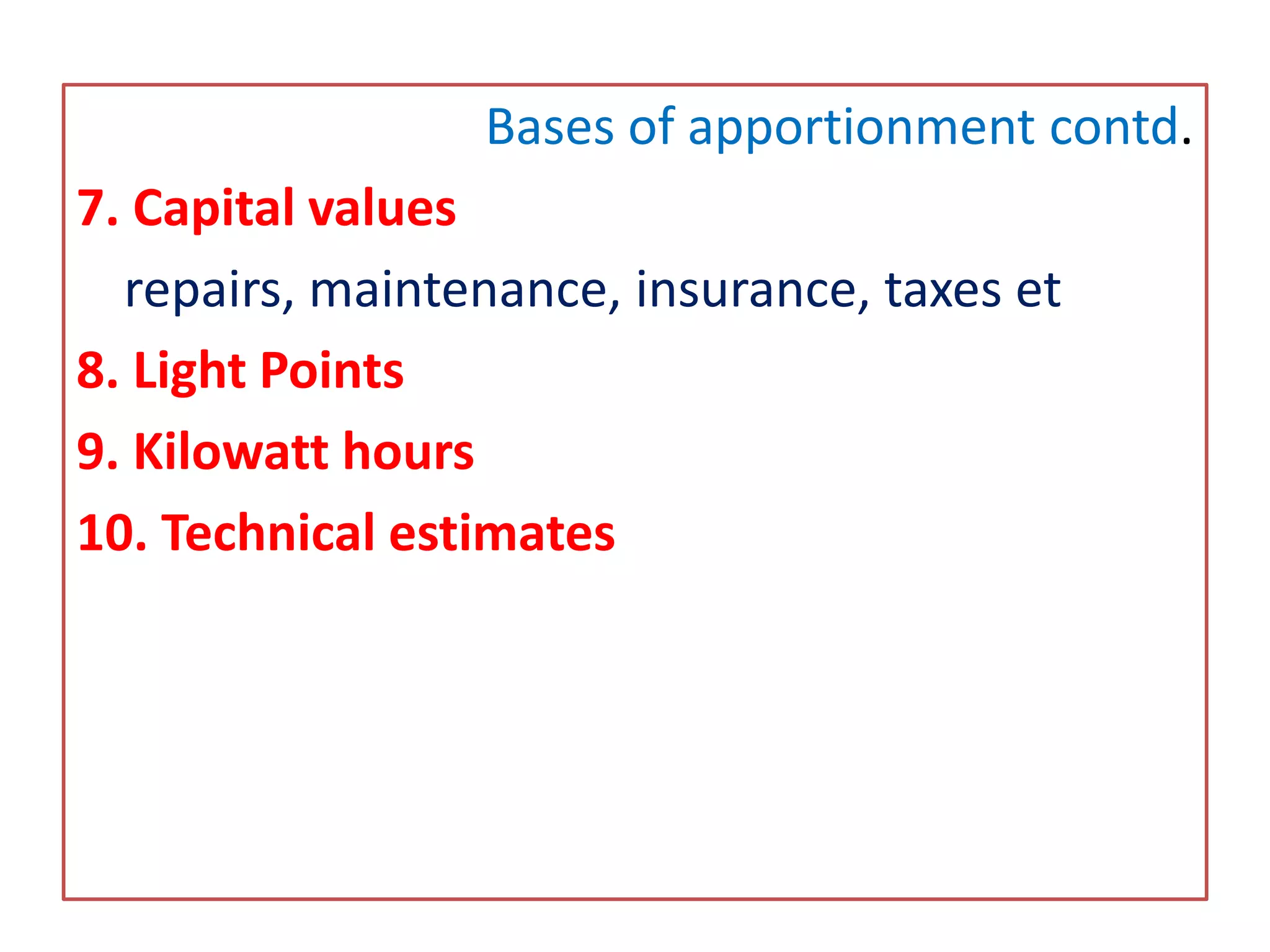
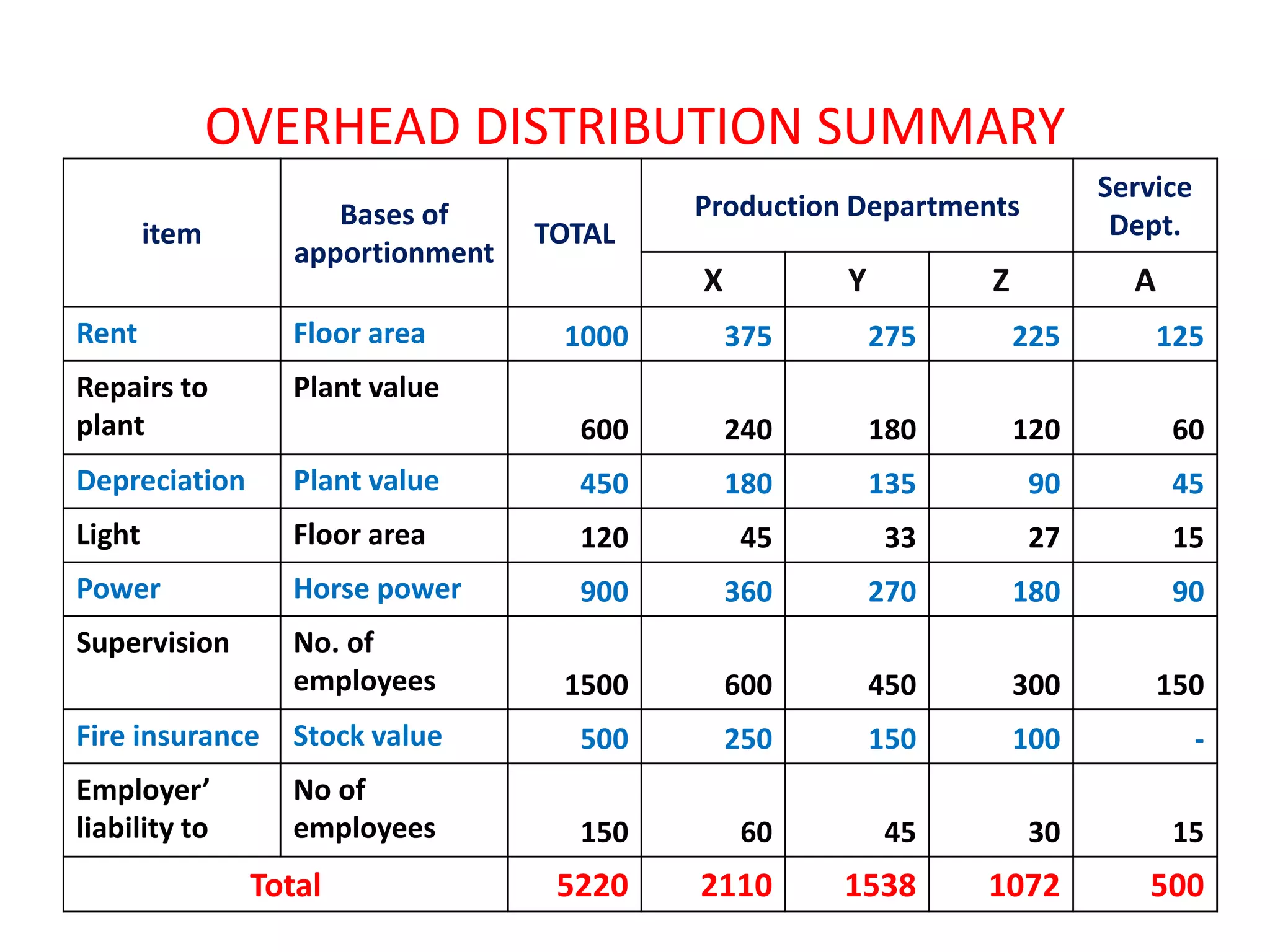
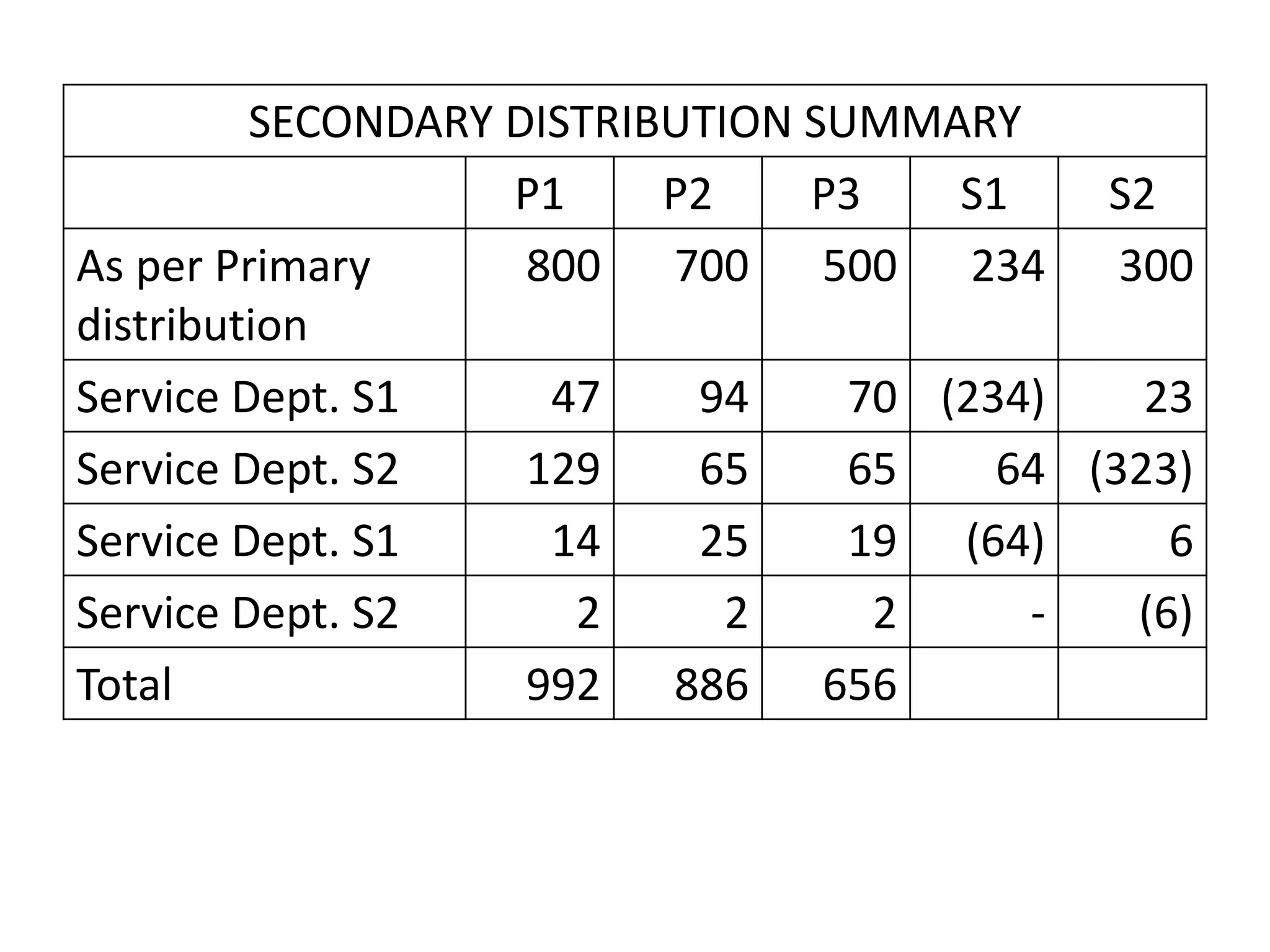
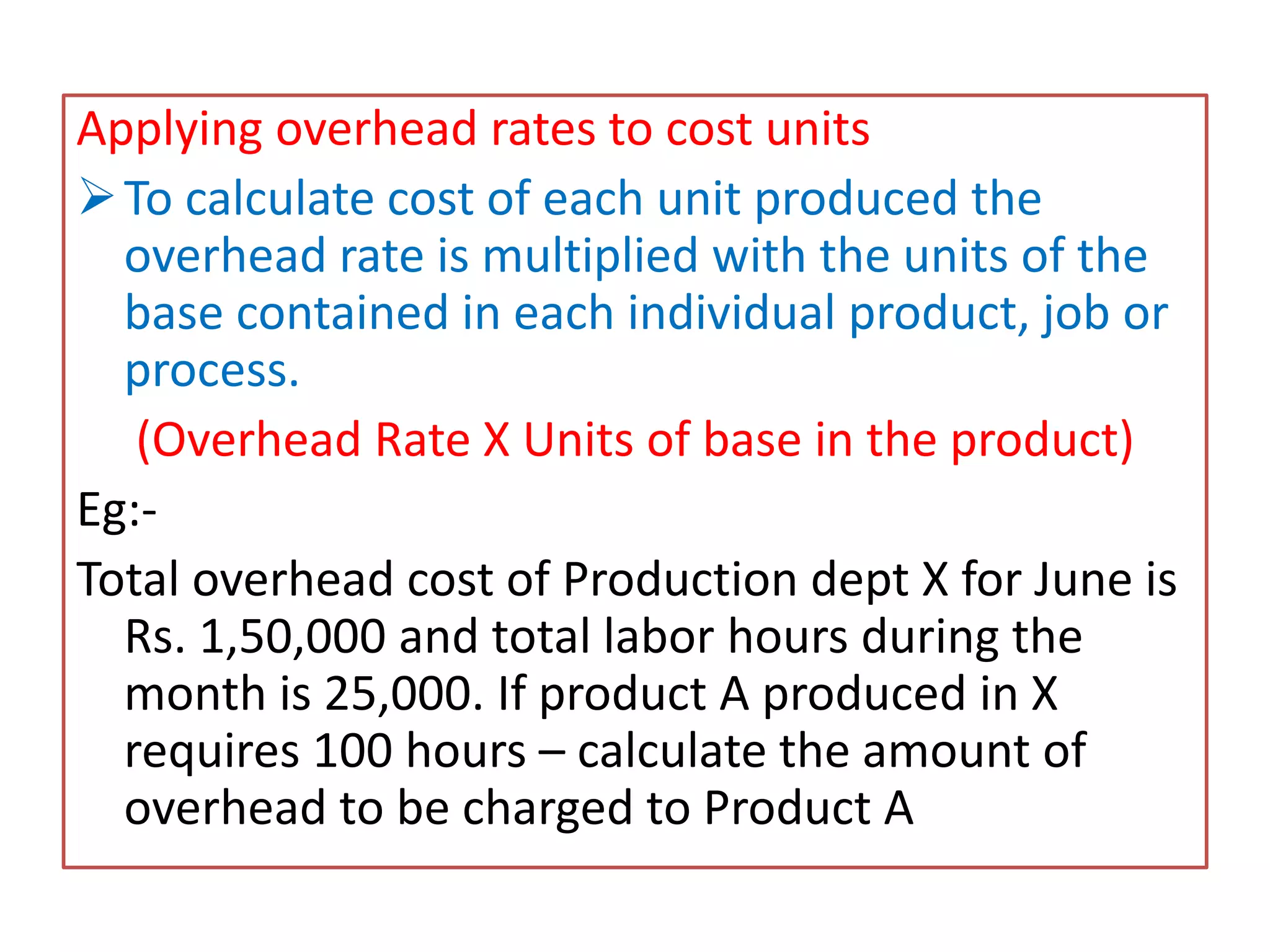
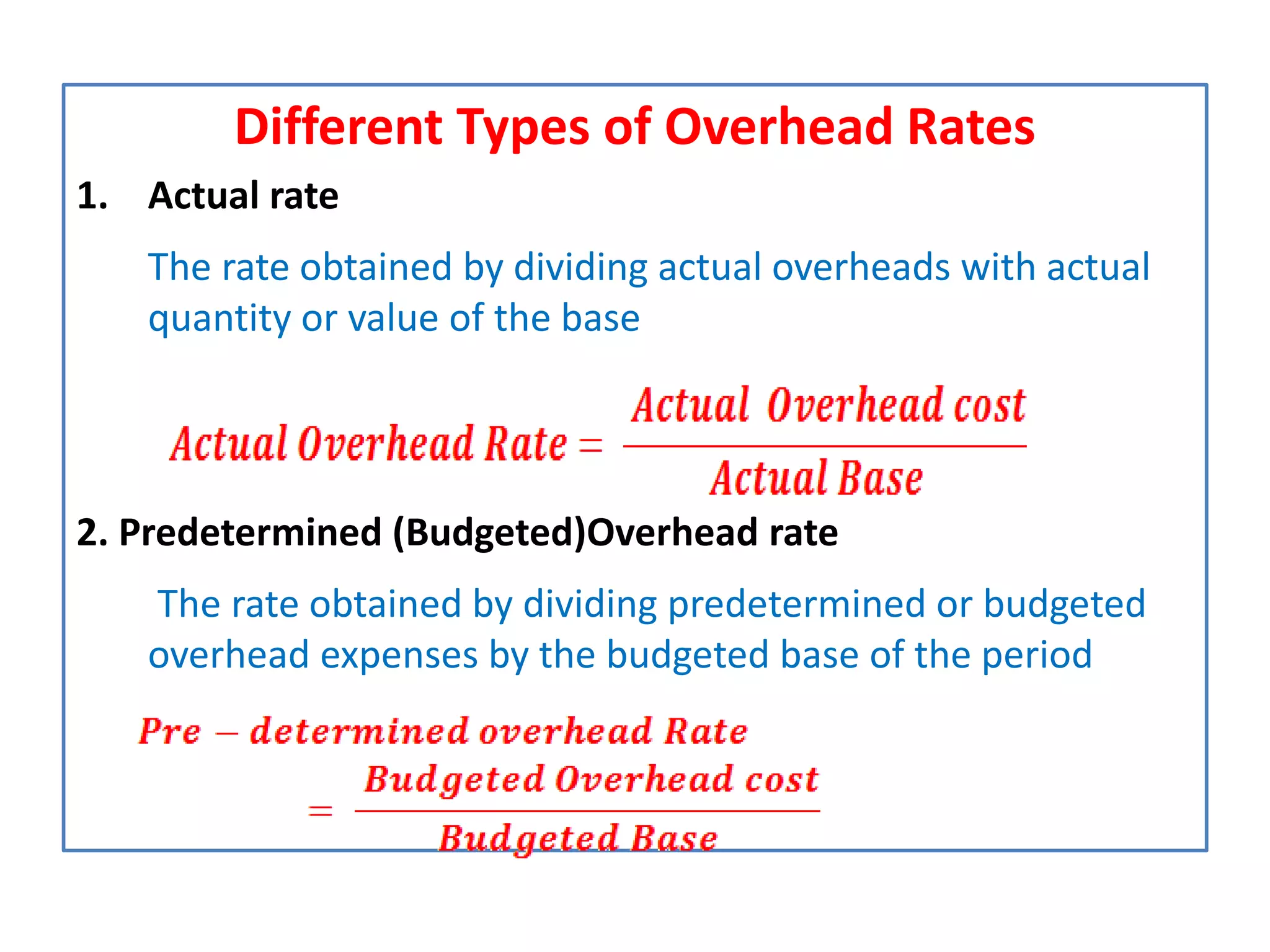
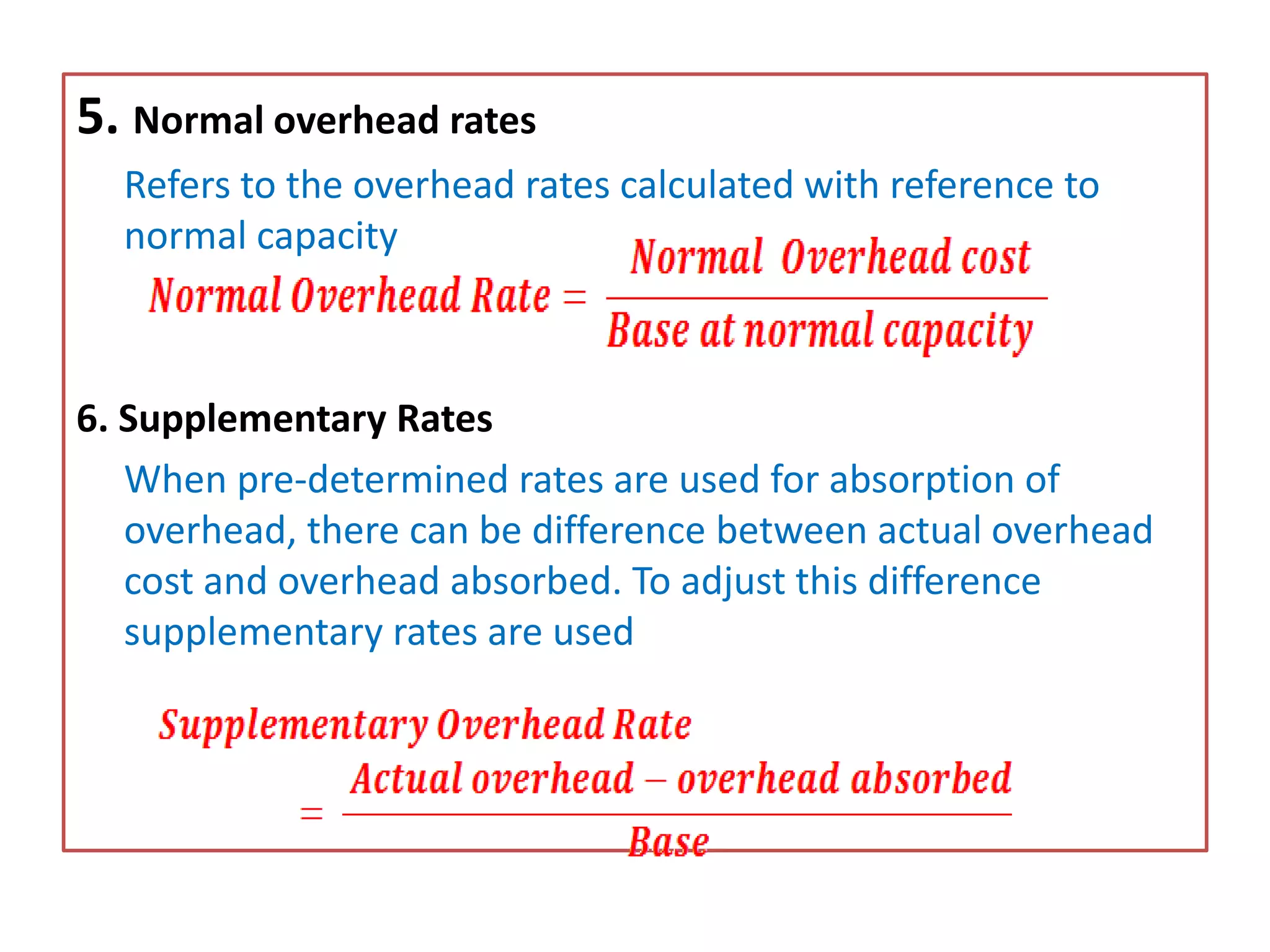
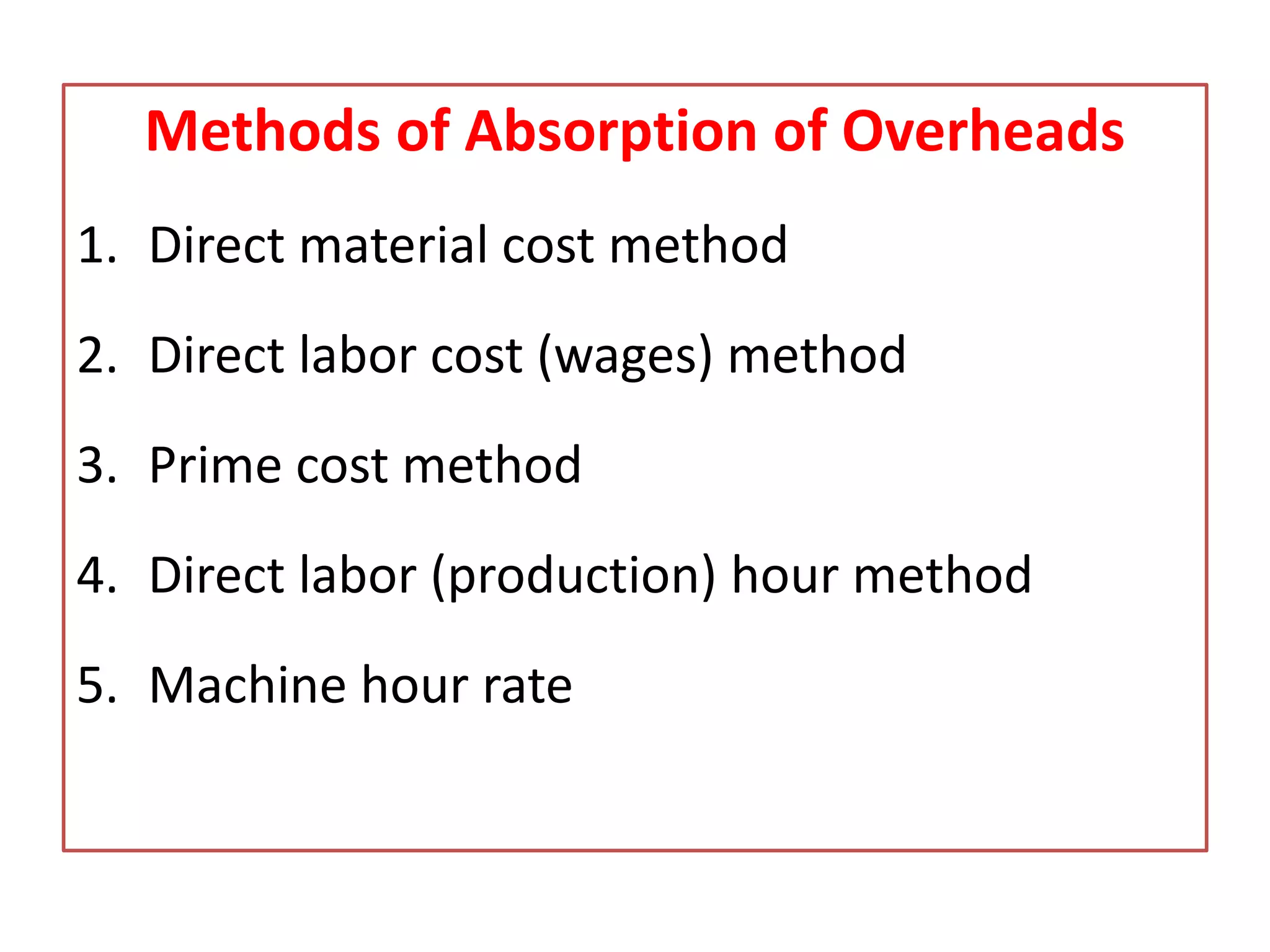
This document discusses overhead costs and their accounting treatment. It defines overheads as indirect costs that cannot be directly attributed to a specific cost object. The document outlines the key steps in overhead accounting: classification of overheads, codification and collection, allocation and apportionment to cost centers, and absorption into product costs. It provides examples of different bases for classifying, allocating, and apportioning overheads. The document also discusses reapportioning service department costs to production departments through various secondary distribution methods like repeated distribution and trial and error.