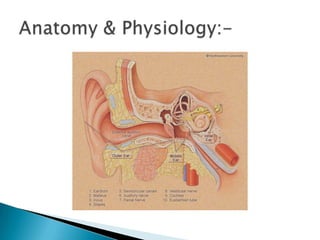
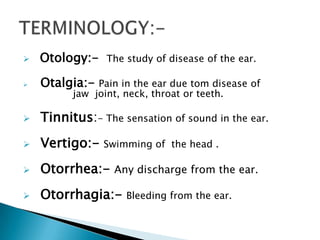
The document defines various diseases and conditions related to the ear, including otology, otitis media, tinnitus, and vertigo. It provides details on acute otitis media, chronic otitis media, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Evaluation and management of otitis media involves assessing symptoms, performing examinations of the ear, identifying causal factors, and using antibiotic treatments or surgical procedures as needed.