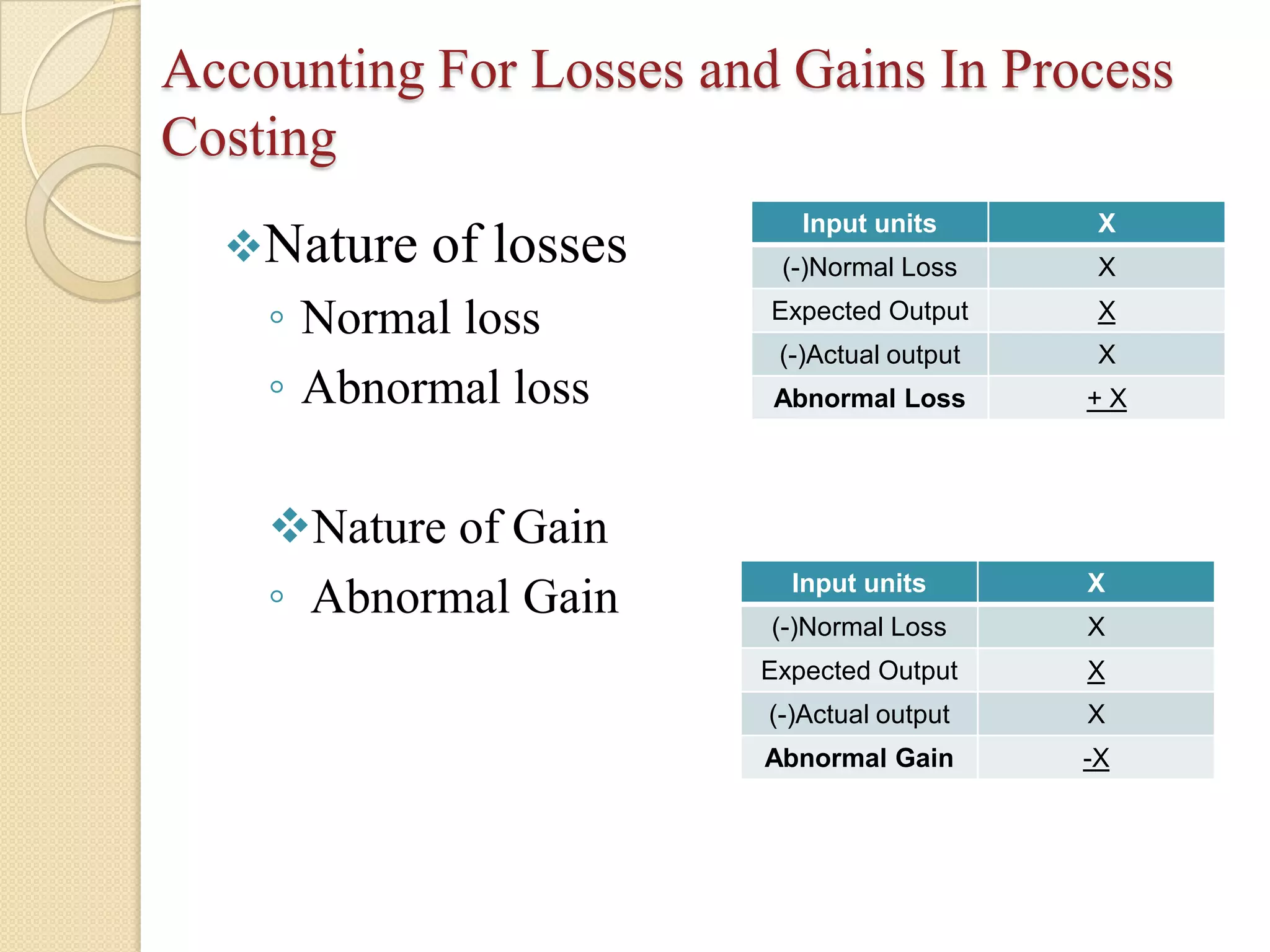
Process costing is a method used in manufacturing to allocate costs to products through a series of defined processes. Each process has its own account where inputs, expenses, and outputs are tracked, with losses and gains managed accordingly. This system is essential for determining average costs per unit and supports effective pricing strategies in a competitive market.