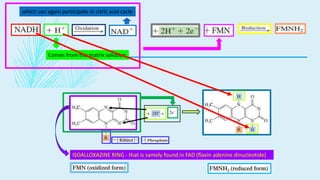
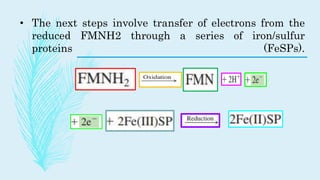
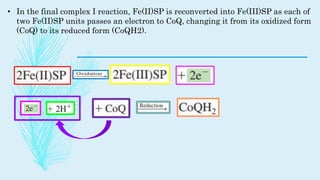
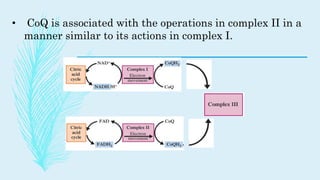
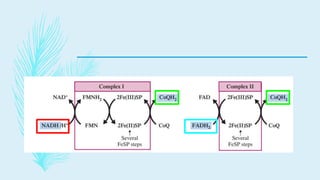
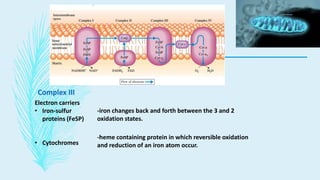
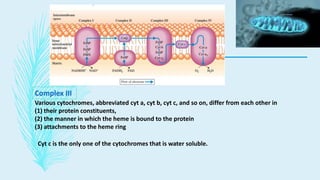
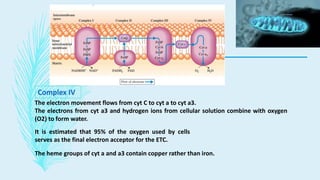
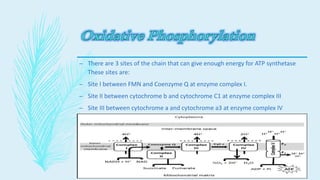
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttle electrons from electron carriers to oxygen. As electrons are passed through four protein complexes, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, generating an electrochemical gradient. ATP synthase harnesses this proton gradient to phosphorylate ADP, producing the majority of a cell's ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The ETC and oxidative phosphorylation are essential metabolic pathways that generate energy to power cellular functions.