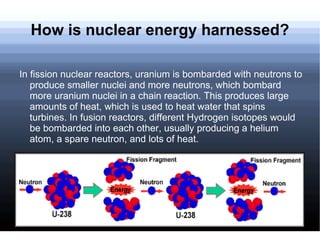
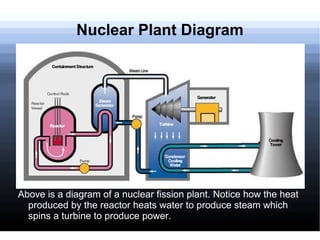
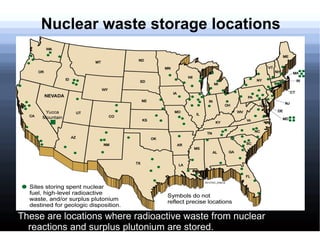
Nuclear power involves harnessing the energy released from nuclear fission or fusion reactions. Nuclear fission is the most commonly used method today and involves splitting uranium atoms, releasing energy. This energy is used to heat water and produce steam to spin turbines and generate electricity. While nuclear power produces little pollution, it also produces hazardous nuclear waste and accidents like meltdowns can be catastrophic releases of radiation. Future nuclear power may increasingly rely on experimental fusion reactors which are safer than current fission reactors.