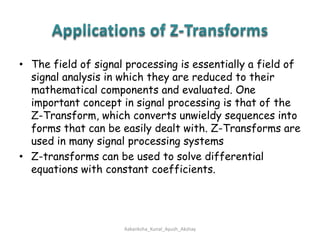
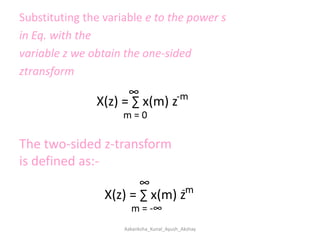
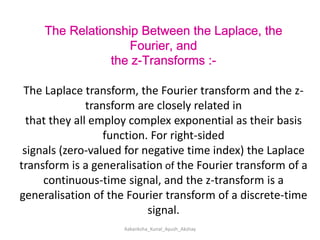
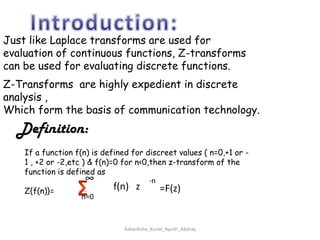
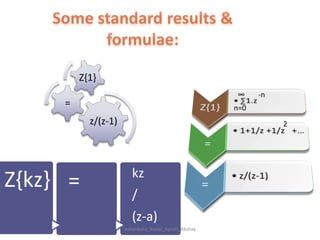
Z-transforms can be used to evaluate discrete functions, similar to how Laplace transforms are used for continuous functions. The z-transform of a discrete function f(n) is defined as the sum of f(n) multiplied by z to the power of -n, from n=0 to infinity. Some standard z-transform results include formulas for exponential, sinusoidal, and polynomial functions. Z-transforms have properties of linearity and shifting, and can be used to solve differential equations with constant coefficients and in applications of signal processing.

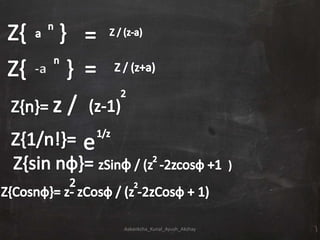

![Initial value theorem:-f(0)= lim F(z)Z∞Final value theorem:-f(∞)= lim f(n) = lim (z-1) F(z)n∞ Z1Shifting Theorem:-Z{ f (n+k) }= z [ F(z) - ∑ f(i) z ]K-i-iKi=0Aakanksha_Kunal_Ayush_Akshay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ztransform-110820102702-phpapp01/85/Z-transform-6-320.jpg)