Embed presentation













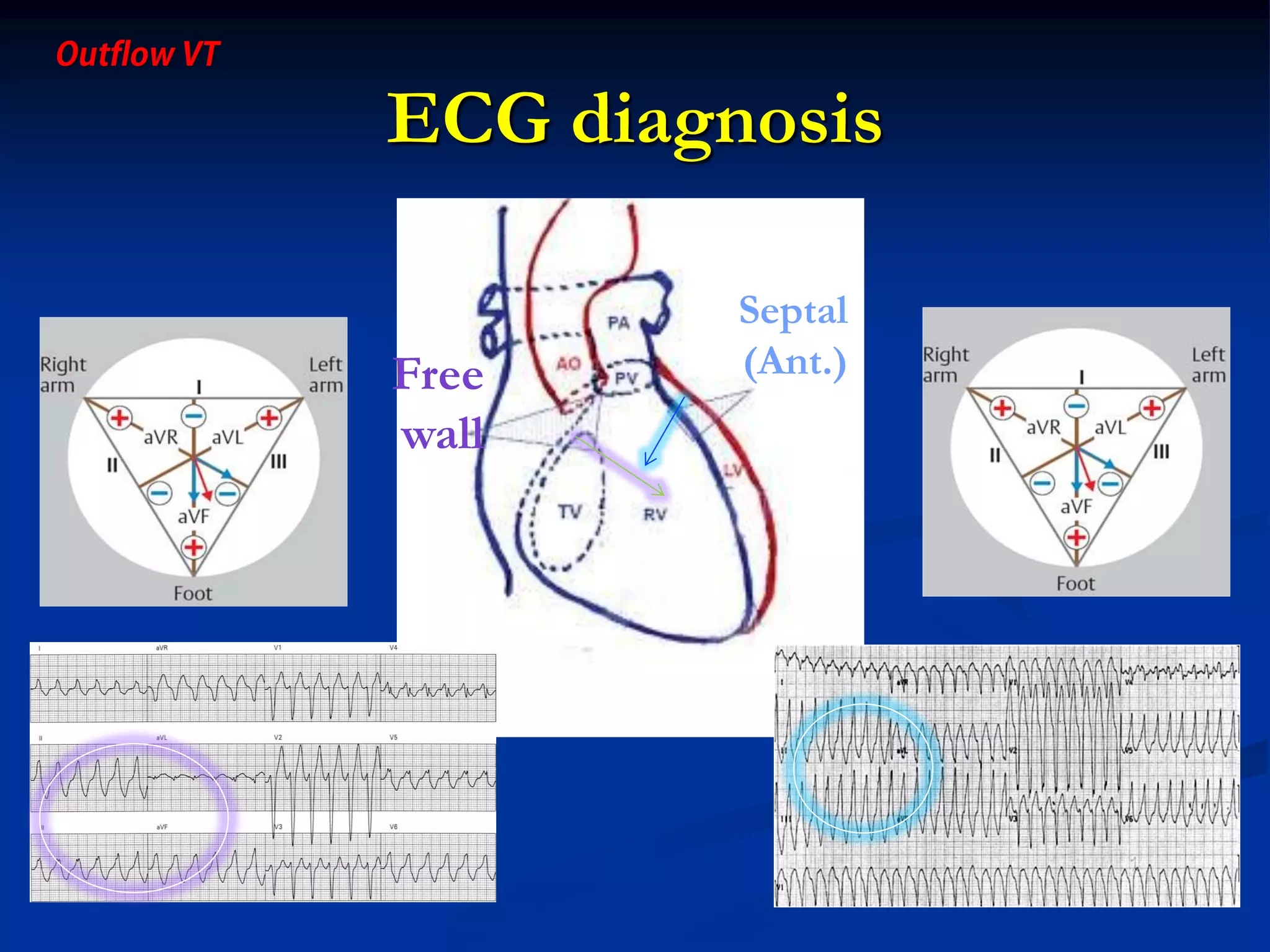
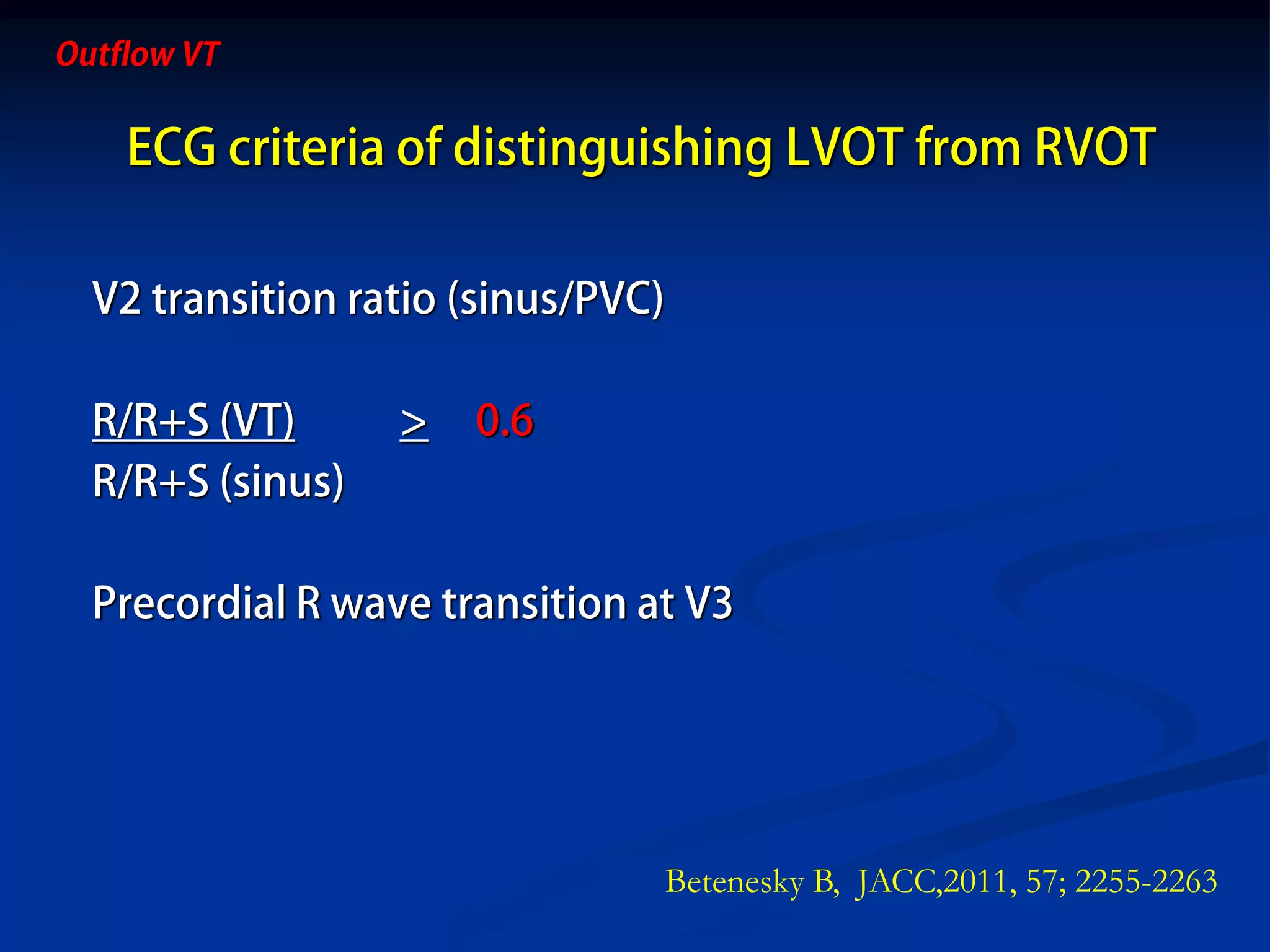

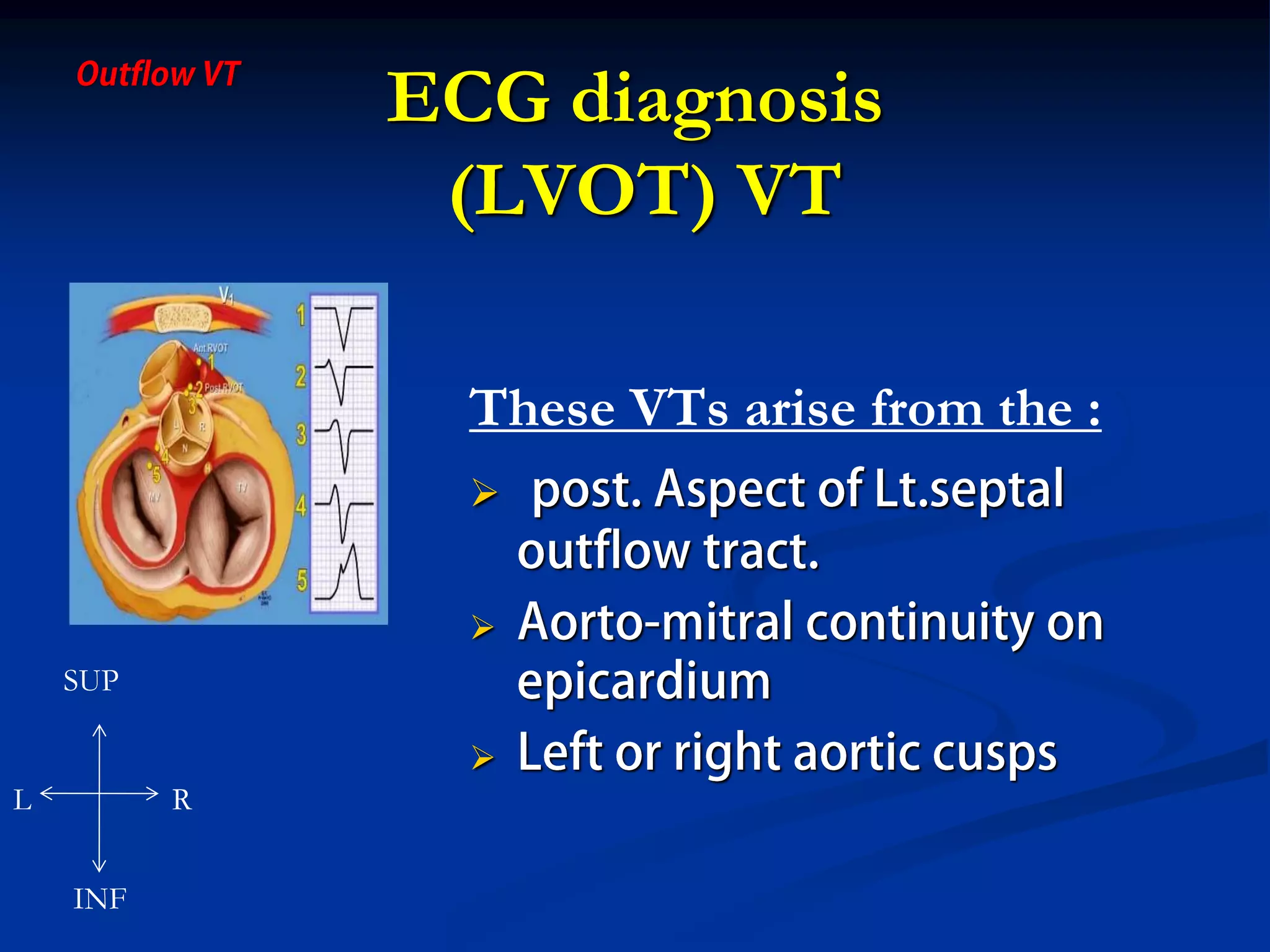
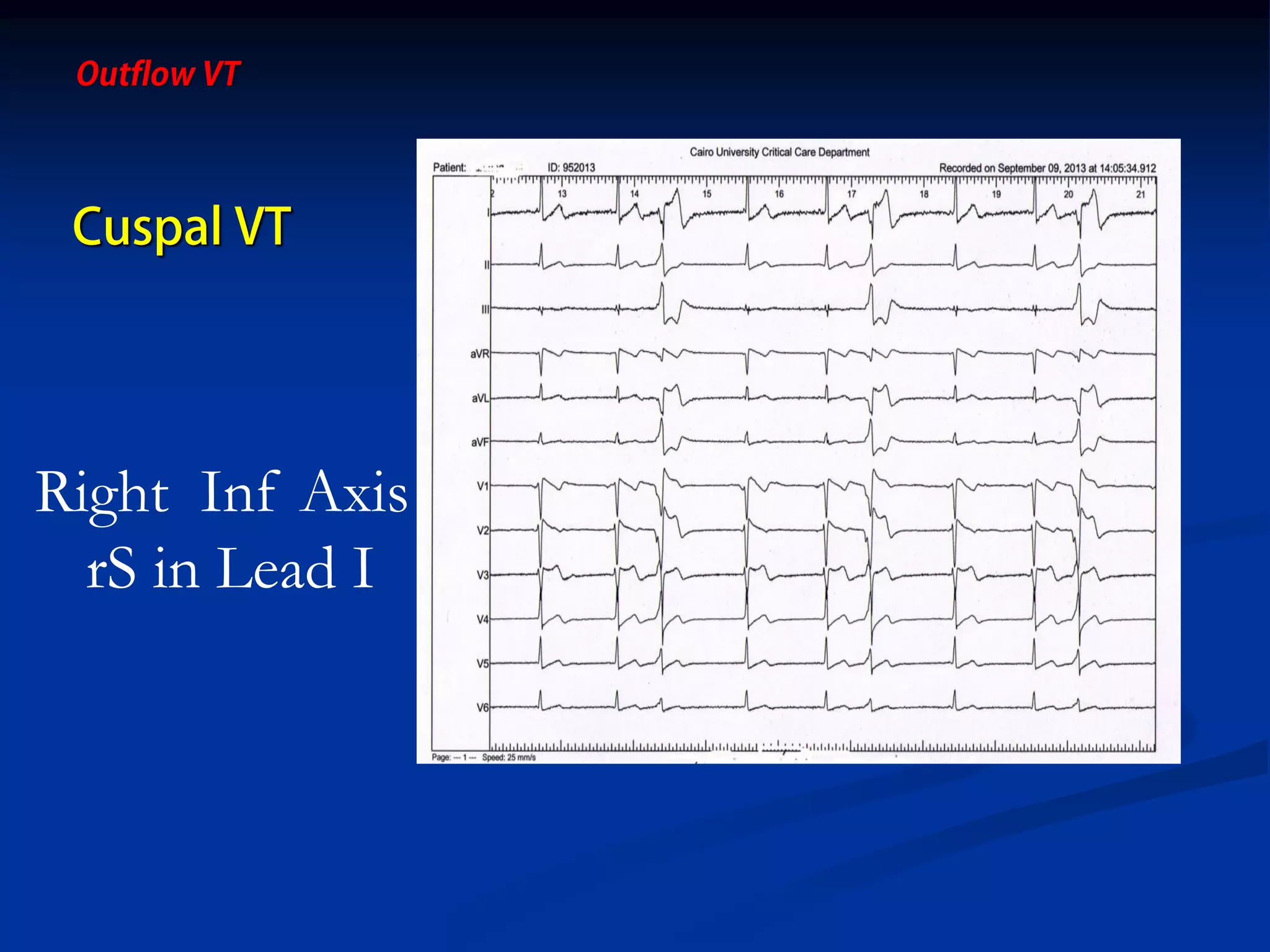


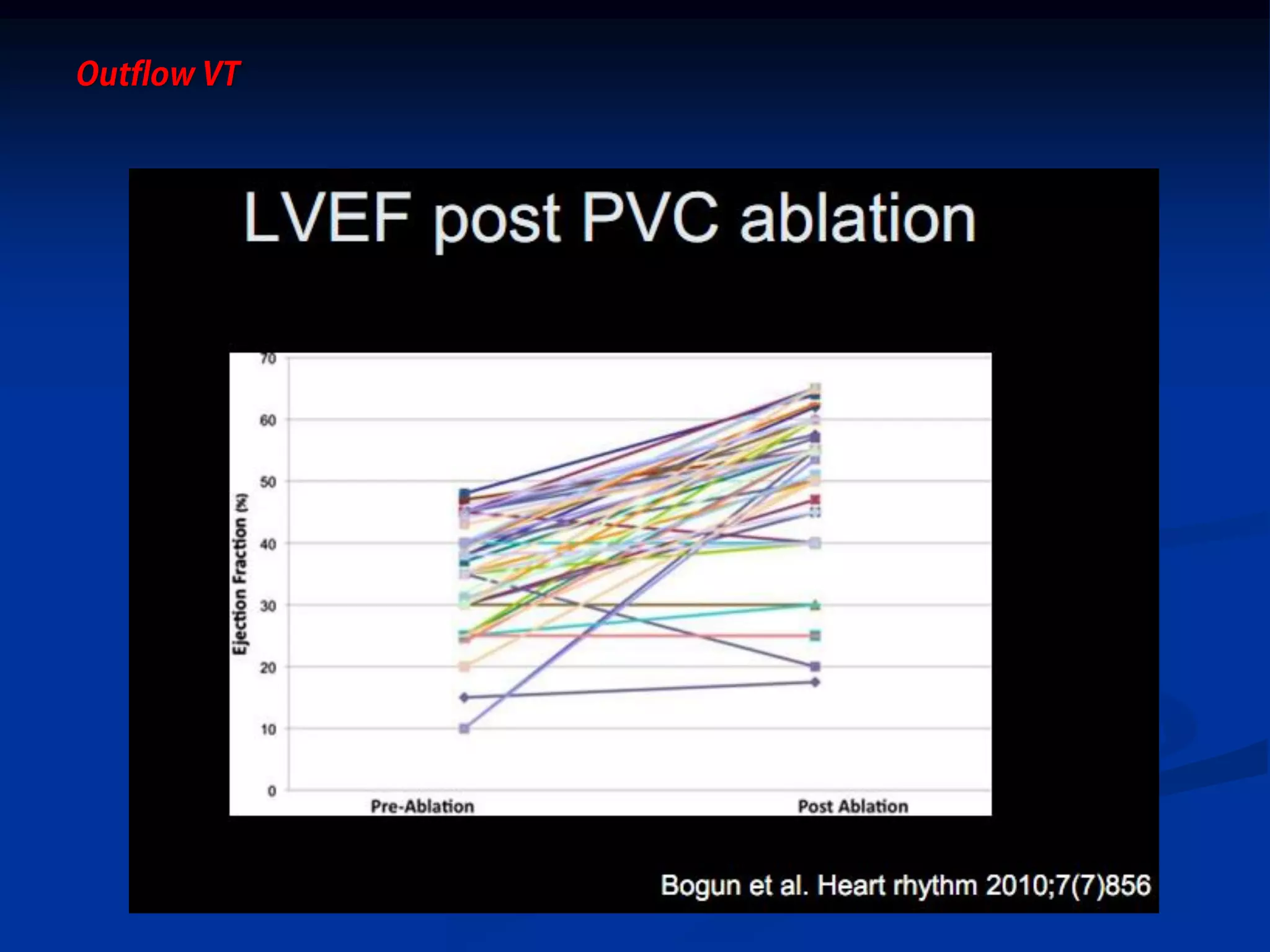
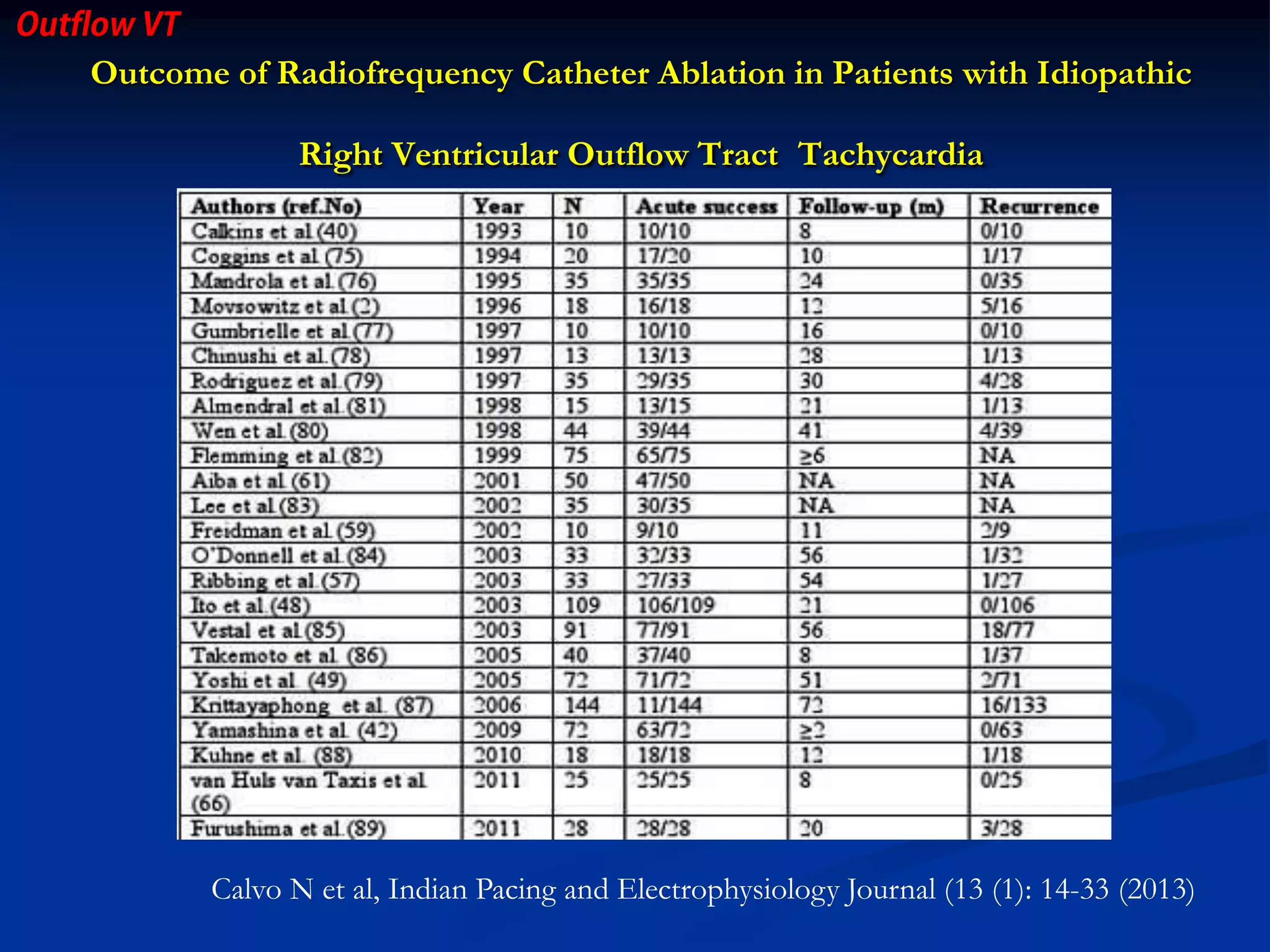




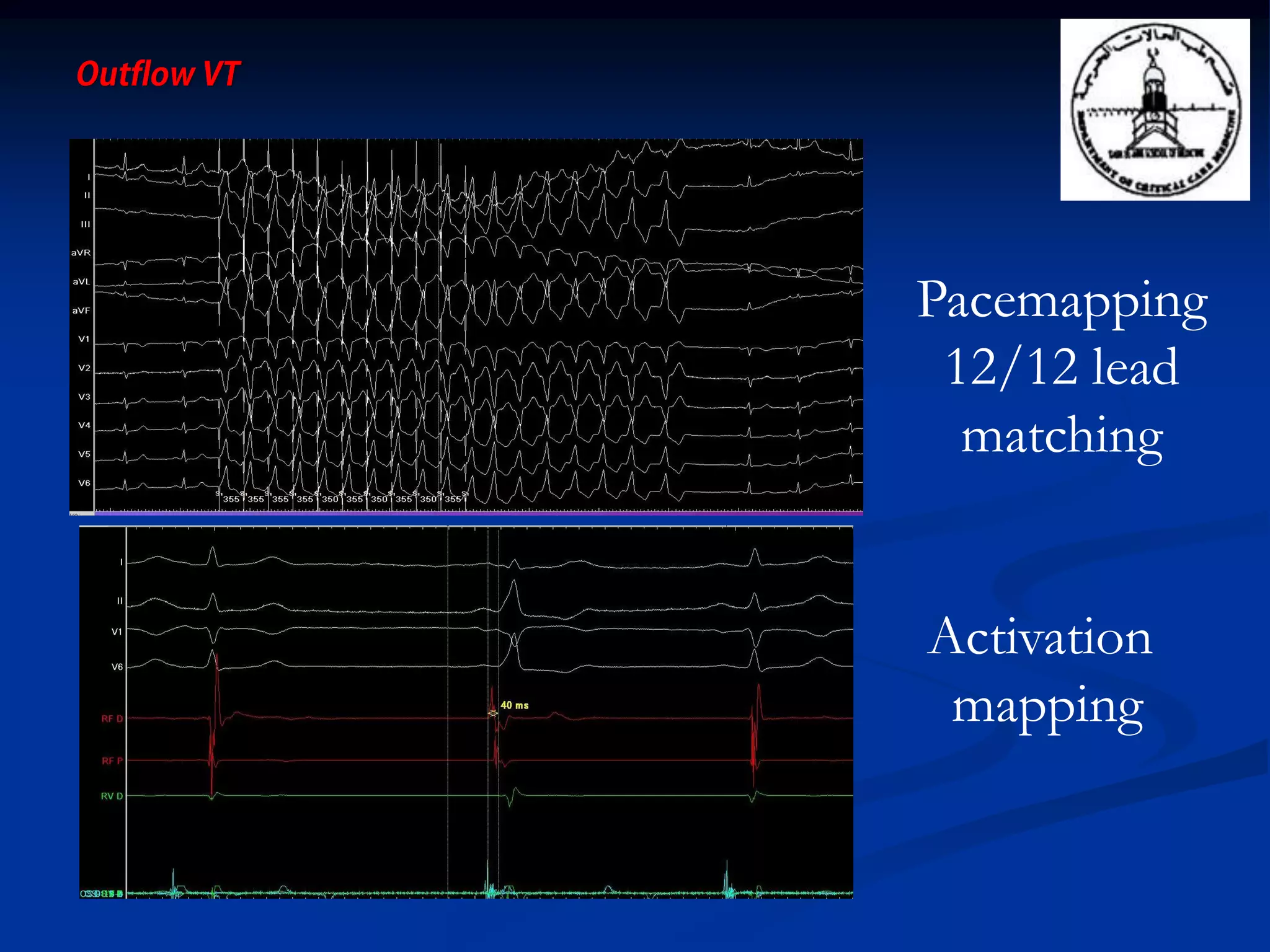





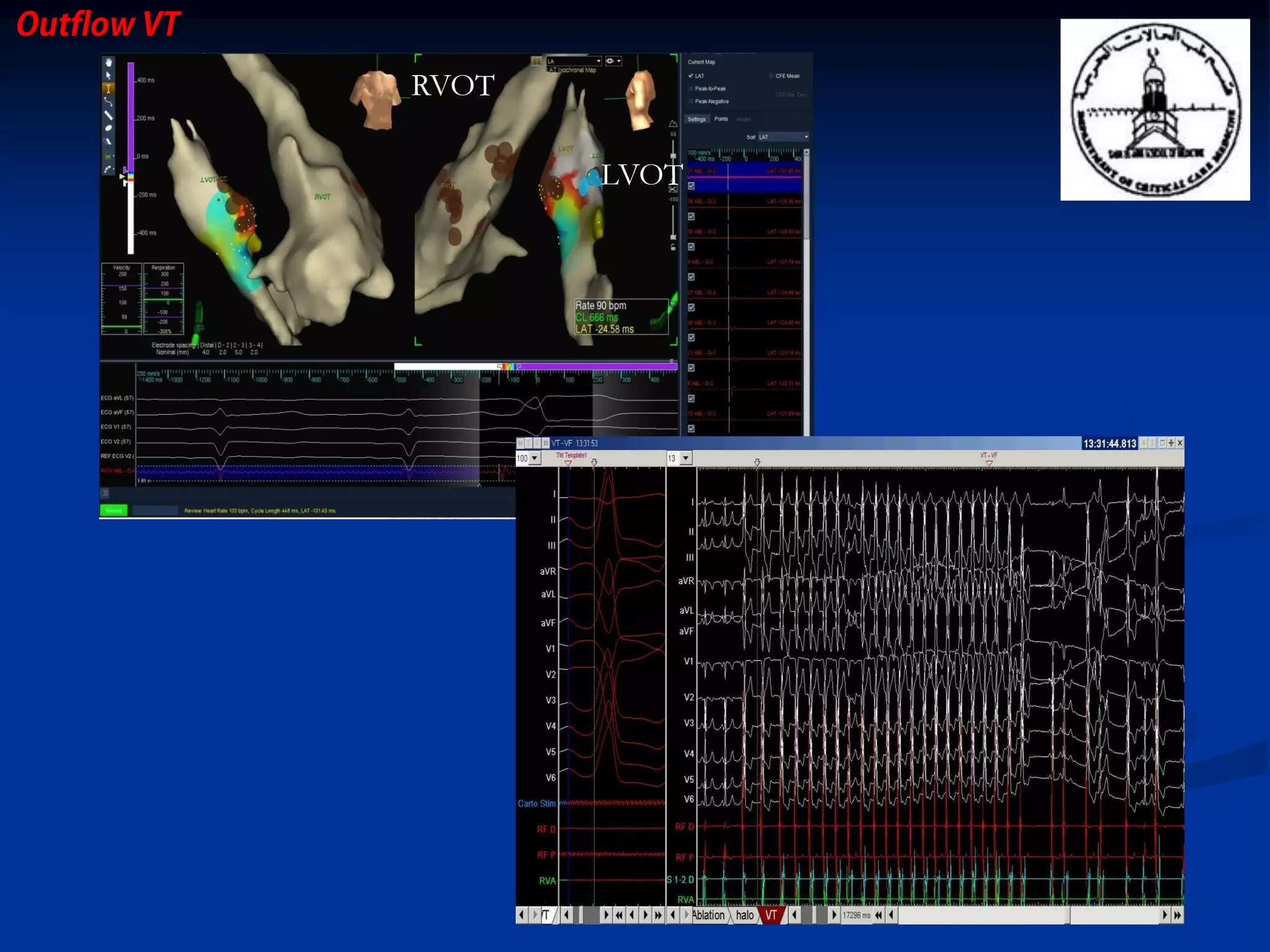

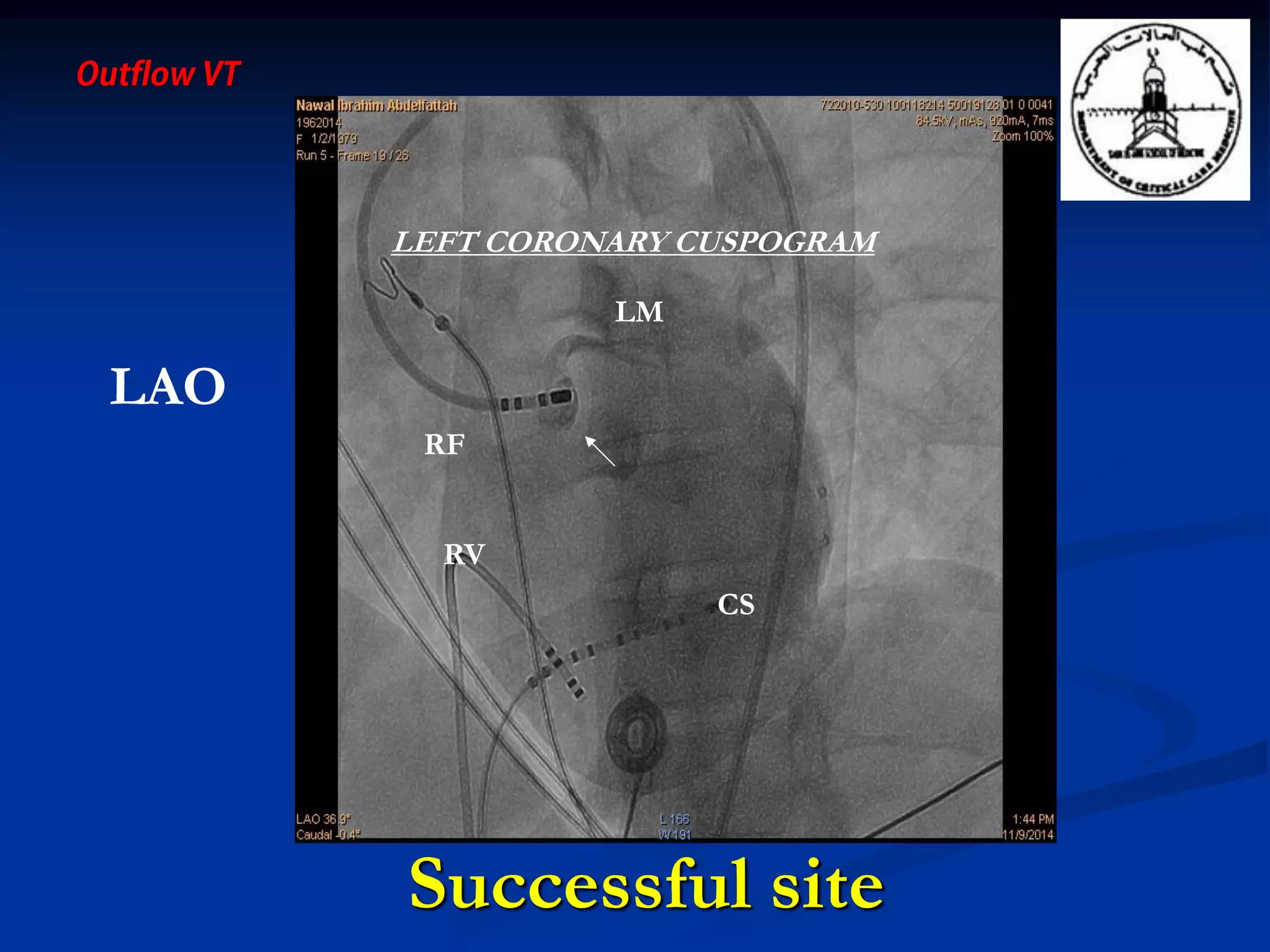


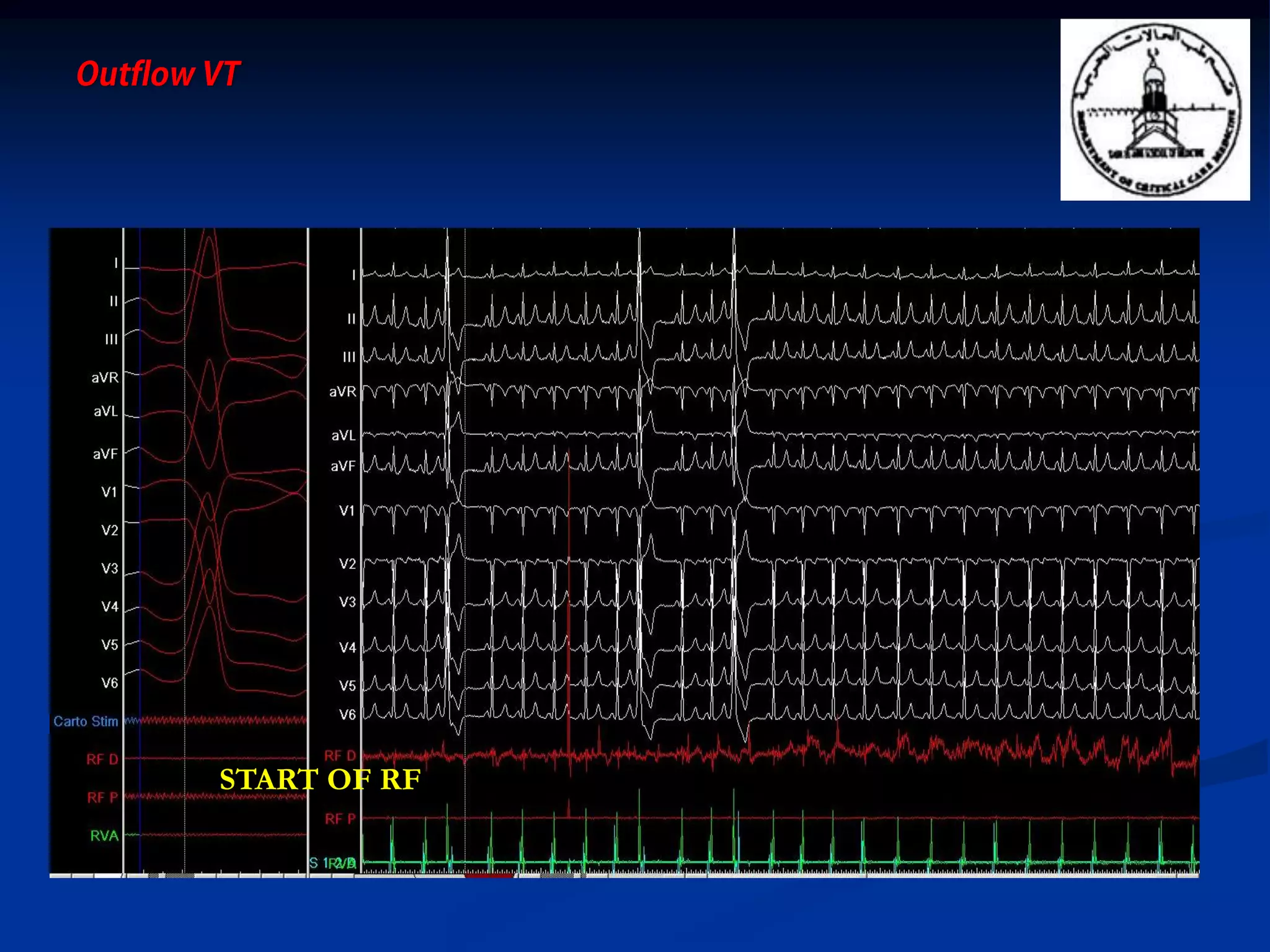





The document discusses various aspects of outflow tract ventricular tachycardia (VT) including its morphology, diagnostic tools, and the effectiveness of catheter ablation. It highlights the clinical characteristics necessary to distinguish malignant forms of right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) VT, and the success rates and risks associated with radiofrequency catheter ablation. Additionally, it presents case studies illustrating the outcomes of such procedures in patients with idiopathic RVOT tachycardia.













































