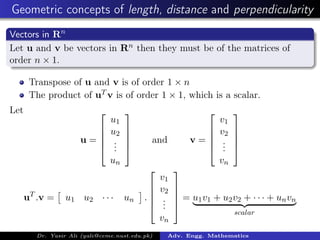
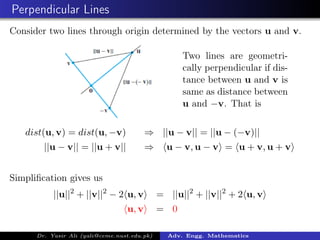
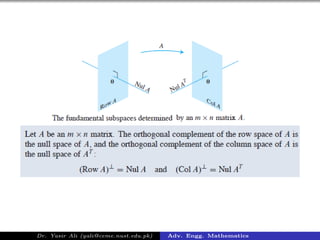
This document discusses orthogonal subspaces and inner products in advanced engineering mathematics. It defines the inner product of two vectors u and v in Rn as the transpose of u dotted with v, which results in a scalar. Two vectors are orthogonal if their inner product is 0. An orthogonal basis for a subspace W is a basis for W that is also an orthogonal set. The document also discusses orthogonal complements, projections, and inner products on function spaces.


























![Inner Product Spaces
Function Space C[a, b] and Polynomial Space P(t)
The notation C[a, b] is used to denote the vector space of all continuous
functions on the closed interval [a, b], that is, where a ≤ t ≤ b. The
following defines an inner product on C[a, b], where f(t) and g(t) are
functions in C[a, b]
f, g =
b
a
f(t)g(t)dt.
It is called the usual inner product on C[a, b].
Example (Consider f(t) = 3t − 5 and g(t) = t2 in P(t) with the inner
product
f, g =
1
0
f(t)g(t)dt.
Find f, g and ||f||.)
Dr. Yasir Ali (yali@ceme.nust.edu.pk) Adv. Engg. Mathematics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/812-os-171231203915/85/Orthogonal-Vector-Spaces-30-320.jpg)
![Inner Product Spaces
Function Space C[a, b] and Polynomial Space P(t)
The notation C[a, b] is used to denote the vector space of all continuous
functions on the closed interval [a, b], that is, where a ≤ t ≤ b. The
following defines an inner product on C[a, b], where f(t) and g(t) are
functions in C[a, b]
f, g =
b
a
f(t)g(t)dt.
It is called the usual inner product on C[a, b].
Example (Consider f(t) = 3t − 5 and g(t) = t2 in P(t) with the inner
product
f, g =
1
0
f(t)g(t)dt.
Find f, g and ||f||.)
f, g is given whereas ||f||2 = f, f
Dr. Yasir Ali (yali@ceme.nust.edu.pk) Adv. Engg. Mathematics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/812-os-171231203915/85/Orthogonal-Vector-Spaces-31-320.jpg)






