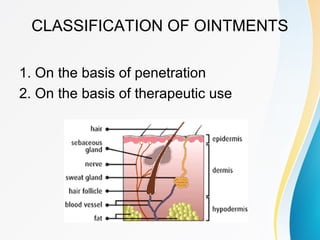
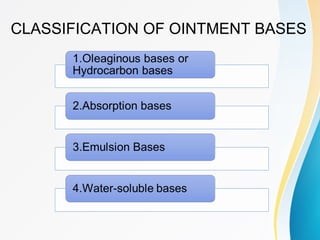
This document discusses ointments, which are semi-solid topical dosage forms used for therapeutic, protective, or cosmetic purposes. Ointments are greasy preparations containing 80% oil and 20% water that are applied to the skin or mucous membranes. They can contain dissolved, emulsified, or suspended drug ingredients. Ointments are classified based on penetration (epidermic, endodermic, diadermic) or therapeutic use (antibiotic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory). Ideal ointment bases are inert, compatible with skin pH, emollient, and release medication readily. Common bases include oleaginous (petrolatum, hard paraffin, liquid paraffin