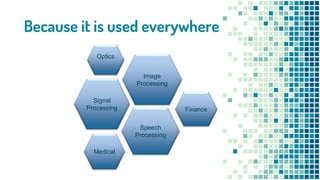
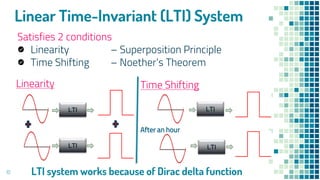
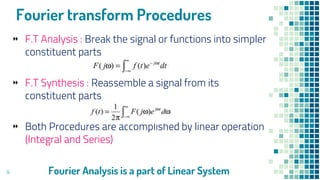
This document discusses Fourier transforms and their applications. It begins by introducing Fourier transforms and noting that they are used widely in optics, image processing, speech processing, and medical signal processing. It then covers key topics such as:
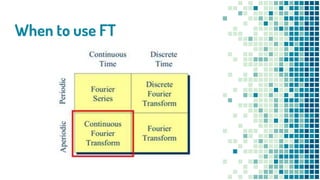
- When periodic and aperiodic signals can be represented by Fourier series versus Fourier transforms
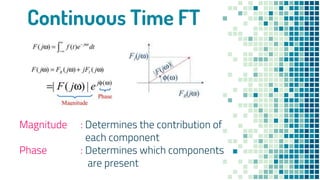
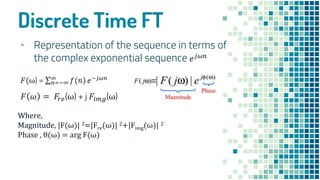
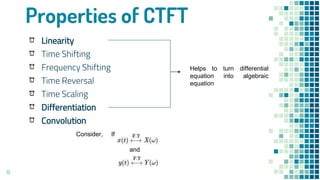
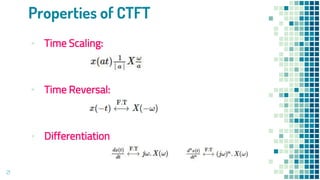
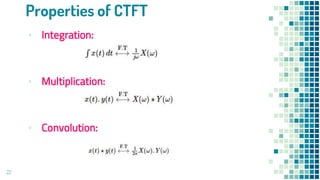
- Properties of continuous-time and discrete-time Fourier transforms
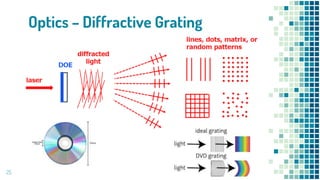
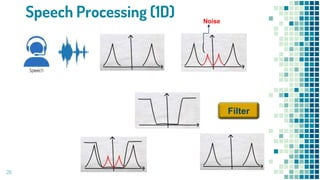
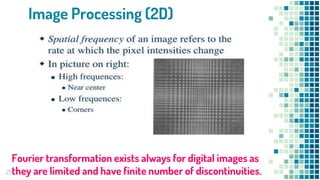
- Applications of Fourier transforms in filtering ECG signals, modeling diffractive gratings in optics, speech processing, and image processing
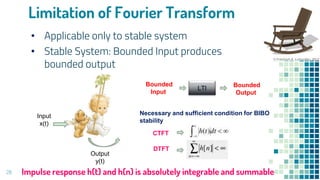
- Limitations of Fourier transforms in representing non-stable systems
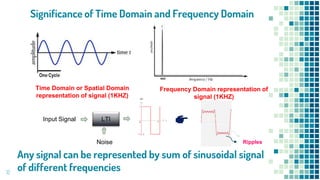
The document provides an overview of Fourier transforms and their significance in decomposing signals into constituent frequencies, as well as examples of where they are applied in