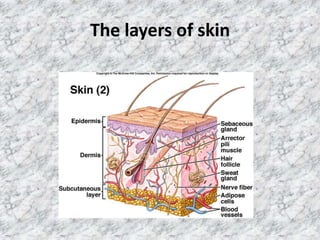
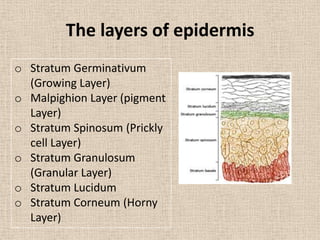
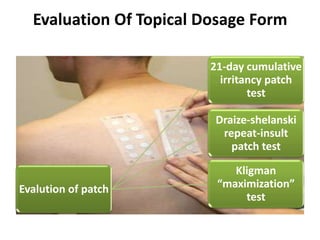
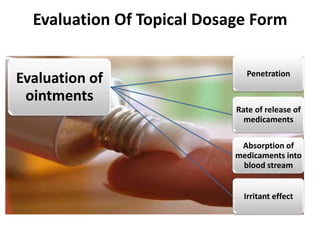
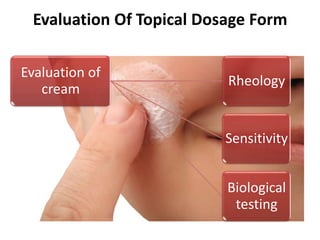
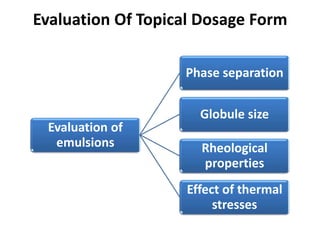
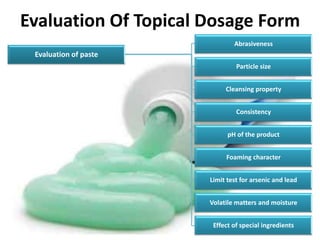
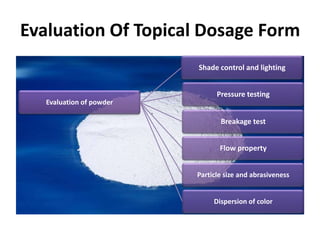
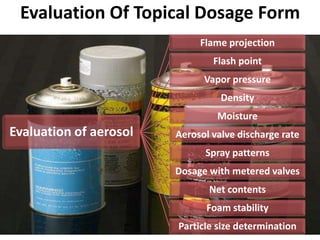
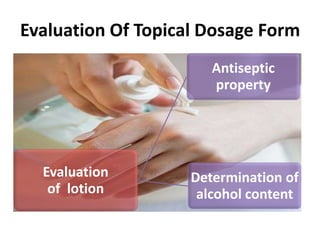
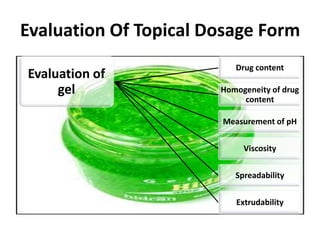
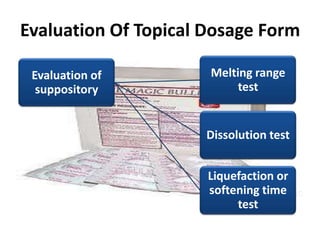
This document discusses topical drug delivery systems and methods for evaluating different topical dosage forms. It begins by defining the two basic types of topical delivery as external and internal. It then lists several advantages of topical drug delivery systems, such as avoiding first-pass metabolism and providing localized treatment. Potential disadvantages include skin irritation and poor drug permeability. The document describes common topical dosage forms like ointments, creams, emulsions, pastes, and gels. It provides details on evaluation methods for things like penetration rate, absorption, irritation effects, rheology, thermal stability, and drug content of different dosage forms. Evaluation methods for specific forms like powders, suspensions, aerosols, and suppositories are