The document discusses the one-sided z-transform, which is used to solve difference equations with initial conditions. It defines the one-sided z-transform and explains that it contains information only about causal signals that are zero for negative time values. Some key properties are described, including shifting properties for time delay and advance, and the final value theorem. An example shows how to use the one-sided z-transform to solve a simple difference equation.


![∑
∞
=
−+
=
0
)()(
n
n
znxzX
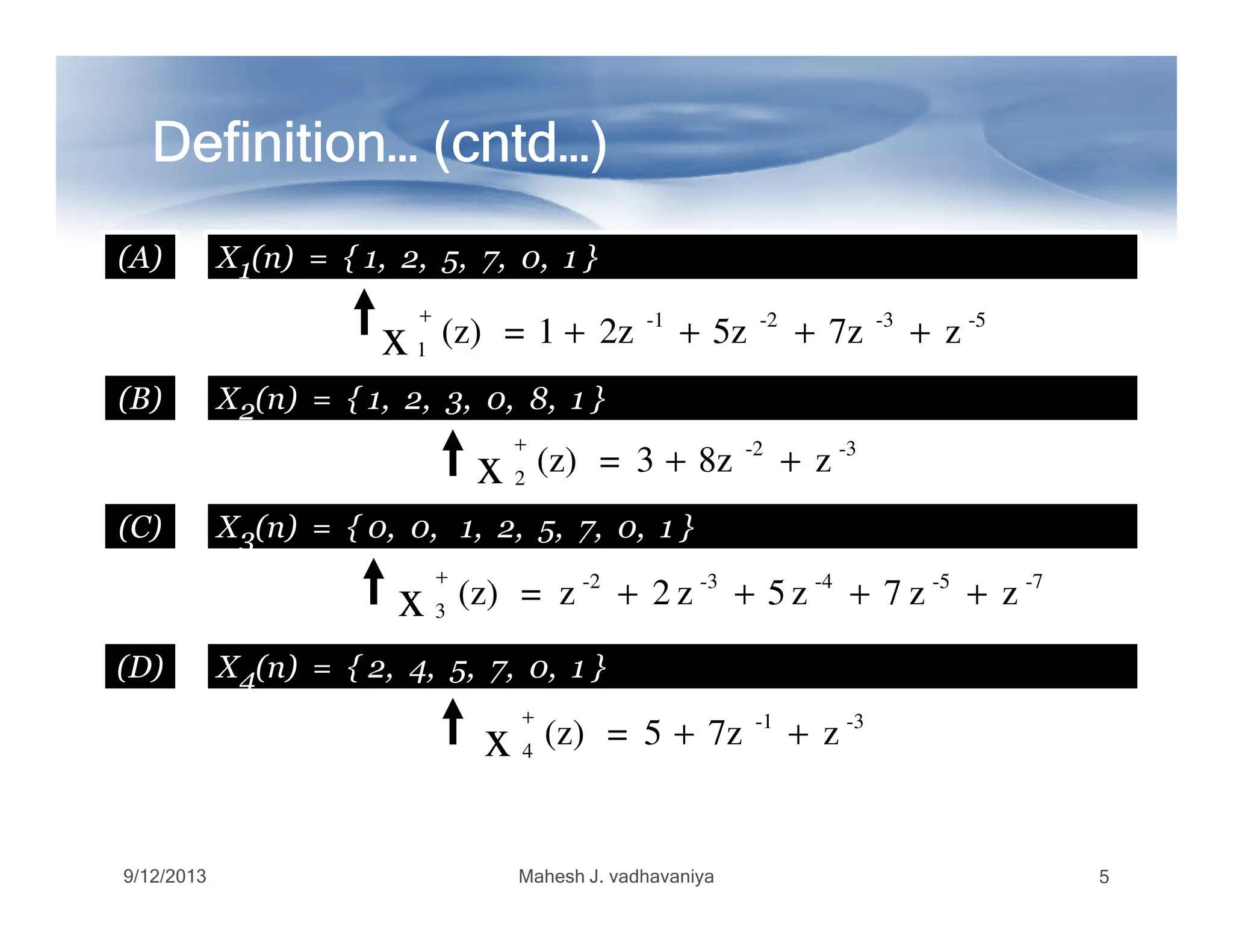
Definition…Definition…Definition…Definition…Definition…Definition…Definition…Definition…
TheThe OneOne sidedsided (Unilateral)(Unilateral) zz--transformtransform ofof aa causalcausal
DTDT signalsignal x[n]x[n] isis defineddefined asas ::
WeWe cancan alsoalso writewrite :: ZZ++{x(n)}{x(n)} andand )()( zXnx
z
+
+
↔WeWe cancan alsoalso writewrite :: ZZ++{x(n)}{x(n)} andand )()( zXnx +
↔
EquivalentEquivalent toto thethe bilateralbilateral zz--transformtransform ofof x[n]u[n]x[n]u[n]
SinceSince x[n]u[n]x[n]u[n] isis alwaysalways aa rightright sidedsided sequence,sequence,
ROCROC ofof X(z)X(z) isis alwaysalways thethe exteriorexterior ofof aa circlecircle..
UsefulUseful forfor solvingsolving differencedifference equationsequations withwith initialinitial
conditionsconditions..
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-4-2048.jpg)
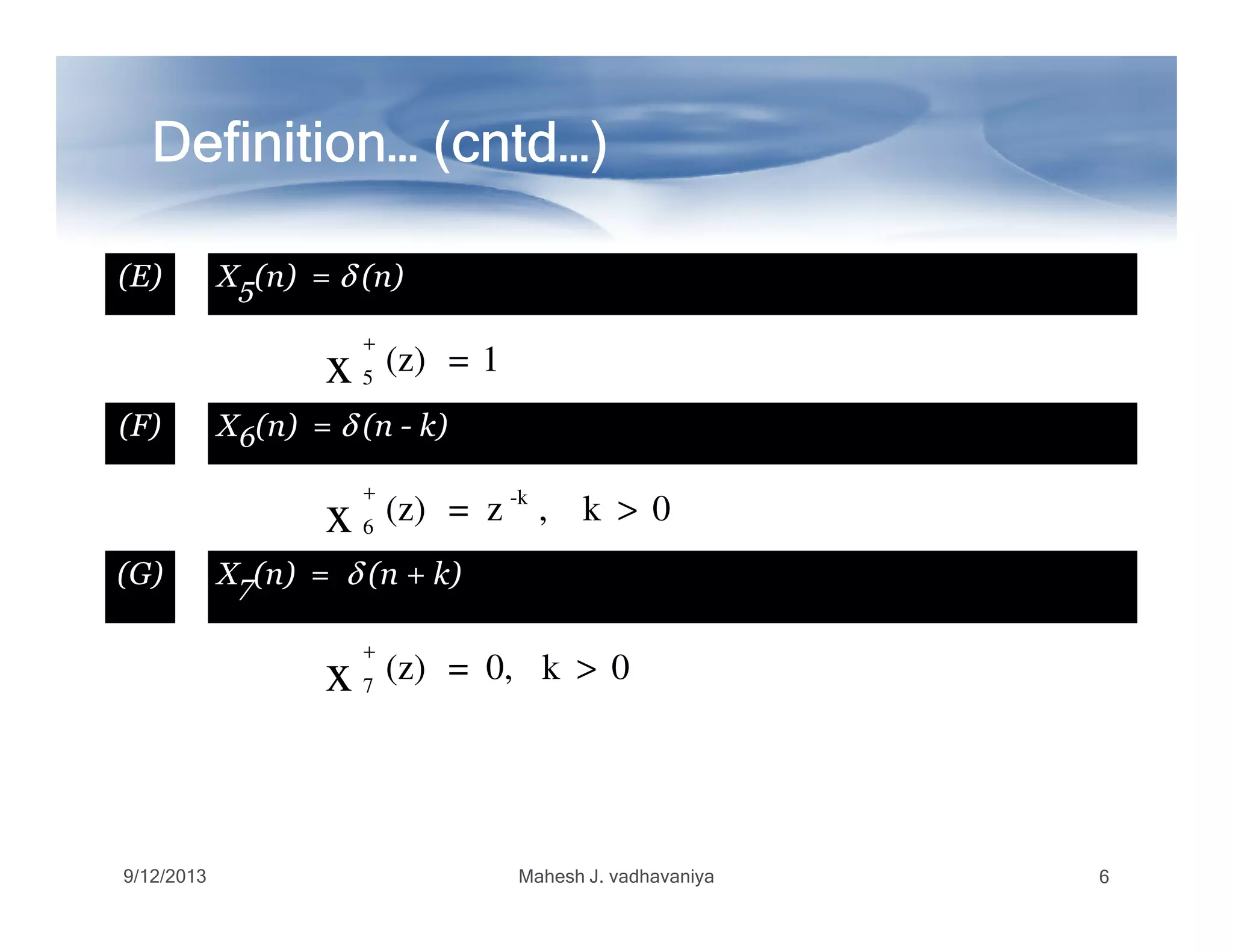
![Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (Definition… (cntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntd…)…)…)…)…)…)…)…)
ItIt doesdoes notnot containcontain informationinformation aboutabout thethe signalsignal
x(n)x(n) forfor negativenegative valuesvalues ofof timetime (for(for nn << 00 ))
ItIt isis uniqueunique onlyonly forfor causalcausal signals,signals, becausebecause onlyonly
thesethese signalssignals areare zerozero forfor nn << 00..thesethese signalssignals areare zerozero forfor nn << 00..
SinceSince x[n]u[n]x[n]u[n] isis alwaysalways aa rightright sidedsided sequence,sequence,
ROCROC ofof X(z)X(z) isis alwaysalways thethe exteriorexterior ofof aa circlecircle.. SoSo whenwhen
wewe dealdeal withwith oneone sidedsided zz--transform,transform, itit isis notnot
necessarynecessary toto referrefer toto theirtheir ROCROC..
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-5-2048.jpg)


![Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (cntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntd…)…)…)…)…)…)…)…)
Example 1: Determine the one-sided z-transform of
X1(n) = x(n-2) where x(n) = an
ApplyApply thethe shiftingshifting propertyproperty forfor kk == 22,, wewe havehaveProof :
12
2-2
)2()1()(
])2()1()([z=2)}-{x(nZ
−+−
++
−+−+=
−+−+
xzxzXz
ZxzxzX
211
1
2
1
1
21
12
1
)(
1
1
)(,)2(,x(-1)Since
)2()1()(
−−−
−
−
+
−
−−
−+−
++
−
=
−
==−=
−+−+=
aza
az
z
zX
obtainwe
az
zXaxa
xzxzXz
ToTo obtainobtain x(nx(n--k)k) (k>(k>00)) fromfrom x(n),x(n), wewe shouldshould shiftshift x(n)x(n) byby kk
samplessamples toto thethe rightright..
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-10-2048.jpg)

![Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (cntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntd…)…)…)…)…)…)…)…)
Example 2: Determine the one-sided z-transform of
X2(n) = x(n + 2) where x(n) = an
ApplyApply thethe shiftingshifting propertyproperty forfor kk == 22,, wewe havehaveProof :
zxxzX −−+ ++ 2
])1()0()([z=2)}{x(nZ
azz
az
z
zX
obtainweazzXaxand
zxzxzXz
−−
−
=
−===
−−=
−
+
−+
+
2
1
2
2
1
1
22
1
)(
)1(1)(and,)1(,1x(0)Since
)1()0()(
ToTo obtainobtain x(x(n+kn+k)) (k>(k>00)) fromfrom x(n),x(n), wewe shouldshould shiftshift x(n)x(n) byby kk
samplessamples toto thethe leftleft..
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-12-2048.jpg)
]()1([)0()()1(
)]()1([)()]0()([
)]()1([)]()1([
)()]([
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
znxnxxzXz
znxnxzXxzzX
znxnxnxnxZ
zxxZ
TakingTaking thethe limitlimit zz 11 onon bothboth sides,sides,
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-13-2048.jpg)
![Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (Properties… (cntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntdcntd…)…)…)…)…)…)…)…)
Final Value Theorem :
exp
)]()1([)]0()()1[(lim
])]()1([[lim)]0()()1[(lim
0
1z
0
1
1z1z
l n termanding tilnow
nxnxxzXz
znxnxxzXz
n
n
∞
=
+
→
∞
=
−
→
+
→
−+=−−
−+=−−
∑
∑
ThisThis theoremtheorem enablesenables usus toto findfind thethe steadysteady statestate valuevalue ofof
x(n)x(n) withoutwithout solvingsolving forfor thethe entireentire sequencesequence..
)()1(lim)(therefore
)0()()]0()()1[(lim
)]}()1([...
)]1()2([)]0()1({[lim)]0()()1[(lim
exp
1
1z
n1z
zXzx
xxxzXz
nxnx
xxxxxzXz
l n termanding tilnow
z
+
→
+
→
∞→
+
→
−=∞
−∞=−−
−++
+−+−=−−
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-14-2048.jpg)
![Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …
Use the one sided z-transformation to determine y(n),
n≥0, if
GivenGiven
Example 1 :
1)1();(
3
1
)();()1(
2
1
)( =−
=+−= ynunxnxnyny
n
Solution :
)()1(
2
1
)( nxnyny +−=
1
TakingTaking zz--transformtransform onon bothboth sidessides )()]1()([
2
1
)( 1
zXyzYzzY +−+= −
SubstituteSubstitute y(y(--11)=)=11 andand
3
1
)(
3
1
)(
−
=
=
z
z
nuZzX
n
3
1
5.0)(5.0)(
3
1
]1)([
2
1
)(
1
1
−
++=
−
++=
−
−
z
z
zYzzY
z
z
zYzzY
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-15-2048.jpg)

![Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) )(]3125.05.3[)(
)(]3125.035.05.0[)(
nuny
nuny
nn
nnn
−=
−+=
TakingTaking inverseinverse zz--transform,transform, wewe getget
( ) ( ) )(]3125.05.3[)( nuny
nn
−=
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-17-2048.jpg)
![The unilateral z transform is well suited to solving difference
equations with initial conditions. For example,
y n + 2[ ]−
3
2
y n +1[ ]+
1
2
y n[ ]= 1/ 4( )n
, for n ≥ 0
Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …
Example 2 :
2 2
y 0[ ]= 10 and y 1[ ]= 4
z transforming both sides,
z2
Y z( )− y 0[ ]− z−1
y 1[ ] −
3
2
z Y z( )− y 0[ ] +
1
2
Y z( ) =
z
z −1/ 4
the initial conditions are called for systematically.
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-18-2048.jpg)
![Applying initial conditions and solving,
Y z( ) = z
16 / 3
z −1/ 4
+
4
z −1/ 2
+
2 / 3
z −1
and
Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …Solution of Difference Equations …
and
y n[ ]=
16
3
1
4
n
+ 4
1
2
n
+
2
3
u n[ ]
This solution satisfies the difference equation and the initial
conditions.
9/12/2013 Mahesh J. vadhavaniya 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onesidedz-transform-130912013914-phpapp01/75/One-sided-z-transform-19-2048.jpg)
