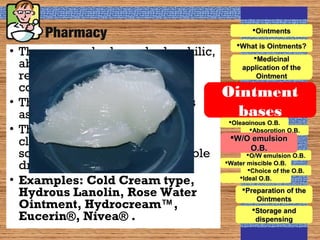
Ointments are semi-solid medicated preparations that are applied topically to the skin. They have several purposes including as protectants, antiseptics, and emollients. There are different types of ointment bases including oleaginous, absorption, water-miscible, and emulsion bases. Selection of the appropriate base depends on factors like the desired drug release rate and whether the active ingredient needs to be dissolved, emulsified, or suspended in the base. Ointments are usually prepared by melting the base and adding the medicated ingredients.