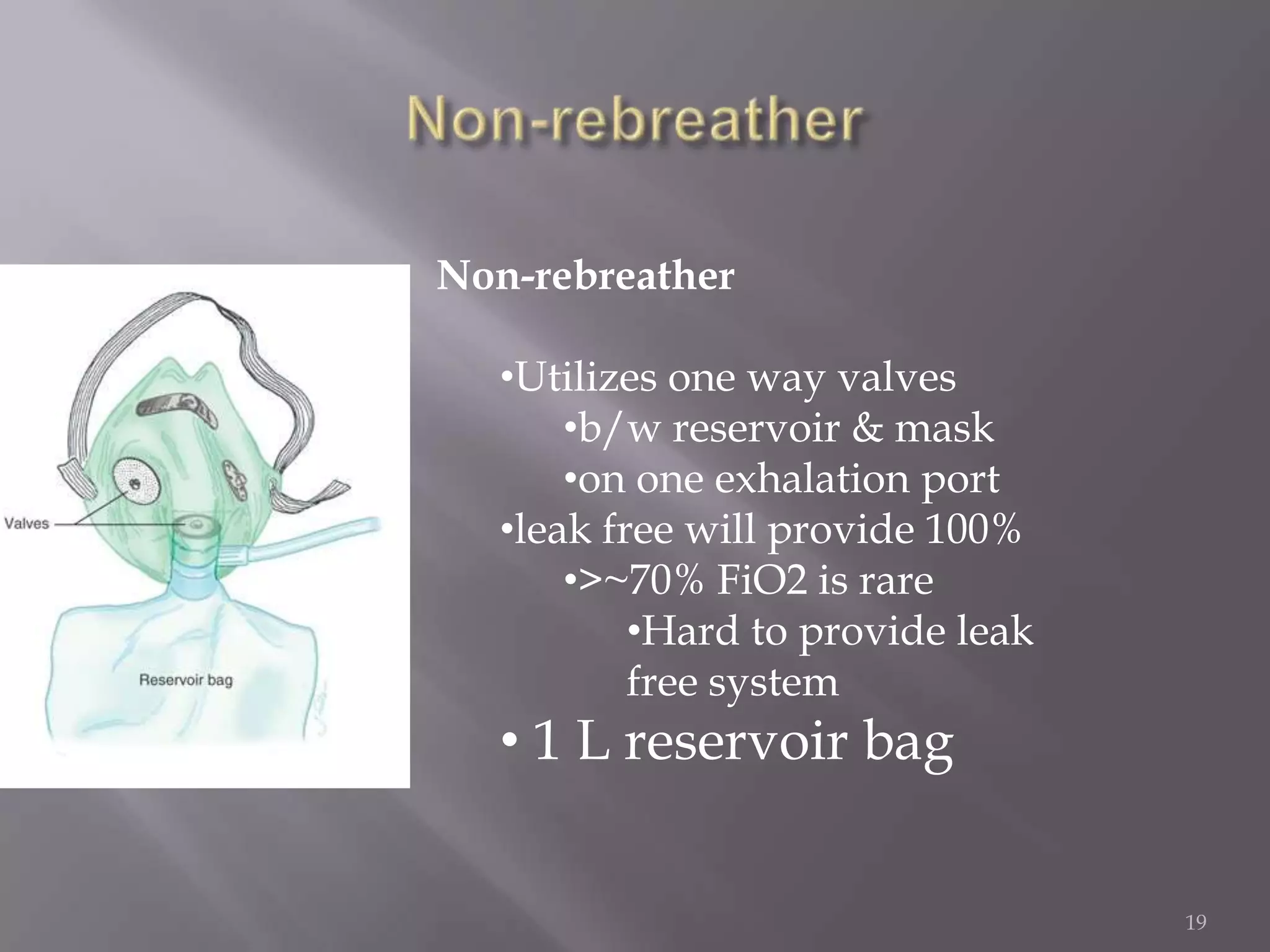
This document discusses oxygen therapy, including its goals of correcting hypoxemia, reducing symptoms, and minimizing workload on the cardiopulmonary system. It describes various oxygen delivery devices like nasal cannulas, masks, and high flow devices. Special considerations are given for COPD patients to avoid depressing ventilation. The key is to carefully assess each patient's needs and monitor their response to oxygen therapy.