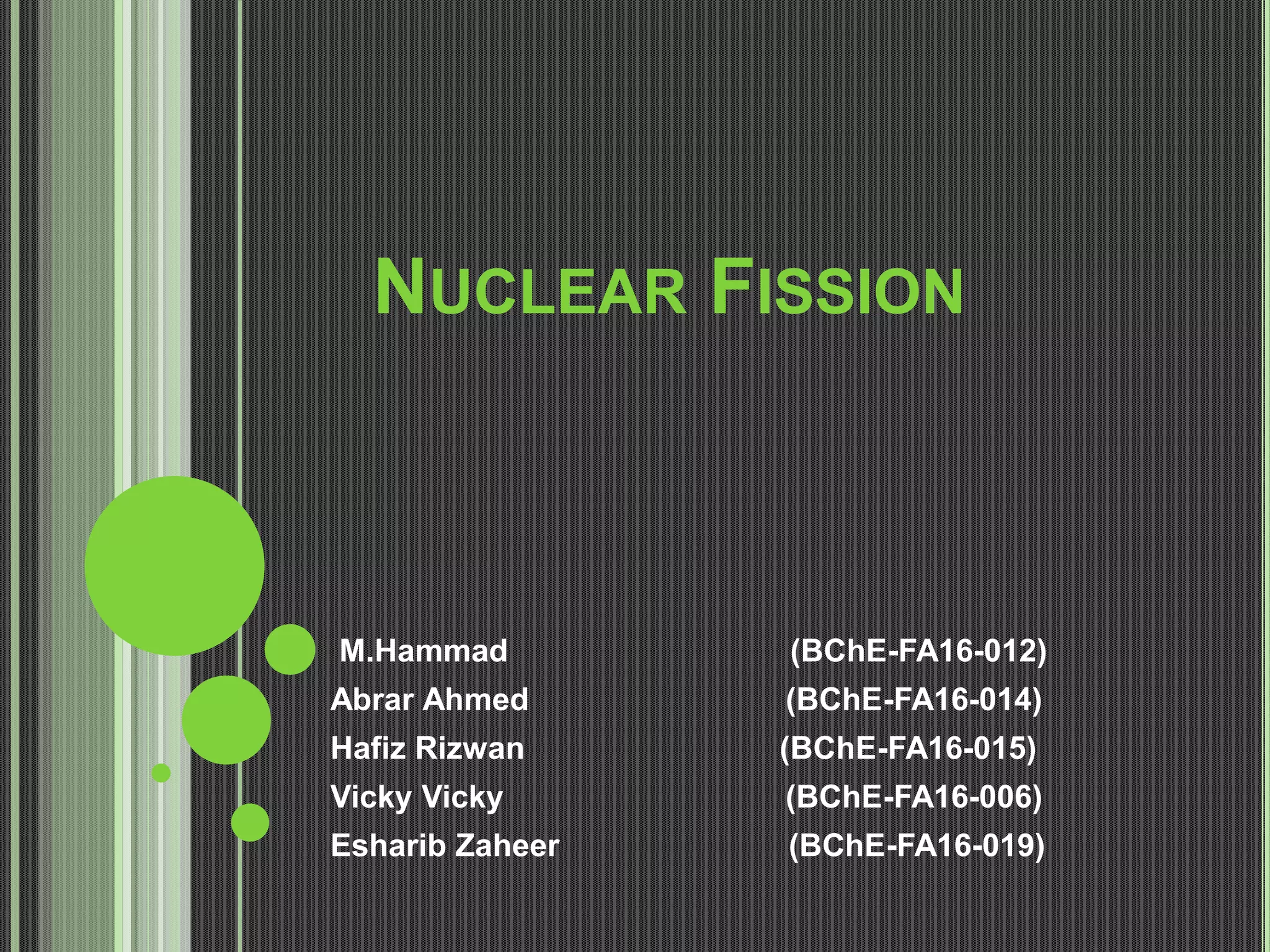
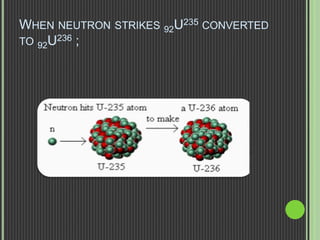
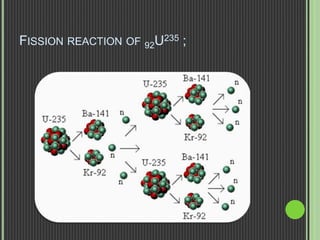
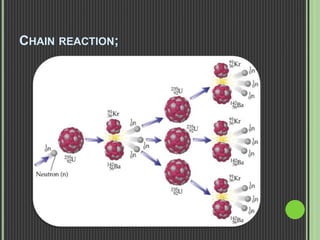
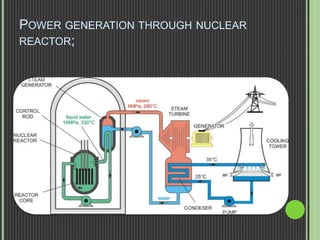
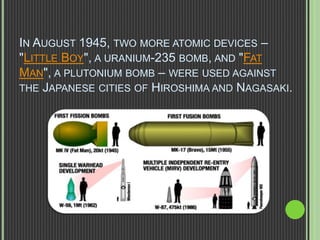
This document discusses nuclear fission, including its history, the fission chain reaction process, nuclear reactors, and applications. It describes how nuclear fission was discovered in 1938 and involves splitting uranium-235 atoms with neutrons, releasing energy and up to 3 neutrons to split more atoms. A self-sustaining chain reaction can occur in a nuclear reactor, where the heat generated is used to produce steam to power generators and produce electricity. Nuclear fission is applied in nuclear power plants, nuclear weapons, and medical and scientific research.