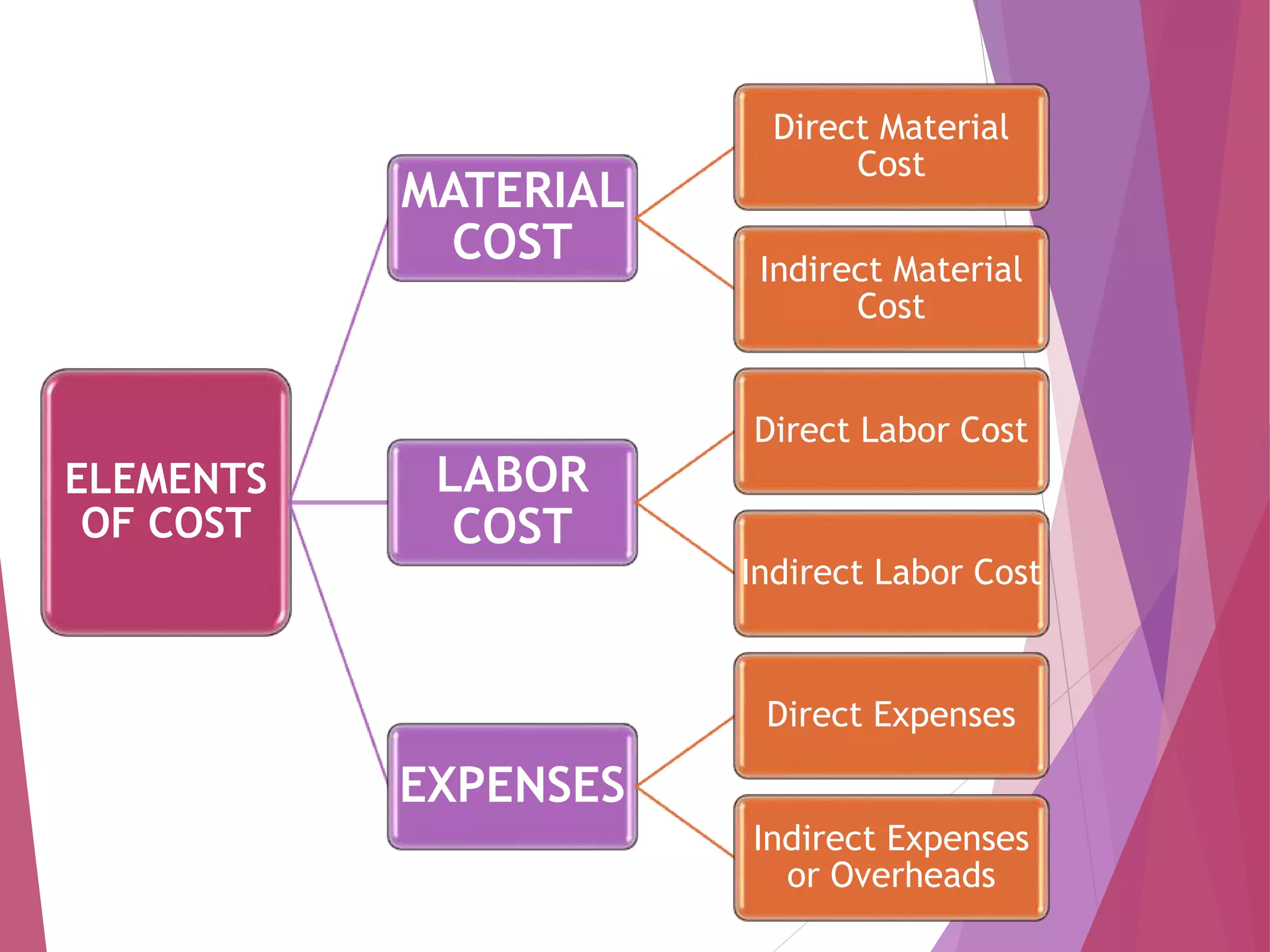
The elements of cost include material cost, labor cost, and expenses. Material cost refers to the cost of materials used in production and includes direct material costs which can be traced to a product and indirect material costs which cannot. Labor cost is the cost of employee wages and salaries, including direct labor costs of employees involved in production and indirect labor costs of support staff. Expenses include direct expenses which can be associated with a product and indirect expenses or overheads which cannot, such as factory overhead, administrative overhead, and selling/distribution overhead. Understanding the elements of cost facilitates cost analysis and provides manufacturers with cost information.