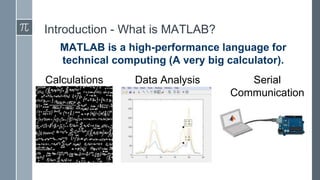
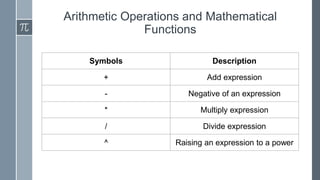
MATLAB is a programming language for technical computing and data analysis. It allows users to perform arithmetic operations, use mathematical functions, manipulate data, create plots and graphs, write programs using conditional statements and loops. The document provides an overview of MATLAB's interface and important terms, and demonstrates how to perform common tasks like creating arrays and matrices, plotting data, writing for and while loops, and defining functions. MATLAB is relevant for tasks in many engineering fields like signal processing, optimization, finite element analysis, and statistical analysis.



![Creating Arrays
● 3 ways to create an array in row
○ [ _ _ _ ];
○ Start : Increment : End;
○ Linspace(Start, End, Amount of Points);
● Convert to Column
○ [ _ _ _]’;
○ transpose(array);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-8-320.jpg)
![Matrices
● Semicolon creates a new row
● A = [ _ _ _ ; _ _ _ ; _ _ _];
● Ex:
B =
1 2 3
0 5 0
7 0 9
● Join matrices
○ [ B A] horizontally
○ [ B;A] vertically](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-9-320.jpg)
![Data Manipulation
● Find data in a matrix using rows and columns
○ data = variable(row, column)
● Use find( ) to manipulate data in an array or matrix
○ [row,column] = find(data, indices returned)
○ [row,column] = find(use conditional statement)
● Use both
Ex:
1. [r,c] = find(B)
2. B(2,3)
3. B(find(B))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-11-320.jpg)


![“if-elseif-else” Statements
Example:
A = ones(2,3);
B = rand(3,4);
If (isequal(size(A),size(B)))
C = [A,B];
else
disp(‘A and B are not the same
size.’)
C = [ ];
end
if (expression)
statements
elseif (expression)
statements
else
statements
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-16-320.jpg)

![FOR Loops
Example:
x=[5,4,8,7,10]
z=[];
for i=1:5 % amount of iterations
z(i)=x(i)*2 %do something
end % always end
RESULT:
z=[10,8,16,14,100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-18-320.jpg)
![FOR Loops and Conditional Statements
Example:
x=[5,4,8,7,0,10]
z=[];
for i=1:6
If x(i)==0 % can add if-else in
loop
Break; % stops the code
else
z(i)=x(i)*2
end
end
RESULTS:
z=[10,8,16,14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-19-320.jpg)

![Functions
● Function: Functions, written in
scripts, are used to simplify entire
scripts into one function with
inputs and outputs
○ A function behave like: y = mx +b,
where y=output & x=input
● In script:
function [output] = name[input]
do something
end
● In command window
out = name(in);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionmatlab1-180729124733/85/Matlab-Workshop-Presentation-21-320.jpg)

