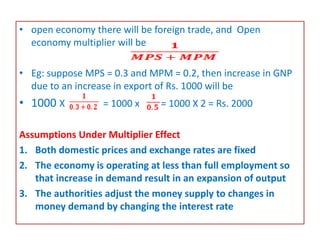
This document discusses open versus closed economies. An open economy is one where exports and imports make up a major share of GDP and there are few trade restrictions. A closed economy has limited international trade. As exports increase in an open economy, national income and employment also increase due to multiplier effects. However, the size of the multiplier depends on factors like marginal propensity to save and import. The national income identity for an open economy accounts for exports, imports, domestic investment and foreign investment.