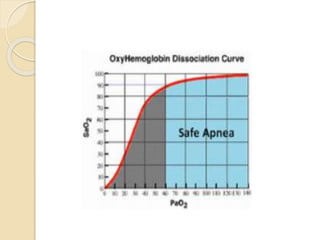
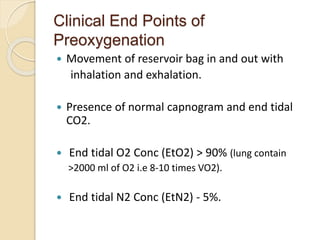
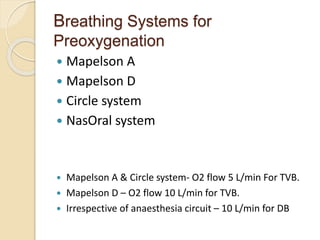
This document discusses preoxygenation and apneic oxygenation techniques. It defines preoxygenation as administering oxygen prior to anesthesia induction to increase oxygen reserves and prolong safe apnea time. Effective preoxygenation requires achieving near 100% oxygen saturation through tidal volume breathing or deep breathing. Apneic oxygenation can further extend safe apnea time by allowing oxygen diffusion during apnea. The document describes several methods of apneic oxygenation including nasal prongs, nasopharyngeal catheters, and THRIVE which uses high flow humidified nasal cannula. Key points emphasize preoxygenation as a safety measure and the effectiveness of tidal volume breathing for preoxygenation.