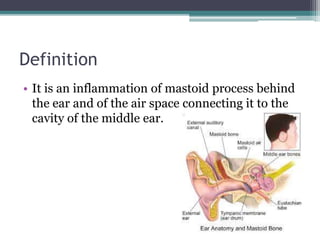
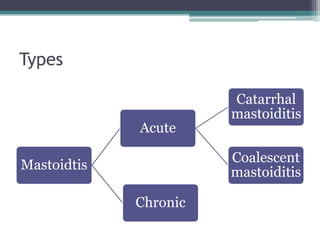
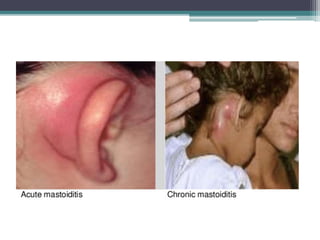
Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the mastoid process behind the ear that can result from untreated or inadequately treated otitis media. It is classified as either acute or chronic mastoiditis. Acute mastoiditis develops as a complication of acute otitis media, while chronic mastoiditis occurs with chronic suppurative otitis media or cholesteatoma formations. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling and tenderness in the mastoid region, fever, and otorrhea. Diagnosis involves tests like CT scans, ear cultures and audiograms. Treatment consists of antibiotics, analgesics, and may require surgical drainage of pus via procedures like mastoidectomy if infection spreads to