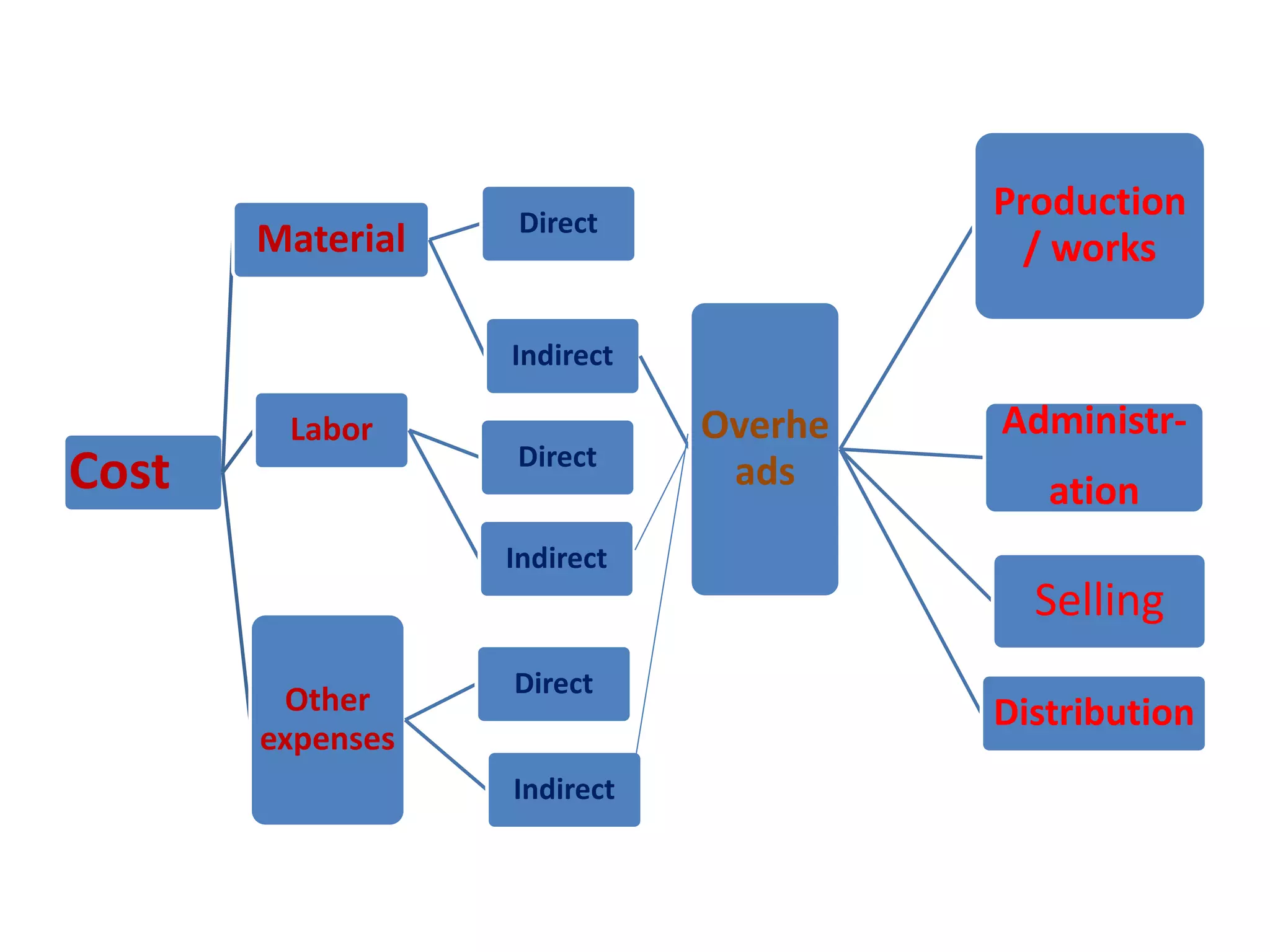
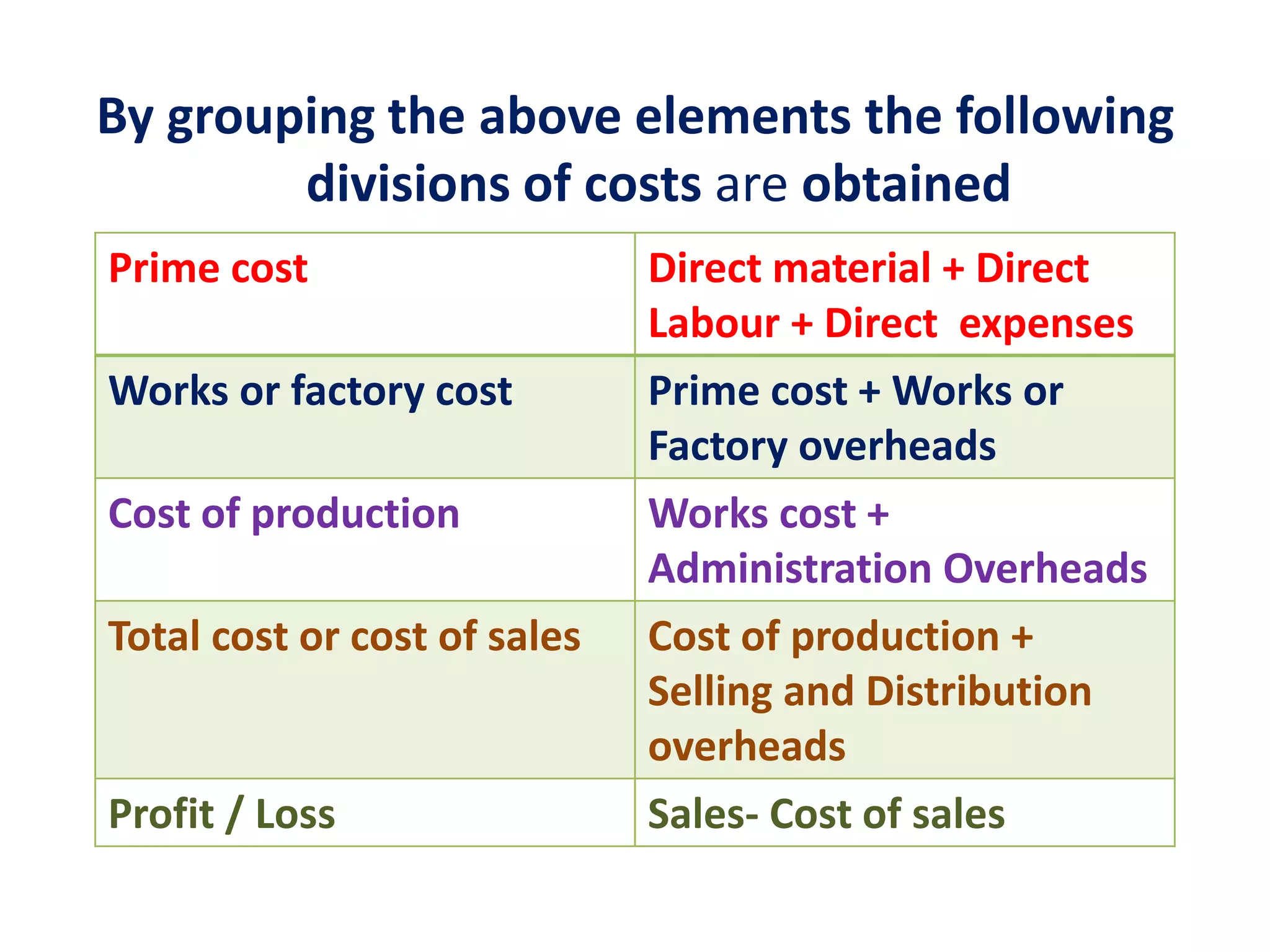
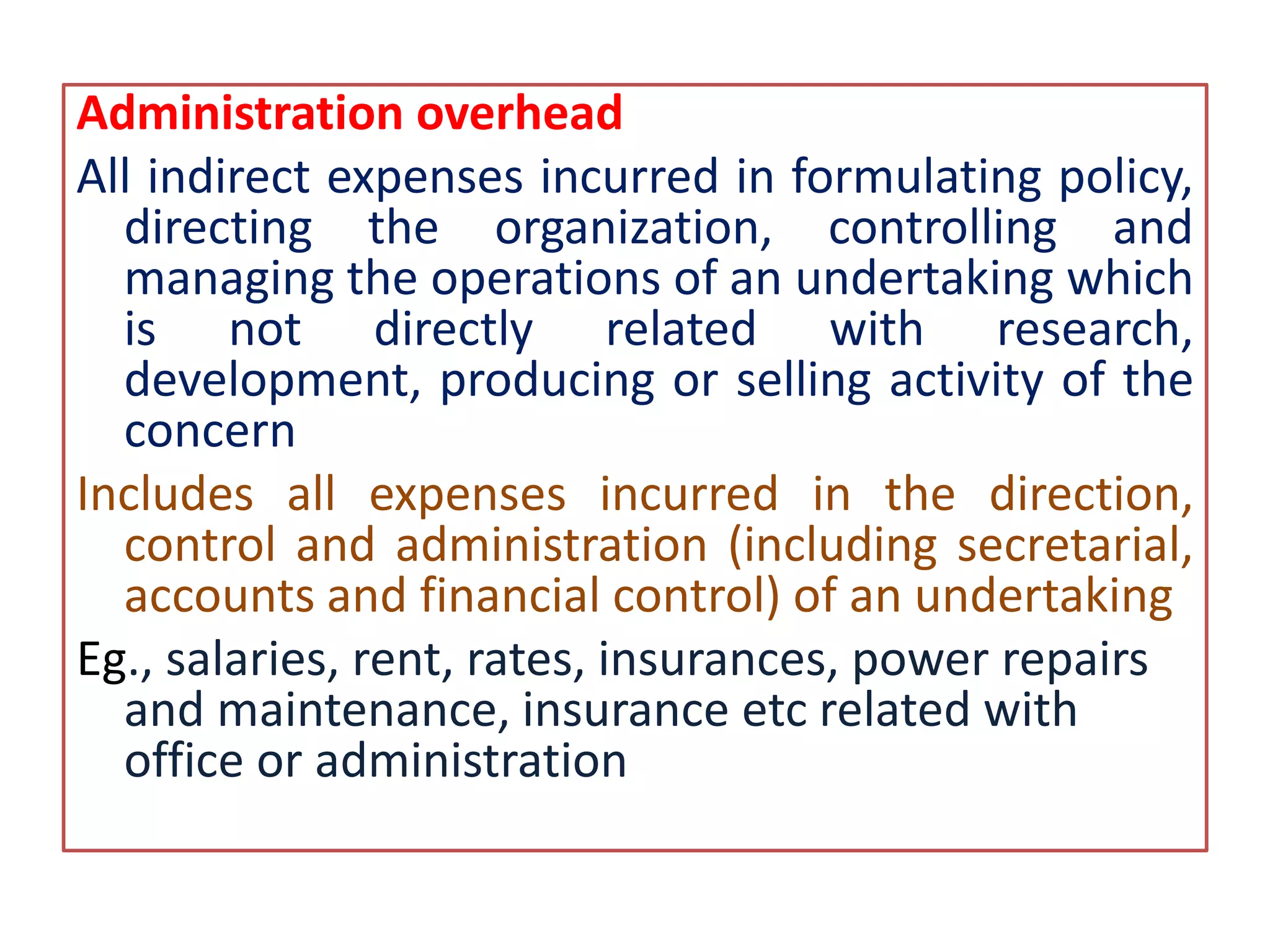
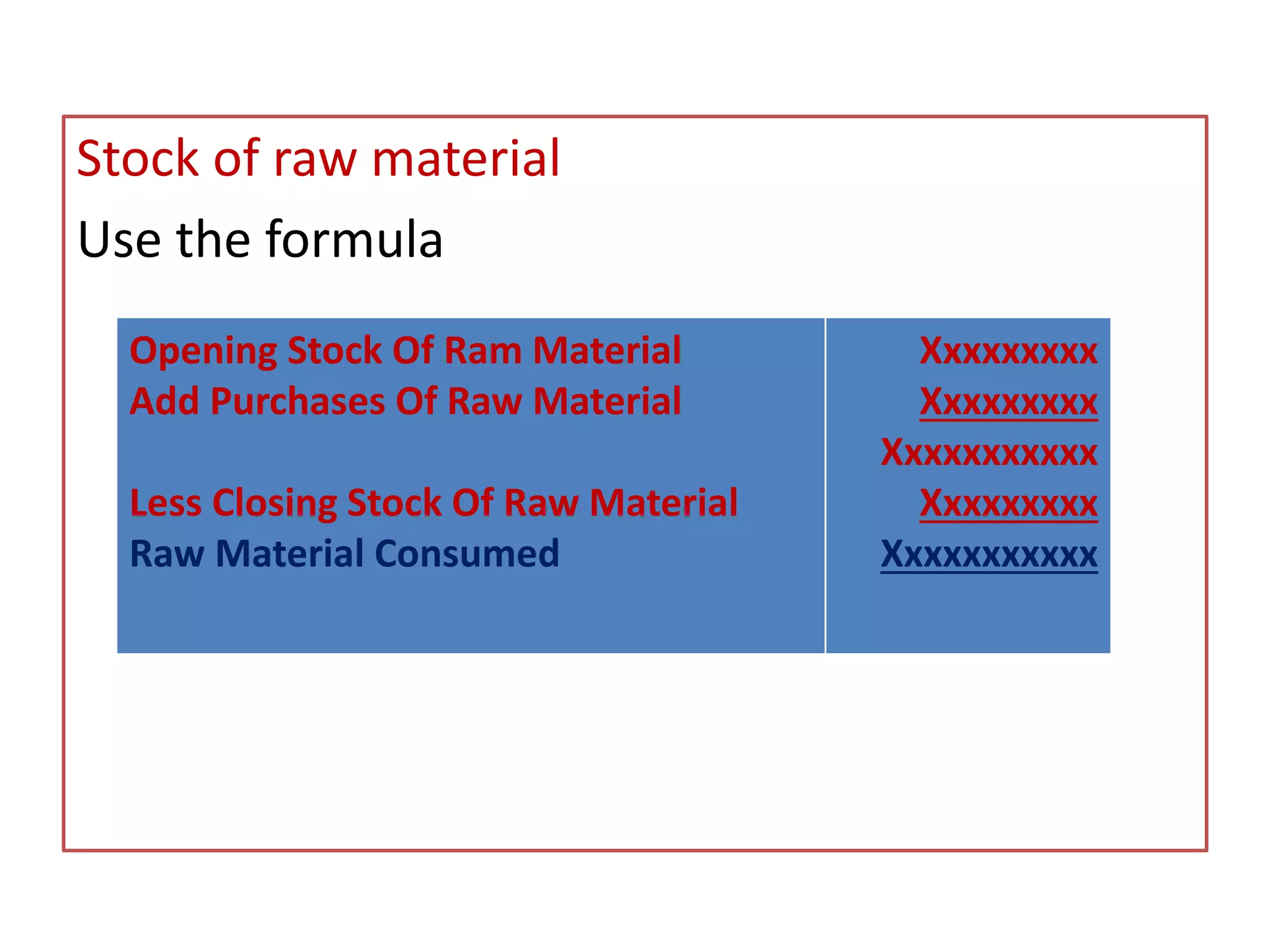
The document outlines the elements of cost in production, detailing the categories such as direct materials, direct labor, and various overheads. It classifies costs into manufacturing, administration, and selling and distribution overheads, emphasizing the importance of accurate cost accounting to control and minimize production costs. Additionally, it discusses the structure of a cost sheet, its purposes, and how to prepare it while considering factors like stock valuation.