- Cost accounting is used to estimate product costs, calculate work-in-progress costs, and control costs by comparing actual and estimated costs.
- There are three elements of cost: direct materials, direct labor, and other expenses which can be direct or indirect.
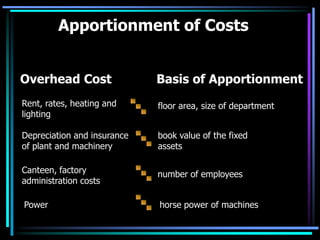
- Costs are traced to cost centers, which are areas responsible for costs like manufacturing departments. Costs are allocated directly to cost centers or apportioned using bases like floor space.
- Overhead costs are apportioned to cost centers and then absorbed into total product costs using bases like direct labor hours to determine absorption rates.