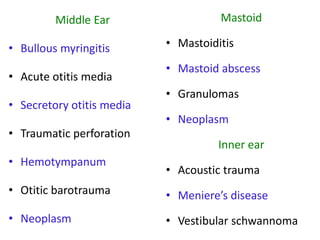
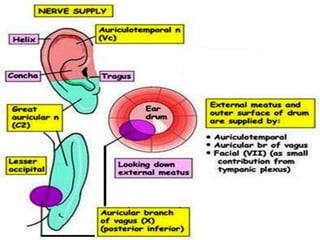
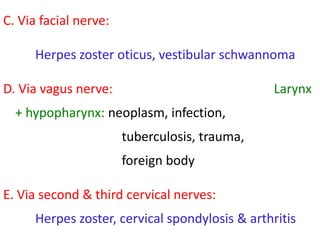
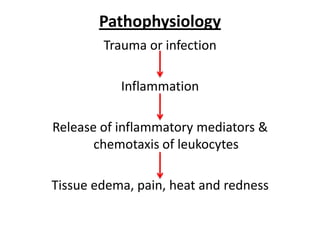
Otalgia refers to ear pain or ear ache, which can be primary (originating in the ear) or referred (originating elsewhere but felt in the ear). Primary causes include infections, wax buildup, trauma, and tumors of the outer ear canal, eardrum, middle ear bones, inner ear, and mastoid bone behind the ear. Referred otalgia can occur via cranial nerves from areas like the teeth, throat, larynx, neck, or due to conditions like shingles. Risk factors include inserting objects in the ear, swimming in polluted water, and respiratory infections. Treatment involves relieving pain, promoting healing, restoring function, and removing foreign bodies through irrigation, antibiotics, surgery