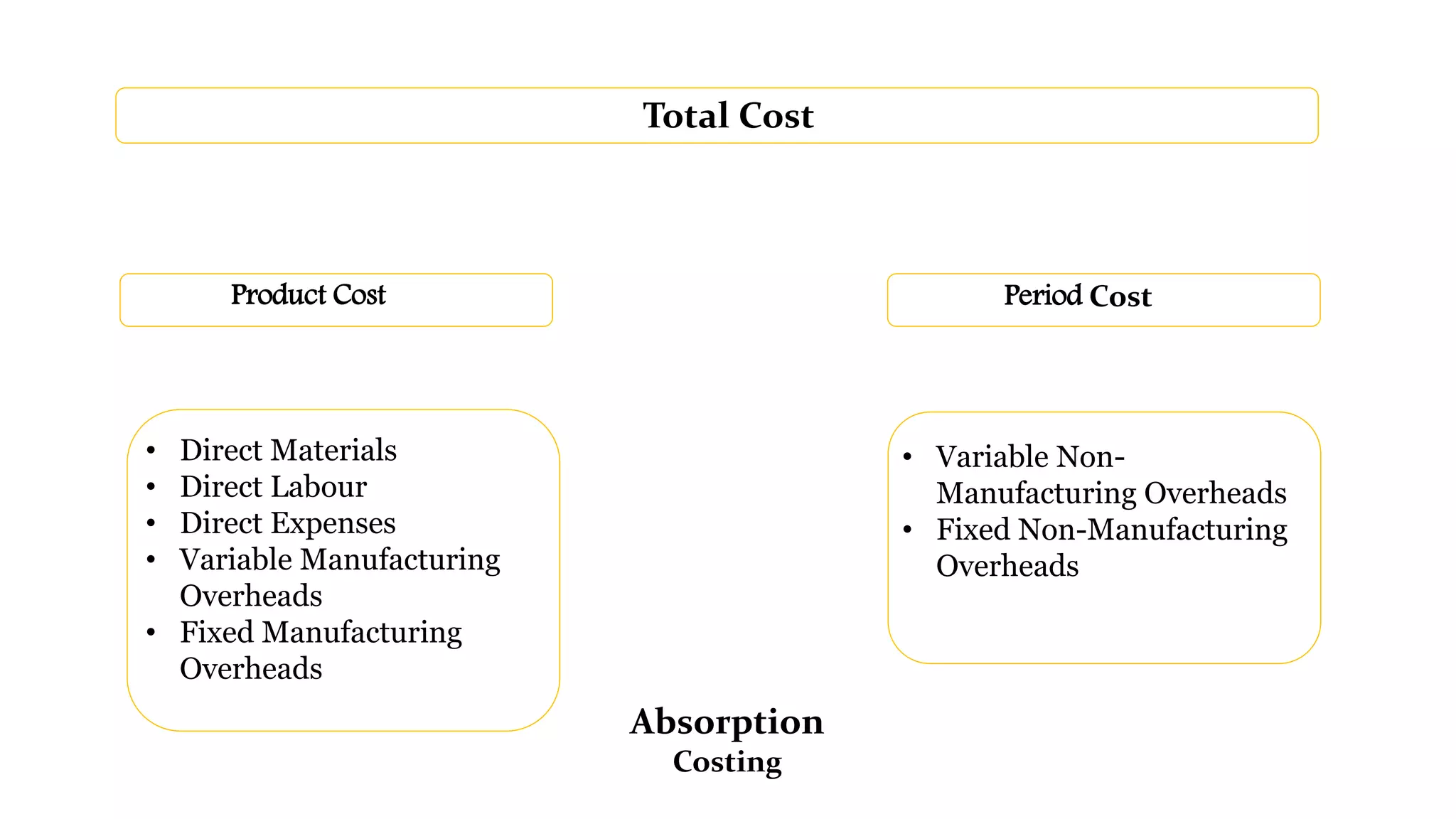
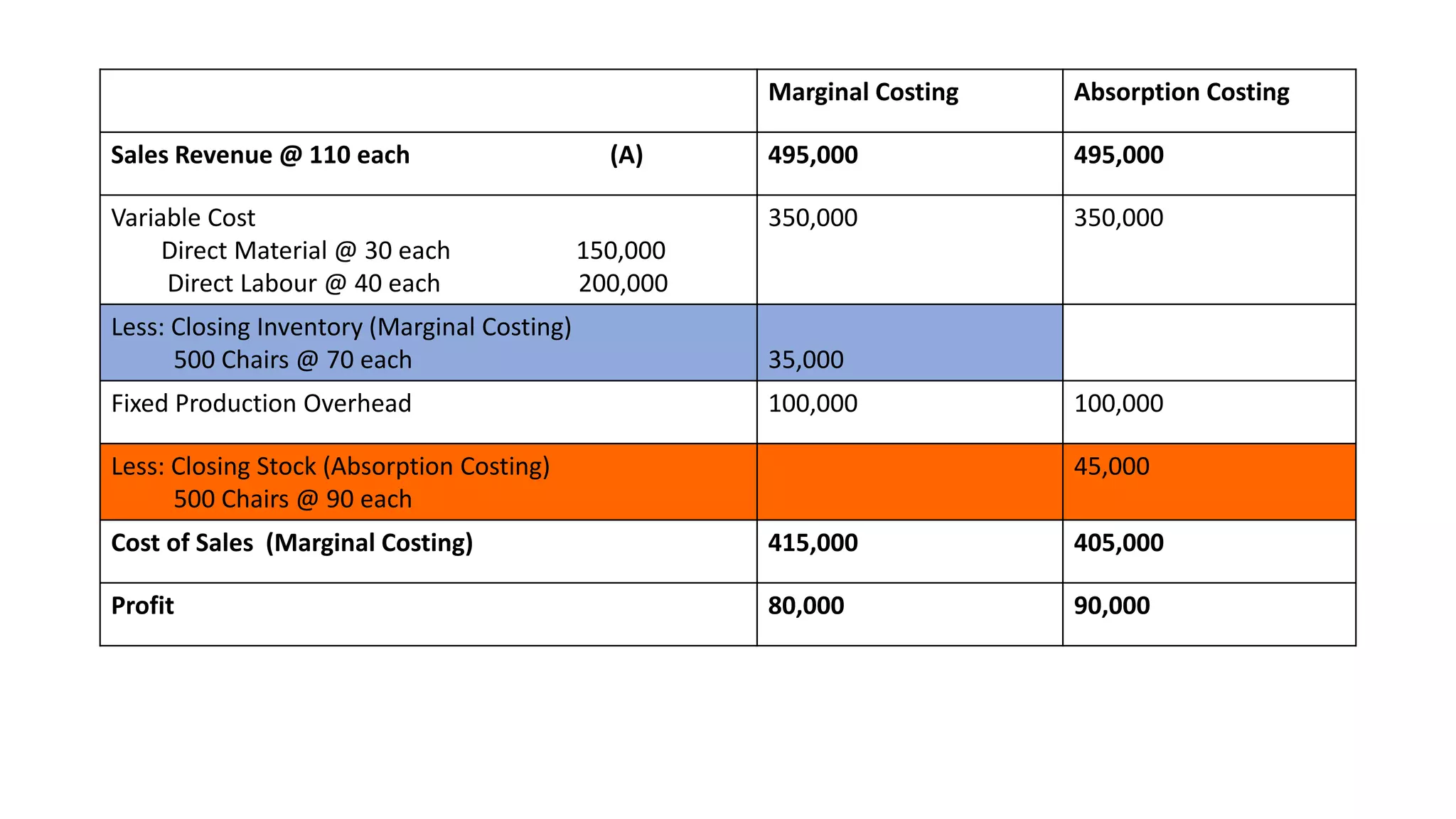
The document explains absorption costing and its distinction from marginal costing, detailing the classification of costs involved in manufacturing. It discusses various cost types such as fixed, variable, direct, indirect, and product costs, and presents an example from Sahani Limited's first year of trading, comparing profit statements derived from both costing methods. Additionally, it highlights advantages of absorption costing, such as effective stock valuation and pricing policy.