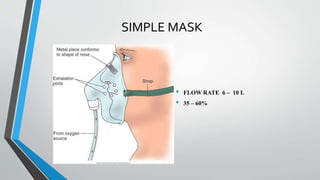
Oxygen therapy involves administering supplemental oxygen to patients who are unable to absorb sufficient oxygen due to various health conditions. Key methods of delivery include simple masks, nasal cannulas, and oxygen tents, each with specific flow rates and indications. Safety protocols must be followed, including risk assessments and the management of equipment to ensure patient safety during therapy.