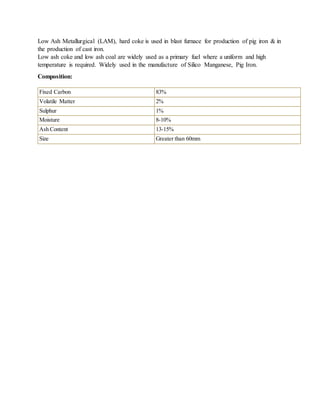
Coke is a porous, high-strength carbon material produced by heating coal in ovens without oxygen. It is a key material used in blast furnaces for ironmaking. Metallurgical coke is made specifically from bituminous coal that can withstand high heat and pressures. The coking process involves heating coal to around 2000°F for 12-36 hours to drive off impurities. Coke is then used as both a fuel and reducing agent in blast furnaces, where its combustion produces carbon monoxide to reduce iron ore into molten iron. High quality coke is necessary to support blast furnace operations and produce quality iron.